-
순도시험
(1) 비선광도 : 이 품목 1g을 정밀히 달아 새로 끓여 식힌 물을 가하여 녹인 다음 정확히 10mL로 한 액의 선광도를 측정하고 다시 건조물로 환산할 때, 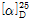 =+103.0~+108.0°이어야 한다.
=+103.0~+108.0°이어야 한다.
(2) 액성 : 이 품목의 수용액(1→50)의 pH는 6.5~8.0이어야 한다.
(3) 비소 : 이 품목을 비소시험법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 4.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(4) 납 : 이 품목 5.0g을 취하여 원자흡광광도법 또는 유도결합플라즈마발광광도법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 2.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(5) 수은 : 이 품목을 수은시험법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 1.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
-
확인시험
(1) 이 품목 0.1g을 메타인산용액(1→50) 100mL에 녹이고 그 5mL에 액이 엷은황색을 나타낼 때까지 요오드시액을 적가한 다음 황산동용액(1→1,000) 1방울 및 피롤 1방울을 가하여 50~60℃에서 5분간 가온하면 청~청록색을 나타낸다.
(2) 이 품목의 수용액(1→100) 10mL에 2,6-디클로로페놀인도페놀나트륨시액 1~2방울을 가할 때, 액의 청색은 곧 없어진다.
(3) 이 품목은 나트륨염의 반응을 나타낸다.
-
정량법
이 품목을 건조한 다음, 약 0.2g을 정밀히 달아 메타인산용액(1→50) 50mL에 녹이고 0.1N 요오드용액으로 적정한다(지시약 : 전분시액).
0.1N 요오드용액 1mL = 9.906mg C6H7NaO6
-
화학적 성질
Sodium ascorbate occurs as a white or slightly yellow-colored,
practically odorless, crystalline powder with a pleasant saline taste.
-
용도
Sodium Ascorbate is an antioxidant that is the sodium form of
ascorbic acid. it is soluble in water and provides a nonacidic taste. a
10% aqueous solution has a ph of 7.3–7.6. in water, it readily reacts
with atmospheric oxygen and other oxidizing agents, making it
valuable as an antioxidant. one part sodium ascorbate is equivalent
to 1.09 parts of sodium erythorbate. see ascorbic acid.
-
생산 방법
An equivalent amount of sodium bicarbonate is added to a solution
of ascorbic acid in water. Following the cessation of effervescence,
the addition of propan-2-ol precipitates sodium ascorbate.
-
정의
ChEBI: Sodium ascorbate is an organic sodium salt resulting from the replacement of the proton from the 3-hydroxy group of ascorbic acid by a sodium ion. It has a role as a food antioxidant, a flour treatment agent, a coenzyme, a plant metabolite, a human metabolite, a Daphnia magna metabolite and a reducing agent. It is an organic sodium salt and a vitamin C. It contains a L-ascorbate.
-
일반 설명
Minute crystals or white powder. pH of aqueous solutions 5.6 to 7.0 or even higher (a 10% solution, made from a commercial grade, may have a pH of 7.4 to 7.7).
-
공기와 물의 반응
Water soluble. Aqueous solutions are subject to quick air oxidation at pH greater than 6.0.
-
반응 프로필
A weak base. Materials in this group are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydroxide ions and have pH's greater than 7.0. They react as bases to neutralize acids. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of the bases in reactivity group 10 (Bases) and the neutralization of amines. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible.
-
건강위험
SYMPTOMS: Ingestion of 10 grams or more of this type of compound may cause diarrhea.
-
화재위험
Flash point data for Sodium ascorbate are not available. Sodium ascorbate is probably combustible.
-
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sodium ascorbate is used as an antioxidant in pharmaceutical
formulations, and also in food products where it increases the
effectiveness of sodium nitrite against growth of Listeria monocytogenes
in cooked meats. It improves gel cohesiveness and sensory
firmness of fiberized products regardless of vacuum treatment.
It is also used therapeutically as a source of vitamin C in tablets
and parenteral preparations.
-
Safety Profile
Human mutation data
reported. When heated to decomposition it
emits toxic fumes of Na2O.
-
Safety
The parenteral administration of 0.25-1.00 g of sodium ascorbate,
given daily in divided doses, is recommended in the treatment of
vitamin C deficiencies. Various adverse reactions have been
reported following the administration of 1 g or more of sodium
ascorbate, although ascorbic acid and sodium ascorbate are usually
well tolerated; see Ascorbic acid. There have been no reports of
adverse effects associated with the much lower concentrations of
sodium ascorbate and ascorbic acid, which are employed as
antioxidants.
The WHO has set an acceptable daily intake of ascorbic acid,
potassium ascorbate, and sodium ascorbate, as antioxidants in
food, at up to 15 mg/kg body-weight in addition to that naturally
present in food.
-
저장
Sodium ascorbate is relatively stable in air, although it gradually
darkens on exposure to light. Aqueous solutions are unstable and
subject to rapid oxidation in air at pH > 6.0.
The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed nonmetallic
container, protected from light, in a cool, dry place.
-
비 호환성
Incompatible with oxidizing agents, heavy metal ions, especially
copper and iron, methenamine, sodium nitrite, sodium salicylate,
and theobromine salicylate. The aqueous solution is reported to be
incompatible with stainless steel filters.
-
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe.
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IV preparations;
oral tablets). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral
medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of
Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.


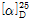 =+103.0~+108.0°이어야 한다.
=+103.0~+108.0°이어야 한다.