What is Ethyl Acetate?
Chemical Properties
Ethyl acetate is a colorless transparent liquid with low toxicity and sweet taste. Ethyl acetate is volatile and has a pungent odor at high concentrations. Because it can absorb water, it can slowly hydrolyze and become acidic. It is miscible with chloroform, ethanol, acetone and ether, and soluble in water (10% ml / ml). Ethyl acetate can dissolve certain metal salts (such as lithium chloride, cobalt chloride, zinc chloride, ferric chloride, etc.). The relative density is 0.902. Melting point is -83°C. The boiling point is 77°C. The refractive index is 1.3719. Flash point is 7.2°C (open cup). Due to the flammable and volatile nature of ethyl acetate, its vapor can form explosive mixtures with air.
Laboratory and industrial preparation methods
The preparation of ethyl acetate in the laboratory includes the following steps [1-3]: first add ethanol, then concentrated sulfuric acid (zeolite is added to prevent bumping), finally add acetic acid, and then heat. Esterification is a reversible reaction. In order to increase the yield of the ester, it is necessary to make the reaction proceed in a direction favorable to the formation of the ester as much as possible. Usually one of the reactants, acid or alcohol, is made in excess. The reaction temperature should not be too high in the preparation of ethyl acetate, because the ether and the impurities such as sulfurous acid or ethylene will be generated when the temperature is too high. The industry includes four preparation methods: direct esterification method, acetaldehyde condensation method, ethylene addition method and ethanol dehydrogenation method. The direct esterification method uses acetic acid and ethanol as raw materials, and sulfuric acid as a catalyst to directly esterify to obtain ethyl acetate, which is then dehydrated and fractionally refined to obtain a finished product. The acetaldehyde condensation method uses an aluminum alkyl as a catalyst, and condenses acetaldehyde to generate ethyl acetate. Most foreign industrial production uses this process. Ethyl acetate can also be prepared by reacting acetic acid, acetic anhydride or ketene with ethanol. It can also be formed by the reaction of two molecules of acetaldehyde under the catalysis of aluminum ethoxide. In addition, ethyl acetate is also produced as a by-product in the industrial production of acetic acid from butane oxidation.
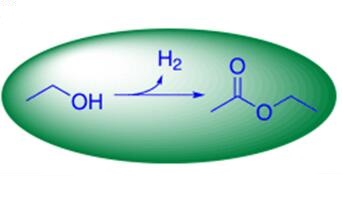
Fig 1. A green process for bulk‐scale synthesis of ethyl acetate[4].
Applications
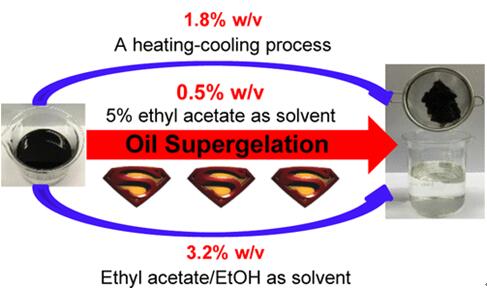
Fig 2. Ethyl acetate as a solvent to assist dissolution of phase-selective organogelators [7].
Ethyl acetate has boarding applications as following [5-7]:
• As an industrial solvent, used in coatings, adhesives, ethyl cellulose, artificial leather, linoleum colorants, artificial fibers and other products
• As a binder, it is used in the production of printing inks and artificial pearls.
• As an extractant, it is used in the production of pharmaceuticals, organic acids and other products.
• As the raw material of spices, it is used as the main raw material of fruit flavors such as pineapple, banana and strawberry, and flavors such as whiskey and cream.
• As an extractant, many compounds (phosphorus, tungsten, arsenic, cobalt) are extracted from aqueous solutions.
• As an organic solvent, it is used as a standard substance for the calibration of thermometers when separating saccharides.
• Test for bismuth, gold, iron, mercury, oxidants and platinum.
• Biochemical research and protein sequence analysis.
• Environmental protection and pesticide residue analysis.
• Important raw materials for the pharmaceutical industry and organic synthesis.
• Fast-drying solvents for nitrocellulose, ethylcellulose, cellulose acetate, and neoprene are also low-toxic solvents used in industry.
• Textile industry cleaners and natural fragrance extractants
• GB 2760—96 stipulates that food flavors allowed to be used. It is mainly used for fragrance, persimmon deastringency, making granules or tablets of spices, and vinegar ingredients. Widely used in the preparation of cherry, peach, apricot and other fruit flavors and brandy and other wine flavors.
References
[1] Larkins Jr T H. Preparation of ethyl acetate: U.S. Patent 4,886,905[P]. 1989-12-12.
[2] Gruffaz M, Micaelli O. Catalytic preparation of ethyl acetate: U.S. Patent 4,275,228[P]. 1981-6-23.
3] Hassan A, Bagherzadeh E, Anthony R G, et al. Method of producing ethyl acetate: U.S. Patent 8,080,684[P]. 2011-12-20.
[4] Nielsen M, Junge H, Kammer A, et al. Towards a green process for bulk‐scale synthesis of ethyl acetate: efficient acceptorless dehydrogenation of ethanol[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2012, 51(23): 5711-5713.
[5] Spangenberg G C, Mann R, Auer D, et al. Bioactive Fungi: U.S. Patent Application 15/762,999[P]. 2018-10-25.
6] Young K H, Bullock S L, Melvin D M, et al. Ethyl acetate as a substitute for diethyl ether in the formalin-ether sedimentation technique[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 1979, 10(6): 852-853.
[7] Juntong L., Yanping H. and Huaqiang Z. Polar Solvent-Induced Unprecedented Supergelation of (Un)Weathered Crude Oils at Room Temperature [J]. Langmuir 2018, 34, 27, 8058-8064
You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Ethyl acetate manufacturers

US $10.00/KG2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 141-78-6
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 100 mt

US $0.00/kg2025-04-15
- CAS:
- 141-78-6
- Min. Order:
- 20kg
- Purity:
- 99.0%
- Supply Ability:
- 20 tons





