Uses and Biodegradation of Morpholine
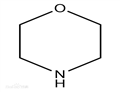
Morpholine (1,4-tetrahydro-oxazine) is a simple heterocyclic compound that has great industrial importance and a wide range of applications. This chemical compound and its derivatives have been used as rubber additives, corrosion inhibitors, solvents, optical brighteners, antioxidants and in the manufacture of a range of drugs and herbicides.

Uses
Industrial applications
Morpholine is a common additive, in parts per million concentrations, for pH adjustment in both fossil fuel and nuclear power plant steam systems. Morpholine is used because its volatility is about the same as water, so once it is added to the water, its concentration becomes distributed rather evenly in both the water and steam phases. Its pH-adjusting qualities then become distributed throughout the steam plant to provide corrosion protection.
Morpholine is often used in conjunction with low concentrations of hydrazine or ammonia to provide a comprehensive all-volatile treatment chemistry for corrosion protection for the steam systems of such plants. Morpholine decomposes reasonably slowly in the absence of oxygen at the high temperatures and pressures in these steam systems.
Organic synthesis
Morpholine undergoes most chemical reactions typical for other secondary amines, though the presence of the ether oxygen withdraws electron density from the nitrogen, rendering it less nucleophilic (and less basic) than structurally similar secondary amines such as piperidine. For this reason, it forms a stable chloramine.
It is commonly used to generate enamines.
Morpholine is widely used in organic synthesis. For example, it is a building block in the preparation of the antibiotic linezolid, the anticancer agent gefitinib (Iressa) and the analgesic dextromoramide.
In research and in industry, the low cost and polarity of morpholine lead to its common use as a solvent for chemical reactions.
Biodegradation
Consequently, morpholine can occur in a number of industrials effluents and can be disseminated in the environment. Morpholine is subject to N-nitrosation by nitrites and this reaction gives the potent mutagen N-nitrosomorpholine. These inconveniences can be avoided by elimination of morpholine from wastewater and effluents by biological treatments.
Recently, biodegradation of morpholine has been established and the isolation of pure cultures of morpholine-degrading bacteria has been reported. Up to date, only Gram positive bacteria have been shown to use this compound as sole source of carbon, nitrogen and energy. Most of these have been identified as Mycobacterium sp.
Mycobacterium aurum MOI was isolated from activated sludge from the Prague Central Wastewater Treatment plant for its abilities to utilize morpholine as the main source of carbon, nitrogen and energy. However in liquid medium this microorganism grows in clumps and aggregates so it is difficult to follow its growth and to obtain a convenient degradation of morpholine. In order to overcome these disadvantages, the bacteria were submitted to physical confinement by immobilization in κ-carrageenan gel beads.
You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Morpholine manufacturers

US $10.00/KG2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 110-91-8
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 10 mt
US $0.00/Kg/Drum2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 110-91-8
- Min. Order:
- 1000KG
- Purity:
- 99.5%
- Supply Ability:
- 1000 tons





