The introduction of Ingenol mebutate
Introduction
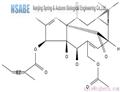
Ingenol mebutate (IM) is a hydrophobic ester of the diterpene ingenol derived from Euphorbia peplus, a typical Australian shrub (Euphorbiaceae). IM is licensed for the topical treatment of actinic keratosis, a common skin disease caused by persistent UV radiation exposure that can progress to squamous cell carcinoma if not treated. At high concentrations (200–300 M), IM produces fast induction of cell death in the treated region; at low doses (0.1 M), it starts an inflammatory response capable of removing leftover cells.

Biological activity
Ingenol mebutate has been evaluated for its antitumor activity in several cancer cell lines, including breast, colon, lung, and melanoma. This compound showed potent antiproliferative effects on different cell lines in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The mechanism of action of ingenol mebutate is partially related to the activation of PKC, which has a potent binding affinity. Vitro-low isozyme selectivity was verified with a Ki ranging from 0.105 to 0.376 nM.
Mechanism of action
The therapeutic effect of ingenol mebutate has been partially explained with a dual mechanism of action; it induces rapid (1–2 hours after application) cell death in transformed keratinocytes through disruption of the plasma membrane and subsequent mitochondrial swelling and, within days, stimulates a neutrophil-mediated form of antibody-dependent cytotoxicity that eliminates residual tumour cells.
Ingenol mebutate is an agonist of intracellular protein kinase C (PKC), which is involved in the signalling pathways of different physiologic functions, such as cell proliferation, differentiation and senescence, cell survival/death, invasion and angiogenesis. The activation of the pro-apoptotic intracellular PKC induces apoptosis of dysplastic keratinocytes, whereas keratinocytes with normal differentiation are resistant to the PKC-mediated pro-apoptotic effects. The activation of the PKC/MEK/ERK pathway also results in immunostimulatory effects with infiltration of neutrophils into the area of application and antibody production that stimulates cytotoxic T cells against dysplastic cells.
Clinic uses
In January 2012, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved ingenol mebutate gel for treating actinic keratoses on the face, scalp, trunk and extremities. Ingenol mebutate gel is available in concentrations of 0.015% and 0.05% and is manufactured by LEO Pharma with the trade name Picato®. Ingenol mebutate gel was registered as a prescription medicine by MedSafe in New Zealand in October 2013. The two or three-day course of ingenol mebutate gel compares favourably to several weeks or months needed for other topical therapies used for actinic keratoses, such as 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod cream. Treatment can be repeated at a later date if required.
References:
[1] MARIA ISABEL RAMOS SARAIVA . Ingenol mebutate in the treatment of actinic keratoses: clearance rate and adverse effects*[J]. Anais brasileiros de dermatologia, 2018, 93 4: 495-629. DOI:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20186982.[2] NEVENA SKROZA. Clinical utility of ingenol mebutate in the management of actinic keratosis: perspectives from clinical practice.[J]. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management, 2018, 14. DOI:10.2147/TCRM.S145779.
You may like
See also
Lastest Price from Ingenol mebutate manufacturers

US $10.00/KG2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 75567-37-2
- Min. Order:
- 100KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 100 mt
US $1500.00/g2022-07-06
- CAS:
- 75567-37-2
- Min. Order:
- 10mg
- Purity:
- 98.00%
- Supply Ability:
- 1000.00 kgs


