The characteristic and application of maltodextrin
Introduction
Maltodextrin is a polysaccharide produced from starch by partial enzymatic hydrolysis of starch. Starch (amylum) is a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units linked by glycosidic bonds and is present in a large quantities in corn, potatoes, wheat etc Maltodextrin has a dextrose equivalence less than 20 which indicates that it has long carbohydrate chains along with 2-3% glucose and 5-7% maltose and is available in white hygroscopic spray-dried powder which is slightly sweet almost flavourless. It is soluble and readily dispersible in water and slightly soluble to almost insoluble in alcohol. The body digests Maltodextrin as a simple carbohydrate and thus can be easily converted to instant energy. Due to this quality it is used in sports drinks and quick energy satchels for endurance athletes. Use of Maltodextrin is also dependant on the grade that is the DE value for instance MD with low DE value are stickier and thus is used in gelatinous products like syrups and jams whereas high DE value MD freeze better and is used as a bulking agent in ice creams.
Maltodextrin like starch consists of a particular ratio of amylose and amylopectin, different ratios. Amylose is made up of α (1→4) bound glucose units whereas amylopectin has glucose units linked in a linear way with α (1→4) glyosidic bonds with α (1→6) bonds occurring every 24 to 30 glucose units
Brief overview of uses of Maltodextrin
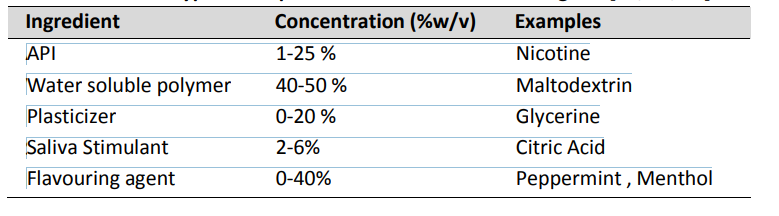
The main aim of novel drug delivery is to achieve targeted and controlled drug release. The encapsulation of drug in a vesicle sustains drug action at a sustained rate and maintains an effective drug concentration level at the same time reduces the number of undesirable effect[1]. Encapsulation of drug also enables to prolong the duration of drug release in systemic circulation and reduce toxicity by increasing the selectivity. One of the major advantages of vesicular drug delivery is the ability to deliver drug into the deeper layer of the skin in this way it bypasses hepatic first-pass effect and provides better compliance[1]. The vesicles passes through skin layer mainly because bilayer act on stratum corneum in the skin which is the rate limiting. Liposomes which are bilayered lipid vesicles constituting cholesterol and phospholipids have shown potential in overcoming the stratum corneum layer in the skin. But the major drawback associated with aqueous dispersions of liposomes is the tendency to aggregate or fuse and susceptibility to hydrolysis and oxidation. Table 1 shows some typical composition of a thin fast dissolving film [1].
Table 1 Typical composition of a thin fast dissolving film
Non-ionic surfactant based vesicles known as niosomes are viewed as an alternative potential drugs delivery system to conventional liposomes. Niosomes or nonionic surfactant vesicles are microscopic lamellar structure which can administer both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs[2, 3]. Proniosomes are dry, free flowing, water soluble carrier particles which are coated with surfactant and can from niosomal dispersion on subsequent hydration with hot water. This avoids the problems related to aqueous niosomal dispersion especially leaking, aggregation and fusion. Moreover proniosomes are stable during sterilization as well as storage .Thus distribution, ease of transfer and storage stability make proniosomes a promising novel delivery system[4].
Maltodextrin as encapsulating material Maltodextrin is considered as good coating material because it exhibits low viscosity at high solids contents and also shows good water solubility. In addition, it is known that polysaccharides having gelling properties and stabilizes emulsions towards flocculation as well as coalescence. Maltodextrin samples show the highest retention of flavour because they could be dispersed in water up to 35.5% of the solution without haze formation. Maltodextrin based micro particles containing up to 1% iodine were stable for periods up to 12 months under a temperature of 40 0 C. The use of a 10:1 Maltodextrin /Pectin weight ratio (11% w/v) led to encapsulate 3% w/v polyphenol-rich extracts and formed stable powders. This combination with pectin may be a useful replacement of the Maltodextrins-alone carrier. Even under harsh storage conditions, neither the bioactive polyphenols nor moisture content of the particles or the antioxidant activity appeared significantly modified. The maltodextrin/pectin matrix is able to mask the unpleasant smell of the extracts and the product is rapidly soluble in water. Maltodextrins were found to be effective in protecting the carotenoids of paprika oleoresin as well. Maltodextrins along with whey proteins were reported as effective wall materials for microencapsulation of ethyl caprylate. Moreover its combination with emulsifier Tween 80 encapsulated a higher amount of bixin than only maltodextrin[5-6] .
Renference
1 Kaur, R., et al., A REVIEW ON PRONIOSOME, A PROMISING CARRIER FOR DELIVERY OF DRUG ACROSS MEMBRANES. 2014.
2. Blazek-Welsh, A.I. and D.G. Rhodes, Maltodextrinbased proniosomes. Aaps Pharmsci, 2001. 3(1): 1-8.
3. Uchegbu, I.F. and S.P. Vyas, Non-ionic surfactant based vesicles (niosomes) in drug delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 1998. 172(1): 33-70.
4. Kakar, R., et al., Proniosomes: An emerging vesicular system in drug delivery and cosmetics. Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2010. 2(4): 227-239.
5. Sudhamani, T., et al., Formulation and evaluation of ibuprofen loaded maltodextrin based proniosome. International Journal of Biopharmaceutics, 2010. 1(2): 75-81.
6. Hu, C. and D.G. Rhodes, Proniosomes: a novel drug carrier preparation. International journal of pharmaceutics, 1999. 185(1): 23-35.
You may like
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Maltodextrin manufacturers

US $0.00-0.00/kg2025-06-05
- CAS:
- 9050-36-6
- Min. Order:
- 1000kg
- Purity:
- 99%min
- Supply Ability:
- 1000 tons

US $0.00/kg2025-04-25
- CAS:
- 9050-36-6
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- 1000kg




