What is Daucosterol?

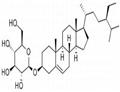
Daucosterol, alias: Citoside, β-Sitosterol β-D-glucoside, and the molecular formula is C35H6. The compound of the formula (description column) belongs to a carotene compound, which is present in mallow family plants, and figs and other plants also contain carotene [1]. Daucosterol exhibits anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory and acaricidal activities, also moderate antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus, and it has anti-cancer and apoptotic effects in human colon cancer cell line HCT-116.
Daucosterol can be used as an efficient and inexpensive neuroprotectants, to which the IGF1-like activity of daucosterol contributes and it could be potentially developed as a medicine for ischemic stroke treatment [2]. Moreover, daucosterol has neuroprotective activity, it has proliferation-enhancing activity of neural stem cells (NSCs), and it as an efficient and inexpensive growth factor alternative that could be potentially developed as a medicine for ischemic stroke treatment, can significantly reduce neuronal loss [3].
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are self-regenerating cells, but their regenerative capacity is limited. Researchers conducted to investigate the effect of daucosterol (a sterolin) on the promotion of NSC proliferation and determine the corresponding molecular mechanism. Results of cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay showed that daucosterol significantly increased the quantity of viable cells and the effectiveness of daucosterol was similar to that of basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF). Flow cytometry detection of CFSE-labeled (CFSE, carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester) NSCs showed that the Div Index (or the average number of cell divisions) and % Divided (or the percentage of cells that divided at least once) of the cells were increased, indicating that daucosterol increased the percentage of NSCs re-entering the cell cycle. In addition, the phosphorylation of AKT was increased, indicating that the proliferation-enhancing activity of daucosterol may be involved in the IGF1-AKT pathway. The study demonstrated that daucosterol works as an efficient and inexpensive growth factor alternative that could be used in clinical medicine and research applications [4].
Cancer is one of the most serious threats to human health, so more remarkable efforts are needed to develop optimal and side effect-reduced treatments for cancer. In the past decades, plants served as the major resources for finding potential anti-cancer agents/compounds due to their relatively low toxicity and preferable cost-effectiveness [5]. Daucosterol is not endogenously synthesized but can be obtained through diet. Emerging studies found that daucosterol exhibits anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating activities and promotes neural stem cell proliferation. However, the anti-cancer effect of daucosterol is not well known. M. Salimi et al. reported that daucosterol, as one of the constituents of chloroform extract of Juglans regia leaves, could inhibit MCF-7 cell proliferation in vitro. Chuanke Zhao and coworkers examined the anti-cancer effect of daucosterol in vitro and in vivo and explored its underlying mechanisms. To investigate the anti-cancer effect of daucosterol in vitro, Chuanke and team firstly examined the effect of daucosterol on the proliferation of MGC803, BGC823, AGS and MCF-7 cells with the MTT assay. Results showed that daucosterol inhibited the proliferation of all these cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner. Consistent with MTT assay results, daucosterol significantly inhibits colony formation in a dose-dependent manner. To confirm the results from in vitro assays and assess the in vivo effect of daucosterol, researchers conducted allograft assay with murine H22 hepatoma cells inoculated in ICR mice and found that 0.5 mg/kg daucosterol significantly inhibits the H22 tumor growth in vivo (scheme 1). Meanwhile, researchers did not observe the significant toxicity of daucosterol reflected by the loss of body weight at the both concentrations used. No lesions were found in the hearts, livers, kidneys, or lungs by macroscopic examination. All these results demonstrate the potential anti-cancer effect and low toxicity of daucosterol in vitro and in vivo.

Scheme 1 Daucosterol inhibits allograft tumor growth in vivo (shows the murine H22 hepatoma from the bearing mice (n = 9–10/group) of control, treatment with CTX and daucosterol (0.5 mg/kg and 2.5 mg/kg))
Reference
[1] Wu YunfengZhao Lei, Application of a carotene compound as an antiviral agent, CN103518752A.
[2] https://www.bocsci.com/eleutheroside-a-cas-474-58-8-item-464514.html
[3] http://www.chemfaces.com/natural/Daucosterol-CFN98713.html
[4] Li-hua Jiang, etc., Daucosterol promotes the proliferation of neural stem cells, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Volume 140, March 2014, Pages 90-99
[5] Chuanke Zhao, etc., Daucosterol inhibits cancer cell proliferation by inducing autophagy through reactive oxygen species-dependent manner, Life Sciences, Volume 137, 15 September 2015, Pages 37-43
[6] https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5742590
[7]http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.4674825.html?rid=7b6cb5f8-3902-4edc-887d-7920ca0071c7&page_num=0
You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from ELEUTHEROSIDE A manufacturers

US $1.00-22.00/KG2024-08-05
- CAS:
- 474-58-8
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 100000KG
US $0.00/mg2023-02-24
- CAS:
- 474-58-8
- Min. Order:
- 5mg
- Purity:
- ≥95%(HPLC)
- Supply Ability:
- 10 g



