Unique properties of triisopropyl chlorosilane
Background
Organosilicon protective agent (OSPA for short), also known as silane protective agent (SBA for short), is used to replace active hydrogen in compounds (such as hydroxyl, carboxyl and amino hydrogen) with silyl groups to generate stable intermediates; then the intermediate Other groups of the body undergo some reactions; after the reaction, the silyl group is removed through the hydrolysis reaction to regenerate the group originally protected by the silyl group to synthesize some specific compounds. Due to the high conversion rate and even quantitative reaction of silane protection and deprotection reactions, it is widely used in organic synthesis, especially in the synthesis of drugs and natural products. The earliest used silicone protective agent is trimethylsilane protective agent. With the deepening of research, it has been found that the trimethylsilyl ether intermediate formed when this silyl group is used for the protection of carboxyl groups is very unstable in polar media, and has certain effects on acid, base catalysis and solvent hydrogenolysis reactions. limitation. The intermediates obtained by using sterically hindered silicone protective agents (silicon atoms connected with large groups such as tert-butyl, isopropyl, and phenyl) are compared in water, sodium alkoxides and neutral reducing media. Stablize. Triisopropyl chlorosilane is a typical sterically hindered monofunctional silicone protective agent[1].
Properties of triisopropyl chlorosilane
Triisopropyl chlorosilane is an important sterically hindered organosilicon protective agent, which is mainly used to protect various types of hydroxyl groups, especially in polyfunctional hydroxyl compounds, which can be selectively protected and deprotected. It is very important to synthesize nucleosides, nucleotides and carbohydrates. Triisopropylchlorosilane is a good hydroxyl protecting agent, and its silanization reaction is carried out in a slight excess of imidazole solution. The acid hydrolytic stability of the protected intermediate is between TBDMS and TBDPS and the alkaline hydrolytic stability is higher than the former two.
The synthetic method of triisopropyl chlorosilane
There are two main methods for synthesizing triisopropyl chlorosilane. One is to use triisopropyl silane as a raw material, and hydrochloric acid and other reagents are used to chlorinate the hydrogen on the silicon[2]. Another method uses silicon tetrachloride as raw material, and reacts with isopropyl lithium to obtain triisopropyl chlorosilane. Because triisopropyl chlorosilane and isopropyl lithium are expensive, in order to further reduce the production cost, we refer to the synthesis methods of other organosilicon protective agents, use silicon tetrachloride as raw material, and react with the Grignard reagent of bromoisopropane, One step obtains triisopropyl chlorosilane, and the yield reaches 74%, and the circuit is shown in Figure 1.
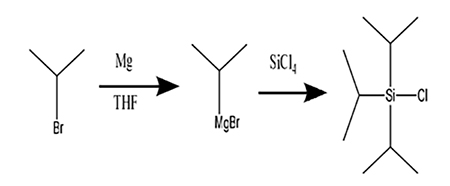
Figture 1 The synthetic method of triisopropyl chlorosilane
Application of triisopropyl chlorosilane
Triisopropyl chlorosilane is mainly used as a basic intermediate in the synthesis of organic silicon materials and a blocking agent for silicone oil or silicone rubber. These triisopropylchlorosilanes can be used as raw materials for preparing functional silanes or silane coupling agents. In the reaction with organometallic compounds, the chlorine atoms of triisopropylchlorosilane are replaced by corresponding organic groups to form organochlorosilanes or organofunctional silanes.
Triisopropyl chlorosilane is mainly used in the production of aminosilane and methacryloxysilane, and can also be used as a rubber processing additive to couple inorganic fillers in various halogenated rubbers, such as neoprene rubber, chlorobutyl rubber , chlorosulfonated polyethylene and other halogenated rubbers. The existence of triisopropylchlorosilane can greatly improve various physical and mechanical properties of composites. Triisopropylchlorosilane can also be used to prepare antifungal and deodorant finishes with special bactericidal, deodorant, antistatic and surface-active properties.
Industry development status
The "Oligomers and Siloxanes" business unit of Degussa AG produces additives, auxiliaries and semi-finished products for the processing of modified silicones and organo-oligomers. Tego's coatings and ink additives business had sales of 3.35 billion euros in 2003, with 970 employees in 10 factories worldwide. Tego Coatings and Ink Additives, a specialist in the coatings industry, manufactures additives, water repellents and heat resistant silicone adhesives. Tego's additive business is primarily for water-based and radiation-vulcanized coatings and printing inks.
Wacker is a multinational chemical company headquartered in Munich, Germany. The product range includes semiconductors, silicones and specialty chemicals. Total sales in 2003 were 2.5 billion euros 80% of the business was done outside Germany. Wacker has about 15,600 employees in 22 production plants in Europe, America and Asia.
Reference
1 Li Wenhai, Kan Zigui, Huangshan. A synthesis method of triisopropyl chlorosilane[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2009,36(10):63.
2 Wen Yuanqing, Xie Qinglan, Deng Fengjie. Steric Hindered Silane Protective Agent [J]. Organosilicon Materials, 2004(06):21-23+49.
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Triisopropylsilyl chloride manufacturers

US $0.00/kg2025-04-18
- CAS:
- 13154-24-0
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 96%
- Supply Ability:
- 20t

US $0.00/KG2025-04-15
- CAS:
- 13154-24-0
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 500000kg



