Triisopropylsilyl Chloride: Applications in Chemical Syntheses and its Safety Hazards
General Description
Triisopropylsilyl chloride is a key reagent in chemical synthesis, notably enhancing enantioselective reactions by sequestering fluoride ions produced during oxidative processes, preventing unwanted side reactions that can affect product yield and enantioselectivity. Its effectiveness is particularly demonstrated in the synthesis of 2-oxazolidinones from N-Boc amines and alkenes. Beyond this specific application, Triisopropylsilyl chloride serves as a versatile protecting group in various organic reactions, stabilizing reactants and intermediates while improving reaction conditions. However, Triisopropylsilyl chloride poses significant safety hazards, being corrosive and a toxic inhalation risk; therefore, proper handling protocols, personal protective equipment, and well-ventilated working environments are essential to minimize exposure and health risks during its use.

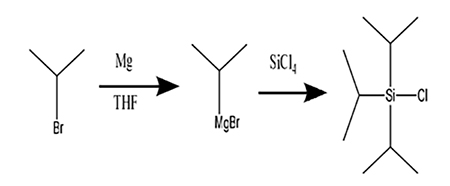
Figure 1. Triisopropylsilyl chloride
Applications in Chemical Syntheses
Triisopropylsilyl chloride plays a pivotal role in various chemical syntheses, prominently in the realm of enantioselective reactions. This reagent is characterized by its ability to effectively sequester fluoride ions generated through oxidative processes, thus preventing unwanted side reactions that could compromise the yield and enantioselectivity of desired products. Its utility was notably demonstrated in the synthesis of 2-oxazolidinones from N-Boc amines and alkenes, where the presence of triisopropylsilyl chloride significantly enhanced the overall efficiency of the reaction and improved the quality of the final product. 1
Mechanistic Contribution
During the catalytic process, triisopropylsilyl chloride operates by binding fluoride ions, which arise from the use of oxidants such as N-fluorocollidinium tetrafluoroborate. By sequestering these fluoride ions, triisopropylsilyl chloride mitigates potential side reactions that could detract from the reaction's productivity. This mechanistic aspect is crucial, as the suppression of such reactivity allows for more efficient generation of the 2-oxazolidinone products. As a result, the use of triisopropylsilyl chloride not only enhances the success of the specific transformation but also broadens the scope of applicable substrates in terms of both the amine and alkene components. 1
Broader Implications and Applications
The incorporation of triisopropylsilyl chloride in synthetic methodologies extends beyond the synthesis of 2-oxazolidinones, highlighting its versatility as a protecting group in a variety of other organic reactions. Its ability to stabilize reactants and coordinate with reactive intermediates is invaluable in fine-tuning reaction conditions across numerous chemical transformations. By refining the reaction environment and reducing side reactivity, triisopropylsilyl chloride stands out as a key reagent in the toolkit of synthetic chemists focused on developing enantioselective processes. Ultimately, its contribution to improved yields and selectivities firmly establishes triisopropylsilyl chloride as an indispensable element in modern organic synthesis. 1
Safety Hazards
Hazard Classes and Potential Risks
Triisopropylsilyl chloride poses significant safety hazards that must be understood to ensure proper handling and use. Classified under the hazard category of Skin Corrosive 1B, this chemical is known to react vigorously with water, producing hydrochloric acid as a byproduct. Such reactions can lead to severe burns upon contact with skin, highlighting the corrosive nature of Triisopropylsilyl chloride. Inhalation of its vapors may result in corrosive injuries to the upper respiratory tract and lungs, potentially causing serious health issues. These risks necessitate thorough safety protocols to minimize exposure during its use in laboratory or industrial settings. 2
Exposure Control and Protective Measures for Triisopropylsilyl Chloride
Due to its designation as a Toxic Inhalation Hazard, caution is required when working with Triisopropylsilyl chloride. This substance can release harmful gases when it comes into contact with water, underscoring the importance of adequate containment and ventilation. Exposure can lead to dermatotoxic effects, such as skin burns, as well as respiratory complications like toxic pneumonitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the lungs resulting from inhaling toxic vapors. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to implement appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves, eye protection, and respiratory protection, as well as to ensure that workspaces are well-ventilated and equipped for emergency response in the event of spills or accidents involving Triisopropylsilyl chloride. 2
References:
[1] CARTER C CUNNINGHAM. Organoselenium-Catalyzed Enantioselective Synthesis of 2-Oxazolidinones from Alkenes.[J]. Organic Letters, 2024. DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.4c02377.Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Triisopropylsilyl chloride manufacturers

US $0.00/kg2025-04-18
- CAS:
- 13154-24-0
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 96%
- Supply Ability:
- 20t

US $0.00/KG2025-04-15
- CAS:
- 13154-24-0
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 500000kg