2-Aminothiazole: synthesis, biological activities and toxicity
General Description
2-Aminothiazole and its derivatives can be synthesized using various methods such as Hantzsch's synthesis, Cook Heilborn, and Tchernic. Hantzsch's synthesis involves the reaction of α-halo carbonyl compounds with thioureas or thioamides in the presence of catalysts. Other methods include condensation of rhodanamine with ethyl acetoacetate or formamidine disulfide hydrobromide, direct combination of carbonyl compounds and thiourea using bromine as a condensing agent, and the reaction of trichloroether with diethylene glycol. These compounds exhibit diverse biological activities including antimicrobial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and enzyme inhibitory properties. They hold potential for drug development in treating infections, inflammatory diseases, cancer, autoimmune disorders, and cell signaling modulation. However, it is important to note that 2-aminothiazole is toxic and can cause adverse effects through oral, inhalation, and skin exposure. Chronic exposure can lead to toxicity in the nervous system, kidneys, and reproductive system. Protective measures should be taken to avoid exposure to this compound.

Figure 1. 2-Aminothiazole
Synthesis
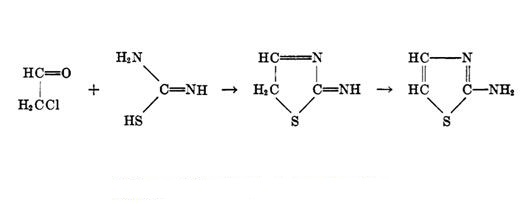
To date, there are many methods for the preparation of 2-aminothiazole and their derivatives such as Hantzsch, Cook Heilborn, and Tchernic have been reported. The first and most frequently used method is Hantzsch’s synthesis, who originated it in 1887, involving the reaction of α-halo carbonyl compounds with thioureas or thioamides in the presence of bromine/iodine, silica chloride, 1,3-di-nbutylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, ammonium 12-molybdophosphate, and cyclodextrin, aq. NaICl2 or using various homogenous and heterogonous catalysts. Another method of 6 preparations involves condensation rhodanamine with the tenfold excess of ethyl acetoacetate in a melt at 100–120 °C. Condensation of ethyl acetoacetate with formamidine disulfide hydrobromide was performed analogously, providing 6 in 57–62% yield. Carbonyl compounds and thiourea can be combined directly into the thiazole ring using bromine as the condensing agent. Reaction of ethyl β-ethoxyacrylate with N-bromosuccinimide produces a novel intermediate, α-bromo-α-formylacetate hemiacetal. Cyclization of the in situ formed hemiacetal with thioureas, also afforded 2-aminothiazole-5-carboxylates. Moreover, reaction of the trichloroether with diethylene glycol gives the cyclic acetal, which may also be converted to 2-aminothiazole. 1
Biological activities
2-Aminothiazole serves as a versatile starting material for the synthesis of various compounds due to its unique structure and reactivity. Sulfur-based compounds have long been used for their antimicrobial properties, and 2-aminothiazole derivatives can be modified to enhance their effectiveness against specific pathogens. These derivatives have also shown promising results as potential antifungal agents, inhibiting the growth of fungi and preventing infections. Additionally, 2-aminothiazole derivatives exhibit anti-inflammatory properties, making them useful in the development of drugs for treating inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and asthma. They have been shown to inhibit the production of inflammatory mediators, reducing inflammation and alleviating symptoms. In addition to these therapeutic applications, 2-aminothiazole derivatives have shown inhibitory activity against enzymes involved in eicosanoid metabolism. Eicosanoids are lipid signaling molecules that play a role in inflammation, immune responses, and other physiological processes. By inhibiting these enzymes, 2-aminothiazole derivatives have the potential to modulate eicosanoid signaling and provide new therapeutic avenues for various diseases. Its derivatives have been investigated as potential inhibitors for specific kinases, which are enzymes involved in cell signaling and regulation. By selectively inhibiting certain kinases, these compounds can modulate cellular processes and have implications in the treatment of diseases such as cancer and autoimmune disorders. Overall, 2-aminothiazole and its derivatives have a wide range of biological activities and potential applications in drug discovery and development. 2
Toxicity
Acute oral exposure to high doses of 2-aminothiazole can cause adverse effects such as vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Inhalation of the compound can result in irritation of the respiratory tract, coughing, and shortness of breath. Skin contact with 2-aminothiazole may cause irritation and burning sensation. Chronic exposure to low levels of 2-aminothiazole can result in cumulative toxic effects. Prolonged exposure has been associated with adverse effects on the nervous system, including tremors, convulsions, and coma. Additionally, 2-aminothiazole has been shown to be nephrotoxic, causing damage to the kidneys, and may also cause reproductive toxicity, affecting male fertility. Overall, 2-aminothiazole is considered a toxic compound, and exposure should be avoided. Workers handling this compound are advised to use appropriate personal protective equipment and follow safety guidelines to minimize exposure. 3
Reference
1. Alizadeh SR, Hashemi SM. Development and therapeutic potential of 2-aminothiazole derivatives in anticancer drug discovery. Med Chem Res, 2021, 30(4):771-806.
2. Khalifa ME. Recent Developments and Biological Activities of 2-Aminothiazole Derivatives. Acta Chim Slov, 2018, 65(1):1-22.
3. Wan Y, Long J, Gao H, Tang Z. 2-Aminothiazole: A privileged scaffold for the discovery of anti-cancer agents. Eur J Med Chem, 2021, 210:112953.
Related articles And Qustion
Lastest Price from 2-Aminothiazole manufacturers

US $0.00-0.00/kg2025-11-20
- CAS:
- 96-50-4
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 98%
- Supply Ability:
- 100tons

US $0.00-0.00/Kg2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 96-50-4
- Min. Order:
- 1Kg
- Purity:
- 99.99%
- Supply Ability:
- 20 tons