-
물성
아스 코르 베이트 음이온에 대한 표준 구조
아스코르브 산은 reductone로 분류되고. 아스 코르 베이트 음이온이 전자의 비편 재화에 의해 안정화, twocanonical 형태 사이의 공진면에 위와 같이. 이러한 이유, 화합물만을 절연 수산기 함유하는 경우 아스코르브 산 훨씬 산성 기대되는 것보다.
-
개요
수용성 비타민 중 하나로, 아스코브산(ascorbic acid)이라고도 한다. 월터 호어스가 최초로 화학구조를 규명해 노벨화학상을 수상했다. 생물의 에너지 대사과정에서 필수적인 조효소로 작용하며 항산화 작용에도 관여하는 물질이다. 다른 동물들의 경우 체내에서 어느 정도 자체적으로 합성이 가능하나, 사람을 포함한 영장류와 설치류 중 기니피그는 체내의 아스코르브산 합성에 관여하는 효소가 결핍되어 있기 때문에 반드시 외부에서 섭취해야만 한다.
-
용도
방부제로써도 널리 사용된다. 당장 통조림 같은 가공식품에서 L-아스코르브산나트륨을 찾아보자.
-
용도
아스 코르 빈산 및 소듐, 칼륨, 칼슘 염은 일반적으로 항산화 식품 첨가물로 사용된다. 이들 화합물은 수용성이고, 그러므로, 산화에서 지방을 보호 할 수 없습니다: 이 목적을 위해, 장쇄 지방산 (아스 코르 빌 팔미 테이트 또는 아스 코르 빌 스테아 레이트)과 아스코르브 산의 에스테르, 지용성 항산화 식품으로 사용될 수있다.
-
용도
제약 산업 , 의약품에에서는 주로 보충 치료 연습 서로 다른 분야에서 임상적으로 중요 한 자료로 다양 한 의약품을 생산 하 사용할 수 있습니다. 그것은 또한 괴 혈 병 치료에 사용 되며 다양 한 급성 및 만성 감염 질환, VC의 부족에 적용.
식품 산업 에, 그것은 둘 다 사용할 수 영양 알 보충, 식품 가공, 보충 VC 및 좋은 항 산화 식품 보존, 육류 제품, 발효 밀가루 제품, 맥주, 차 dtinks, 과일 주스, 통조림된 과일, 통조림 고기와.
의약품 화장품, 사료 첨가제 및 기타 산업용 영역에에서 일반적으로 사용 됩니다.
-
순도시험
(1) 비선광도 : 이 품목 약 1g을 정밀히 달아 새로 끓여서 식힌 물에 녹여 10mL로 하고 이 액의 선광도를 측정하고 다시 건조물로 환산할 때, 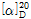 =+20.5~+21.5°이어야 한다.
=+20.5~+21.5°이어야 한다.
(2) 비소 : 이 품목을 비소시험법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 4.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(3) 납 : 이 품목 5.0g을 취하여 원자흡광광도법 또는 유도결합플라즈마발광광도법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 2.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
(4) 수은 : 이 품목을 수은시험법에 따라 시험할 때, 그 양은 1.0ppm 이하이어야 한다.
-
확인시험
(1) 이 품목의 융점은 187~192℃이어야 한다.
(2) 이 품목의 수용액(1→100) 2mL에 니트로프루시드나트륨시액 5~6방울을 가한 다음 수산화나트륨시액 1방울을 가하면 곧 청색을 나타낸다.
(3) 이 품목 0.1g을 메타인산용액(1→50) 100mL에 녹이고 그 액에 액이 엷은 황색을 나타낼 때까지 요오드시액을 적가한 다음 황산동용액(1→1,000) 1방울과 피롤 1방울을 가하여 수욕 중에서 50~60℃로 5분간 가온하면 청~청록색을 나타낸다.
(4) 이 품목의 수용액(1→100) 10mL에 과망간산칼륨시액 1mL를 가하면 시액의 색은 곧 없어진다.
(5) 이 품목의 수용액(1→100) 5mL에 수산화나트륨시액 0.3mL를 가한 다음 초산우라닐시액 2방울을 가하면 갈색을 나타내고 이 액에 수산화나트륨시액 2mL를 가하면 액의 색은 엷은황색으로 변한다.
-
정량법
이 품목을 건조한 다음 약 0.2g을 정밀히 달아 메타인산용액(1→50) 50mL에 녹여 0.1N 요오드용액으로 적정한다(지시약 : 전분시액).
0.1N 요오드용액 1mL = 8.806mg C6H8O6
-
강열잔류물
이 품목의 강열잔류물은 0.1% 이하이어야 한다.
-
개요
Ascorbic acid, a water-soluble dietary supplement, is consumed by humans more than any other supplement. The name ascorbic means antiscurvy and denotes the ability of ascorbic to combat this disease. Vitamin C is the l-enantiomer of ascorbic acid. Ascorbic acid deficiency in humans results in the body’s inability to synthesize collagen, which is the most abundant protein in vertebrates.
-
화학적 성질
White crystals (plates or needles). Soluble in water; slightly soluble in alcohol;
insoluble in ether, chloroform, benzene, petroleum
ether, oils and fats. Stable to air when dry. One
international unit is equivalent to 0.05 milligram of
l-ascorbic acid.
-
물리적 성질
Appearance: white crystal or crystalline powder, and it is odorless and flavors sour. The color changes yellowish when exposed in the air for a long time. Its aqueous solution is acidic reaction. Solubility: vitamin C is soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, and insoluble in chloroform or ether. Melting point: 190–192? °C.? It would decompose when it melts. Specific optical rotation: +20.5 to +21.5°. Ascorbic acid is two-base acid (the pKa is 4.1 and 11.8). It occurs mainly in the form of sodium salt and calcium salt, and its aqueous solution is strongly acidic reaction. Ascorbic acid is a strong reducing agent.
-
역사
Vitamin C is a general term for compounds having ascorbic acid activity, including ascorbic acid, dehydroascorbic acid, and its isomers.
The understanding of vitamin C has gone through a long and painful process. Although the relationship between scurvy and stored food is obvious, but the
treatments of this disease have been misguided. By 1601, British armed Captain
James Lancaster discovered the disease on the ship of the East India Company and
regarded the scurvy as “rot,” which could be made tissue alkaline.
At the early stage of the nineteenth century, the understanding and treatment of scurvy had developed to a right approach. The exposition of
scurvy etiology and metabolic theory took more than a century.
By the early stage of the twentieth century, inspired by the animal model of beriberi, researchers in the Christchurch Oslo University discovered one animal that
could suffer scurvy accidentally and then established a valuable scurvy animal
model. This experiment demonstrated that the extract isolated from lemon had antiscurvy activity. Until 1932, many research groups obtained the anti-scurvy crystal
from different plants and identified the crystal as ascorbic acid vitamin C. Next year,
the chemical structure of ascorbic acid was elucidated, and then its artificial synthesis was accomplished.
-
용도
antiscorbutic, antiviral
-
정의
ChEBI: L-ascorbic acid is the L-enantiomer of ascorbic acid and conjugate acid of L-ascorbate. It has a role as a coenzyme, a flour treatment agent, a food antioxidant, a plant metabolite, a cofactor, a skin lightening agent and a geroprotector. It is an ascorbic acid and a vitamin C. It is a conjugate acid of a L-ascorbate. It is an enantiomer of a D-ascorbic acid.
-
Indications
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is essential for the maintenance
of the ground substance that binds cells together
and for the formation and maintenance of collagen.The
exact biochemical role it plays in these functions is not
known, but it may be related to its ability to act as an
oxidation–reduction system.
-
일반 설명
White to very pale yellow crystalline powder with a pleasant sharp acidic taste. Almost odorless.
-
공기와 물의 반응
May be sensitive to prolonged exposure to air and light. Sensitive to moisture. Soluble in water. Aqueous solutions are oxidized by air in a reaction that is accelerated by alkalis, iron and copper. The rate depends on the pH and on oxygen concentration. Also subject to degradation under anaerobic conditions.
-
반응 프로필
L(+)-Ascorbic acid is a lactone. Reacts as a relatively strong reducing agent and decolorizes many dyes. Forms stable metal salts. Incompatible with oxidizers, dyes, alkalis, iron and copper. Also incompatible with ferric salts and salts of heavy metals, particularly copper, zinc and manganese .
-
화재위험
Flash point data for L(+)-Ascorbic acid are not available; however, L(+)-Ascorbic acid is probably combustible.
-
Pharmacology
Vitamin C is considered as a classical enzyme cofactor or antioxidant but also as a transition material in metal ion reaction. And all of these functions of vitamin C are related to the property of antioxidation.
-
Clinical Use
Vitamin C is indicated for the treatment and prevention of known or suspect deficiency. Although scurvy occurs infrequently, it is seen in the elderly, infants, alcoholics, and drug users.Ascorbate can also be used to enhance absorption of dietary nonheme iron or iron supplements. Ascorbic acid (but not the sodium salt) was historically used to acidify the urine as a result of excretion of unchanged ascorbic acid, although this use has fallen into disfavor. Ascorbate also increases iron chelation by deferoxamine, explaining its use in the treatment of iron toxicity.
-
부작용
Megavitamin intake of vitamin C may result in diarrhea
due to intestinal irritation. Since ascorbic acid is
partially metabolized and excreted as oxalate, renal oxalate
stones may form in some patients.
-
Toxicology
L-Ascorbic acid, or vitamin C, is widely present in plants. The structures of ascorbic acid and dehydroascorbic acid are shown in Figure 10.5. Vitamin C is not only an important nutrient but is also used as an antioxidant in various foods. However, it is not soluble in fat and is unstable under basic conditions. Vitamin C reduces cadmium toxicity and excess doses prolong the retention time of an organic mercury compound in a biological system. Overdoses of vitamin C (106 g) induce perspiration, nervous tension, and lowered pulse rate. WHO recommends that daily intake be less than 0.15 mg/kg. Toxicity due to ascorbic acid has not been reported. Although repeated intravenous injections of 80 mg dehydroascorbic acid was reported to be diabetogenic in rats, oral consumption of 1.5 g/day of ascorbic acid for six weeks had no effect on glucose tolerance or glycosuria in 12 normal adult males and produced no change in blood glucose concentrations in 80 diabetics after five days. The same report noted that a 100-mg intravenous dose of dehydroascorbic acid given daily for prolonged periods produced no signs of diabetes. Ascorbic acid is readily oxidized to dehydroascorbic acid, which is reduced by glutathione in blood.
-
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by
ingestion and intravenous routes. Human
systemic effects by intravenous route: blood,
changes in tubules (including acute renal
failure, acute tubular necrosis). An
experimental teratogen. Other experimental
reproductive effects. Mutation data
reported. When heated to decomposition it
emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
-
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from MeOH/Et2O/pet ether [Herbert et al. J Chem Soc 1270 1933]. [Beilstein 18/5 V 26.]



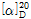 =+20.5~+21.5°이어야 한다.
=+20.5~+21.5°이어야 한다.