2-Aminothiazole: structural characteristics and its derivatives as anti-cancer agents
General Description
2-Aminothiazole derivatives have emerged as promising anti-cancer agents with versatile structural characteristics. The presence of the thiazole core and amino group allows for diverse modifications, leading to potent biological activities. Approved drugs like famotidine, abafungin, cefdinir, and riluzole containing the 2-aminothiazole moiety highlight its therapeutic potential. In cancer treatment, these derivatives act as tubulin inhibitors by targeting the colchicine site, inducing significant anti-proliferative effects and apoptosis in cancer cells. Moreover, as inhibitors of HAT and HDAC enzymes, they modulate histone acetylation, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells. The selectivity and improved activity of 2-Aminothiazole derivatives make them promising candidates for further development as effective anti-cancer therapies.

Figure 1. 2-Aminothiazole
Structural characteristics
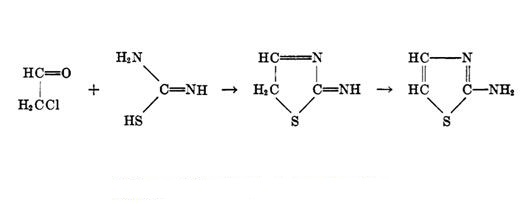
2-Aminothiazole moiety is composed of a thiazole core and an amino group. The thiazole core is a five-membered heterocycle with sulfur and nitrogen at positions 1 and 3, respectively. This core is present in various bioactive compounds such as vitamin thiamine B1. The amino group attached to the thiazole core is an actively functional group that can be linked to many active fragments through different reactions. Due to its versatile scaffold, 2-aminothiazole has been widely modified to construct diverse derivatives with excellent biological activities. Many agents containing 2-aminothiazole moiety have been approved for marketing. Famotidine is an antagonist of histamine H2 receptor used to cure peptic ulcer and gastroesophageal reflux by inhibiting the secretion of gastric juices. Abafungin is an anti-fungal drug used in the therapy of dermatomycoses. Cefdinir is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, and tonsillitis. Riluzole is an approved drug for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and recently it has also shown promising anti-cancer effects against breast cancer, melanoma, glioma, and prostate cancer. Previously, 2-Aminothiazole derivatives were known for their antimicrobial, antibacterial, and antifungal properties. 1
2-Aminothiazole derivatives as anti-cancer agents
Tubulin inhibitors
2-Aminothiazole derivatives have shown promise as potential anti-cancer agents by inhibiting microtubules, which are vital for various cellular processes. While tubulin inhibitors targeting taxanes or vinca alkaloids binding sites have limitations, those binding to the colchicine site offer advantages. Recent studies have demonstrated that 2-aminothiazole derivatives with different substituents at the C-2 position exhibit significant anti-proliferative activities and act as potent tubulin inhibitors, inducing cancer cell apoptosis through caspase activation. Compound 6, with an amino group at the C-2 position, showed the most potent activities against cancer cell lines. Additionally, novel colchicine binding site inhibitors (CBSIs) incorporating three aromatic rings, such as compound 7 with 2,4-dimethoxy substitution, displayed potent anti-proliferative activities. Molecular docking studies confirmed their ability to target the colchicine binding sites in tubulin. These findings suggest that 2-aminothiazole derivatives hold promise for the development of effective anti-cancer agents by specifically targeting microtubule dynamics and inducing cell apoptosis. 2
HAT/HDAC inhibitors
2-Aminothiazole derivatives also have shown promising potential as anti-cancer agents, particularly as inhibitors of Histone Acetyltransferases (HAT) and Histone Deacetylases (HDAC). HAT enzymes acetylate histones, leading to open chromatin configuration and gene transcription, while HDAC enzymes remove these acetyl groups, causing chromatin condensation and transcriptional repression. The balance between acetylation and deacetylation plays a crucial role in cell growth and differentiation. Researchers have developed a series of 2-aminothiazole derivatives with modifications to enhance their inhibition of HAT and HDAC activity. By optimizing the structure, they achieved compounds with potent inhibitory effects on histone acetylation, leading to cell cycle arrest, redifferentiation, and apoptosis in cancer cells. 2-Aminothiazole derivatives showed selectivity for specific histone acetylation marks and demonstrated significant anti-proliferative activities in various cancer cell lines. Additionally, some compounds exhibited improved HDAC inhibitory activity compared to existing drugs like SAHA, making them promising candidates for further development as anti-cancer therapies. 2
Reference
1. Das D, Sikdar P, Bairagi M. Recent developments of 2-aminothiazoles in medicinal chemistry. Eur J Med Chem. 2016;109:89-98.
2. Wan Y, Long J, Gao H, Tang Z. 2-Aminothiazole: A privileged scaffold for the discovery of anti-cancer agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;210:112953.
You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from 2-Aminothiazole manufacturers

US $0.00-0.00/kg2025-11-20
- CAS:
- 96-50-4
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 98%
- Supply Ability:
- 100tons

US $0.00-0.00/Kg2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 96-50-4
- Min. Order:
- 1Kg
- Purity:
- 99.99%
- Supply Ability:
- 20 tons