The Duality of Sanguinarine: Anticancer Potential, Carcinogenic Controversy and Clinical Outlook
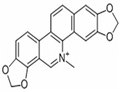
Sanguinarine is an alkaloid found in many medicinal plants. It has diverse biological activities, including modulation of nuclear factor-KB and of several enzymes. It is also known to induce apoptosis, perturb microtubules, and to have antimicrobial effects. This article reviews its cardiovascular properties, including hypotensive, antiplatelet, and positive inotropic effects. Its pharmacokinetics, and toxicology, including its carcinogenic potential, are also discussed. Further pharmacological and toxicological studies with sanguinarine are needed before its therapeutic use can be considered.
;
Bioactivity and mechanism of action of sanguinarine
Sanguinarine is a quaternary ammonium benzophenanthine alkaloid found in traditional herbs such as Chelidonium, Corydalis, Sanguinarum, and Borovula. It has been proven to possess broad-spectrum biological activities, such as antitumor, anti-inflammatory, antiosteoporosis, neuroprotective, and antipathogenic microorganism activities. In this paper, recent progress on the biological activity and mechanism of action of sanguinarine and its derivatives over the past ten years is reviewed. The results showed that the biological activities of hematarginine and its derivatives are related mainly to the JAK/STAT, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, NF-κB, TGF-β, MAPK and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. The limitations of using sanguinarine in clinical application are also discussed, and the research prospects of this subject are outlined. In general, sanguinarine, a natural medicine, has many pharmacological effects, but its toxicity and safety in clinical application still need to be further studied. This review provides useful information for the development of sanguinarine-based bioactive agents.[1]
Sanguinarine ;(SA) is an ;isoquinoline alkaloid ;extracted from poppy plants that contains benzene and ;phenanthrene. Its chemical name is 1,3-methyl ;benzodioxacyclopentene [5,6,-c]-1,3-dioxacyclopentene [4,5-i] phenylidonium ;. It was originally found in the rhizomes of ;Sanguinaria ;canadensis ;(Papaveraceae) by native Americans as a traditional medicine used to treat various disorders. n this paper, we summarize the results of previous studies on sanguinarine over the past ten years and show that sanguinarine has many ;pharmacological activities. In 2014, Cristina Kalogris et al. reported that ;sanguinarine ;reduced the viability of A17 (the IC50 ;value was 1.293 µM) and MDA-MB-231 (the IC50 ;value was 1.616 µM) by inhibiting the activation of STAT3. SA (0.5–2 µM) showed inhibition of ;telomerase ;activity and ;cell viability ;in HTC75 cancer cells (the IC50 ;value was 2.18 µM), resulting in cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase. Long-term treatment with sanguinarine chloride (SC) could cause telomere wear (the IC50 ;value was 1.21 µM) and cell ;growth retardation, increase the accumulation of senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal)-positive cells, upregulate the p16/p21/p53 pathway and induce telomere dysfunction-induced foci (TIFs). Fang-Jun Cao et al. published paper about the cytotoxicity and structure-activity relationship of the pseudocyanides sanguinarine and ;chelidonine. The results showed that the sanguinarine derivatives CNS (2) and CNC (3) had potential anti-NB4 activity (IC50 ;values were 0.53 µM and 1.85 µM, respectively) and anti-MKN-45 activity (IC50 ;values were 1.53 µM and 12.72 µM, respectively)
Sanguinarine: A Double-Edged Sword of Anticancer and Carcinogenesis
Sanguinarine, a kind of benzophenanthridine alkaloid, is a natural compound with potential development value for its anticancer activity. Hundreds of studies have been carried out in vivo or in vitro, trying to make it feasible for the anticancer clinic medication of sanguinarine. However, sanguinarine was branded as a toxicant or even a carcinogen according to some toxicological experiments and cancer investigations. Aiming at safety and effectiveness of sanguinarine, this article reviews the extant information on present studies of sanguinarine, and both anticancer carcinogenesis mechanism details are summarized. The future potential research directions of this valued compound are also discussed to provide reference for future drugs development.[2]
Our results indicated that sanguinarine exhibited anticancer effect through anti-proliferation, anti-invasion, anti-angiogenesis and apoptosis within cancer lesion. Also, many clinical investigations indicated that sanguinarine and its related products might be associated to pre-carcinoma within oral or skin potentially.;Sanguinarine is a natural compound with good development value for its potent anticancer activity; however, its carcinogenesis effect should also be taken seriously. Studies on structural modification and analogue design should be carried out to improve its safety and efficiency in the future.
Sanguinarine and Its Role in Chronic Diseases
The use of natural products derived from plants as medicines precedes even the recorded human history. In the past few years there were renewed interests in developing natural compounds and understanding their target specificity for drug development for many devastating human diseases. This has been possible due to remarkable advancements in the development of sensitive chemistry and biology tools. Sanguinarine is a benzophenanthridine alkaloid derived from rhizomes of the plant species Sanguinaria canadensis. The alkaloid can exist in the cationic iminium and neutral alkanolamine forms. Sanguinarine is an excellent DNA and RNA intercalator where only the iminium ion binds. Both forms of the alkaloid, however, shows binding to functional proteins like serum albumins, lysozyme and hemoglobin.[3]
The molecule is endowed with remarkable biological activities and large number of studies on its various activities has been published potentiating its development as a therapeutic agent particularly for chronic human diseases like cancer, asthma, etc. In this article, we review the properties of this natural alkaloid, and its diverse medicinal applications in relation to how it modulates cell death signaling pathways and induce apoptosis through different ways, its utility as a therapeutic agent for chronic diseases and its biological effects in animal and human models. These data may be useful to understand the therapeutic potential of this important and highly abundant alkaloid that may aid in the development of sanguinarine-based therapeutic agents with high efficacy and specificity.
Sanguinarine Suppresses Prostate Tumor Growth and Inhibits Survivin Expression
Sanguinarine, a benzophenanthridine alkaloid derived primarily from the bloodroot plant, was identified as a novel inhibitor of survivin that selectively kills prostate cancer cells over “normal” prostate epithelial cells. The authors found that sanguinarine inhibits survivin protein expression through protein degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Sanguinarine induces apoptosis and inhibits growth of human prostate cancer cells and ;in vivo ;tumor formation. Administration of sanguinarine, beginning 3 days after ectopic implantation of DU145 human prostate cancer cells, reduces both tumor weight and volume. In addition, sanguinarine sensitized paclitaxel-mediated growth inhibition and apoptosis, offering a potential therapeutic strategy for overcoming taxol resistance. These results suggest that sanguinarine may be developed as an agent either alone or in combination with taxol for treatment of prostate cancer overexpressing survivin.[4]
Sanguinarine was identified as a potential inhibitor of survivin that selectively kills prostate cancer cells over “normal” prostate epithelial cells. Sanguinarine, which is derived primarily from the bloodroot plant, induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor formation and growth of human prostate cancer cells. Administration of sanguinarine, beginning 3 days after ectopic implantation of DU145 human prostate cancer cells, delays tumor formation by 2 weeks and reduces both tumor weight and volume. In addition, sanguinarine inhibits survivin protein expression through protein degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. ;Because sanguinarine inhibits survivin expression, it is possible that sanguinarine could enhance paclitaxel anticancer activity by suppressing paclitaxel-induced survivin expression in prostate cancer. Our data support this hypothesis by showing that sanguinarine sensitizes paclitaxel-mediated growth inhibition and apoptosis. Although the efficacy of combination treatment was evaluated ;in vitro ;and needs further evaluation ;in vivo, the combination of sanguinarine and paclitaxel effectively induces cell death in DU145 cells, offering a potential therapeutic strategy for overcoming taxol resistance.
In conclusion, scientists have identified sanguinarine as a potential inhibitor of survivin and an anticancer agent for prostate cancer by a cell-based rapid screen of the Prestwick Chemical Library that consists of 1120 FDA-approved compounds. Sanguinarine exhibits anticancer efficacy both ;in vitro ;and ;in vivo ;and sensitizes prostate cancer cells to paclitaxel-mediated growth inhibition and apoptosis, offering a potential therapeutic strategy for overcoming taxol resistance.
References
[1]Huang, L.-J., Lan, J.-X., Wang, J.-H., Huang, H., Lu, K., Zhou, Z.-N., Xin, S.-Y., Zhang, Z.-Y., Wang, J.-Y., Dai, P., & Chen, X.-M., Hou, W. (2024). Bioactivity and mechanism of action of sanguinarine and its derivatives in the past 10 years. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 173, 116406.
[2]Lou G, Wang J, Hu J, Gan Q, Peng C, Xiong H, Huang Q. Sanguinarine: A Double-Edged Sword of Anticancer and Carcinogenesis and Its Future Application Prospect. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021 Oct 28;21(16):2100-2110.
[3]Basu P, Kumar GS. Sanguinarine and Its Role in Chronic Diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;928:155-172.
[4]Sun M, Lou W, Chun JY, Cho DS, Nadiminty N, Evans CP, Chen J, Yue J, Zhou Q, Gao AC. Sanguinarine suppresses prostate tumor growth and inhibits survivin expression. Genes Cancer. 2010 Mar;1(3):283-92.
You may like
Lastest Price from SANGUINARINE manufacturers

US $0.00/kg2024-04-12
- CAS:
- 2447-54-3
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 2000ton
US $0.00/mg2023-02-24
- CAS:
- 2447-54-3
- Min. Order:
- 20mg
- Purity:
- ≥98%(HPLC
- Supply Ability:
- 100 g


