2-aminothiazole——Application, Synthesis, Reaction etc.
2-aminothiazole is a heterocyclic amine featuring a thiazole core and it can also be considered a cyclic isothiourea. 2-aminothiazole possesses an odor similar to pyridine and is soluble in water, alcohols and diethyl ether [1].
Application of 2-aminothiazole
The term 2-aminothiazole simply refers to this heterocyclic ring with an S and 2 Ns. The monoazo heterocyclic compounds containing sulphur and/or nitrogen atoms are of widespread use as building blocks in chemistry, where they are known as biologically active compounds with a broad range of activity, and textile dyes as well. As a typical heterocyclic amine, 2-aminothiazole is the starting point for the synthesis of many compounds, including sulfur drugs, biocides, fungicides, dyes and chemical reaction accelerators and as intermediates in the synthesis of antibiotics [2].
Synthesis of 2-aminothiazole
The synthesis of 2-aminothiazole involves basically a reaction between chloroacetaldehyde and thiourea as shown in scheme 1, which presented the preparation of 2-aminothiazole from cyclic acetals, which were readily formed by the action of glycols on -chloroethers.
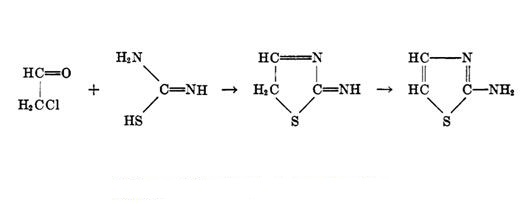
Scheme 1 Synthesis of 2-aminothiazole
Since chloroacetaldehyde shows this tendency to polymerize and cannot be obtained pure, several preparations of 2-aminothiazole avoid its use. In some preparation method, diethylchloroacetal replaced chloroacetaldehyde and was converted to aminothiazole by reaction with thiourea. After reaction, the isolation of 2-aminothiazole in all of the processes above was accomplished in much the same way. This involved treating the product mixture with activated carbon, neutralizing the clear filtrate with a concentrated solution of NaOH (30-40%), and extracting the free base with ether. After the ether was removed, the solid product was recrystallized from ethanol. The reported yields varied from about 50 to more than 90% per cent of the theoretical [3].
Reaction of 2-aminothiazole
As react with saturated electrophilic reagents, the reactivity of 2-aminothiazole towards the reactants bearing an sp3 C electrophilic center follows the general pattern (Scheme 2). If the thiazole reacts in its neutral form, the ring nitrogen atom is the more reactive center, except when bulky substituents are present at the C-4 position. If the thiazole reacts in the form of its conjugate base, the ambident anion leads to a mixture of products resulting from the N-ring and N-exocyclic reactivity.
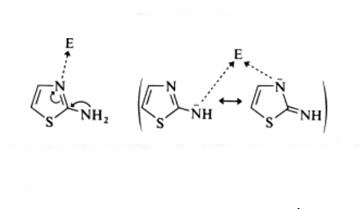
Scheme 2 The general pattern of 2-aminothiazole as react with saturated electrophilic reagents
As react with unsaturated electrophilic reagents under mild conditions, 2-aminothiazole react at their exocyclic nitrogen atom with aromatic aldehydes, yielding Schiff bases as shown in scheme 3 [4]. These Schiff bases, under stronger conditions, may afford benzylidenebisaminothiazoles (scheme 4).

Scheme 3 Schiff bases synthesis with 2-aminothiazole
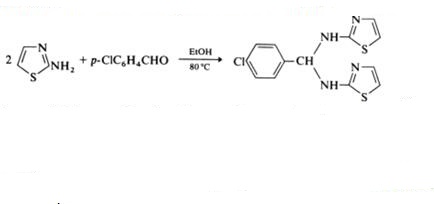
Scheme 4 The synthesis of benzylidenebisaminothiazoles
References
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aminothiazole
[2] Mohamed Ezzat Khalifa, Recent Developments and Biological Activities of 2-Aminothiazole Derivatives, Acta Chim. Slov. 2018, 65, 1–22.
[3] Melvin J. Astlejames B. Pierce, The Preparation of 2-Aminothiazole from Cycle Acetals, J. Org. Chem. 1955, 20, 2, 178-181.
[4] https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/pharmacology-toxicology-and-pharmaceutical-science/2-aminothiazole
You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from 2-Aminothiazole manufacturers

US $0.00-0.00/kg2025-11-20
- CAS:
- 96-50-4
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 98%
- Supply Ability:
- 100tons

US $0.00-0.00/Kg2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 96-50-4
- Min. Order:
- 1Kg
- Purity:
- 99.99%
- Supply Ability:
- 20 tons




