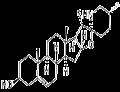
SOLASODINE
- Product NameSOLASODINE
- CAS126-17-0
- CBNumberCB5132193
- MFC27H43NO2
- MW413.64
- EINECS204-774-2
- MDL NumberMFCD00037844
- MOL File126-17-0.mol
- MSDS FileSDS
Chemical Properties
| Melting point | 200-202° |
| alpha | D25 -98° (c = 0.14 in methanol); D -113° (CHCl3) |
| Boiling point | 532.75°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0159 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6400 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble0.5mg/mL, clear (warmed) |
| pka | pKb 6.30(at 25℃) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to beige |
| optical activity | [α]/D -88 to -98°, c = 0.2 in methanol |
| InChIKey | KOZCINYDCJVLDW-GCGBSLFCSA-N |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 126-17-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| FDA UNII | L40Y453Y96 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Solasodine(126-17-0) |
| UNSPSC Code | 12352200 |
| NACRES | NA.77 |
Safety
| Safety Statements | 22-24/25 |
| RTECS | WF1300000 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 126-17-0(Hazardous Substances Data) |