Costunolide: A plant extract with anticancer properties
Introduction
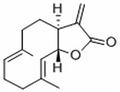
Costunolide, a biologically potent germacranolide-type SL, is present in several plants, such as Magnolia grandiflora and Tanacetum parthenium. Indeed, it is predominantly isolated from the roots of Saussurea costus and Magnolia grandiflora. Costunolide is a representative sesquiterpene lactone extensively investigated for various biological activities. Various studies have indicated that this compound possesses antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, anticancer, and antidiabetic properties. Recent studies have found that Cos possesses anticancer effects against human gastric adenocarcinoma, prostate cancer, liver cancer, bladder cancer, and esophageal cancer and promotes apoptosis of a variety of cancer cells.

Biological functions and uses
Costunolide from roots of Saussurea costus inhibited contractions of the rabbit-isolated aorta induced by KCl (Potassium chloride) but exerted considerably less effect on those induced by norepinephrine, indicating the possible calcium antagonistic action of costunolide. Dehydrocostuslactone caused similar inhibitory effects on the aorta, but its specificity to potassium chloride induced contractions appeared to be less than that observed with costunolide.
Costunolide selectively inhibited the endothelial cell proliferation induced by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). It was also found to inhibit the VEGF-induced chemotaxis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in a dose-dependent manner. The result showed that costunolide might inhibit angiogenesis by blocking the angiogenic factor signaling pathway. VEGF interacts with its cognate receptors, KDR/Flk-1 and Flt-1, and exerts its angiogenic effect. Costunolide inhibited the autophosphorylation of KDR/Flk-1 without affecting that of Flt-1. These results suggest that costunolide may be helpful for developing a novel angiogenesis inhibitor.
Kim et al. studied the mechanism of action of costunolide and suggested that it acts by inhibiting the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced NF-κB activation pathway in a dose-dependent manner. Detailed mechanistic studies revealed that the drug molecule also significantly inhibits the degradation of IκB (inhibitory κB)-α and IκB-β. In addition, the compound inhibited the phosphorylation of IκB-α. These accumulative results indicate that SL 1 inhibits NF-κB activation by preventing the phosphorylation of IκB proteins. Kassuyaa et al. also isolated costunolide from the ethanolic extract of Magnolia ovata and evaluated its anti-inflammatory activity. Results showed the effectiveness of the natural molecule in preventing the formation of edema. Butturini et al. studied the efficacy of costunolide and dehydrocostunolide in a carrageenan-induced model of lung injury. The downregulation of parameters such as NF-κB, signal transducer, and activator of transcription 3 activation were recorded. Results showed that both molecules possess potential biological activity against lung inflammation.
References:
[1] CUIXIANG XU. Costunolide-Induced Apoptosis via Promoting the Reactive Oxygen Species and Inhibiting AKT/GSK3β Pathway and Activating Autophagy in Gastric Cancer.[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021. DOI:10.3389/fcell.2021.722734.You may like
See also
Lastest Price from Costunolide manufacturers

US $0.00/G/KG2025-04-22
- CAS:
- 553-21-9
- Min. Order:
- 1G/KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 100MT
US $0.00/mg2023-02-24
- CAS:
- 553-21-9
- Min. Order:
- 5mg
- Purity:
- ≥98%(HPLC)
- Supply Ability:
- 10 g


