Biological Activity
Potent anticancer agent th at induces cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase.
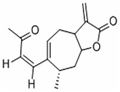
Xanthatin, a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from Xanthium plants (Asteraceae), is a potent anticancer agent th at induces cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase in hepatocellular carcinoma and colon cancer cells. Xanthatin induces apoptosis in numerous cancer cell lines including colon, breast, lung, cervix, and skin cancers, while apparently spearing human normal LO2 hepatocytes. It appears to activate endoplasmic reticulum stress through activation of the PERK/eIF-2α/ATF4 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Also, xanthatin exhibit potent phytotoxic activity, which suppressed root growth of receiver plants.
Purification Methods
Crystallise xanthatin from MeOH, aqueous MeOH, EtOH or aqueous EtOH. UV: 213 and 275nm (max 7300). The 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone has m 240o(dec) (twice recrystallised from CHCl3/MeOH). [Geissman et al. J Am Chem Soc 76 685 1954, Deuel & Geissman J Am Chem Soc 79 3778 1957, Beilstein 17 III/IV 6221, 17/1 V 305.]