Morpholine: Application, synthesis and toxicity
General description
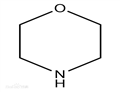
Morpholine is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula O(CH2CH2)2NH. This heterocycle features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base; its conjugate acid is called morpholinium. For example, treating morpholine with hydrochloric acid makes the salt morpholinium chloride. The naming of morpholine is attributed to Ludwig Knorr, who incorrectly believed it to be part of the structure of morphine. Its appearance is as follows:

Figure 1 Appearance of Morpholine.
Application
Morpholine is a common additive, in parts per million concentrations, for pH adjustment in both fossil fuel and nuclear power plant steam systems. Morpholine is used because its volatility is about the same as water, so once it is added to the water, its concentration becomes distributed rather evenly in both the water and steam phases. Its pH-adjusting qualities then become distributed throughout the steam plant to provide corrosion protection. Morpholine is often used in conjunction with low concentrations of hydrazine or ammonia to provide a comprehensive all-volatile treatment chemistry for corrosion protection for the steam systems of such plants. Morpholine decomposes reasonably slowly in the absence of oxygen at the high temperatures and pressures in these steam systems.
Morpholine undergoes most chemical reactions typical for other secondary amines, though the presence of the ether oxygen withdraws electron density from the nitrogen, rendering it less nucleophilic (and less basic) than structurally similar secondary amines such as piperidine. For this reason, it forms a stable chloramine [1]. Morpholine is widely used in organic synthesis. For example, it is a building block in the preparation of the antibiotic linezolid, the anticancer agent gefitinib (Iressa) and the analgesic dextromoramide. In research and in industry, the low cost and polarity of morpholine lead to its common use as a solvent for chemical reactions.
Morpholine is used as a chemical emulsifier in the process of waxing fruit. Naturally, fruits make waxes to protect against insects and fungal contamination, but this can be lost as the fruit is cleaned. A small amount of new wax is applied to replace it. Morpholine is used as an emulsifier and solubility aid for shellac, which is used as a wax for fruit coating [2]. The European Union has forbidden the use of morpholine in fruit coating. Morpholine derivatives used as agricultural fungicides in cereals are known as ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitors.
Synthesis
Morpholine can be synthesized by deallyloxycarbonylation reaction [3]. A mixture of allyl 2-phenylethyl carbonate (10.8 g, 52.2 mmol) and methanol (95 mL), which was placed in a 150 mL Schlenk tube containing a Teflon-coated magnetic stirring bar under argon atmosphere, was degassed by three freeze-thaw cycles. To this solution, [CpRu(π-C3H5)(2- quinolinecarboxylato)]PF6 (55.0 mg, 105 μmol) was added. The inlet was sealed by a glass stopper coated in silicon grease. The yellow solution was stirred for 0.5 h at 30 °C. The reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure (100 mmHg) to give a crude product in which the yield and purity were determined to be >99% by 1H NMR analysis ((600 MHz, CDCl3) This product was distilled (55 °C/0.01 mmHg) to give the compound Morpholine (6.28 g) in 99% isolated yield. 1H NMR spectra of crude product were attached at the end of this material Morpholine: δ 4.00 (t, 4H, J = 4.82 Hz, CH2OCH2). 1H NMR data was consistent with the commercially available authentic sample.
Toxicity
The inhalation toxicity of 25-, 100-, and 250-ppm morpholine was investigated by 6 hr/day, 5 day/week exposures to Sprague-Dawley rats for 13 weeks. Irritant effects of morpholine exposures were evident mostly in the high exposure group; a reddish discharge was observed around the nose and mouth in the 250-ppm group rats after the first week; salivation was also observed. Ten rats/sex/dose level were sacrificed after 7 weeks. The high-level (250-ppm) exposure resulted in focal erosion and focal squamous metaplasia of the maxilloturbinates; effects were observed in 610 male rats and 210 female rats. There was also a sporadic increase of secretions in the Harderian gland sections [4].
References
[1]Lindsay et al. 4-Chlorination of Electron-Rich Benzenoid Compounds: 2,4-Dichloromethoxybenzene. Organic Syntheses. (1993), Collective Volume, 8: 167.
[2]McGuire et al. Evaluation of Shellac and Sucrose Ester Fruit Coating Formulations that Support Biological Control of Post-harvest Grapefruit Decay. Bio-control Science and Technology. (1999), 9 (1): 53–65.
[3]Tanaka et al. Catalytic removal of N-allyloxycarbonyl groups using the [CpRu(IV)(π-C3H5)(2-quinolinecarboxylato)]PF6 complex. A new efficient deprotecting method in peptide synthesis. Journal of Organic Chemistry. (2006), 71(12): 4682-4684.
[4]Conaway et al. Subchronic inhalation toxicity of morpholine in rats. Fundamental and Applied Toxicology. (1984), 4(3): 465-472.
You may like
Related articles And Qustion
Lastest Price from Morpholine manufacturers

US $10.00/KG2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 110-91-8
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 10 mt
US $0.00/Kg/Drum2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 110-91-8
- Min. Order:
- 1000KG
- Purity:
- 99.5%
- Supply Ability:
- 1000 tons





