Different synthetic routes to vortioxetine hydrobromide
Introduction
Vortioxetine hydrobromide is an atypical antidepressant made by Lundbeck and Takeda. It was approved by the United States Federal Drug Agency and the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) on September 30, 2013 and December 27, 2013 respectively, for the treatment of major depressive disorder in adults. Vortioxetine has also been investigated as a treatment for generalized anxiety disorder.
Two synthetic routes to vortioxetine hydrobromide
Two synthetic routes to vortioxetine hydrobromide (1) were developed on a gram scale. Bang-Andersen and coworkers used a polystyrene resin bound piperazine, a 1,2- dichlorobenzene–ferrocene complex, and 2,4-dimethylbenzenethiol (4) (picture 1, route 1) through nucleophilic substitution, photolysis, and resin dissociation to give 1 with a total yield of about 9%. Bang-Andersen and co-workers and Christensen reported improved routes to vortioxetine based on palladium catalyzed coupling as shown in Scheme 1 (routes 2 and 3). In route 2, 1-bromo-2-iodobenzene (5) and 1-Boc-piperazine 6 were coupled under tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium and BINAP catalysis to give 7 which was isolated by column chromatography; 7 was coupled with 2,4-dimethylbenzenethiol (4) under similar conditions to obtain 8. Vortioxetine hydrochloride (9) was obtained by treating 8 with hydrochloric acid in moderate yield. A ‘one-pot’ method was used in route 3; 2-bromobenzenethiol (10), piperazine (3), and 1-iodo-2,4-dimethylbenzene (11) were treated with tris(dibenzylideneacetone)di[1]palladium or palladium(II) acetate and BINAP to give vortioxetine, which was treated with hydrobromic acid to give 1 in good yield over two steps. An expensive palladium catalyst and phosphine ligand are used in these synthetic routes, this increases the overall cost and column chromatography is necessary to remove heavy metal residues, hence a practical synthetic process for 1 is needed.
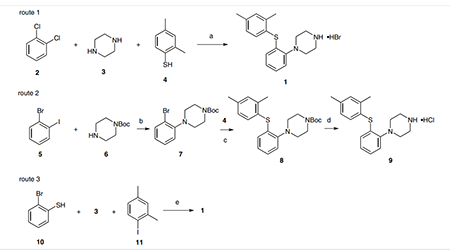
pic. 1 Reagents and conditions: (a) 1. ferrocene, AlCl3, 110 °C, 6 h; 2. K2CO3, THF, r.t., 3 h; 3. HCl, H2O, r.t.; 4. HBr, H2O, toluene, 35 °C, total yield 9%; (b) t-BuONa, Pd2dba3 (2.5 mol%), BINAP (7.5 mol%); (c) t-BuOK, Pd2dba3 (2.5 mol%), DPEphos (10 mol%), 79%; (d) HCl, 78%; (e) 1. t-BuONa, Pd2dba3 (1– 2 mol%) or Pd(OAc)2 (1.5 mol%), BINAP (2–4 mol%); 2. HBr, 77–84% [4]
A practical and commercial process for the preparation of vortioxetine hydrobromide
A practical and commercial process for the preparation of vortioxetine hydrobromide was developed by a new and practical synthetic route that afforded the piperazine ring of 1 by reacting the aniline 14 with bis(2-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride (15) (picture 2). Commercially available 1- chloro-2-nitrobenzene (12) and 2,4-dimethylbenzenethiol (4) were used as the starting materials and reacted with potassium carbonate in acetonitrile to give crude 13 which was purified by recrystallization in acetonitrile giving pure product in 89% overall yield. Catalytic hydrogenation of 13 with hydrogen, Raney nickel catalyst, and methanol as the solvent at room temperature gave aniline 14. The final cyclization of 14 with 15 was carried out in 1,2-dichlorobenzene at 160–170 °C for three to four hours. After cooling to room temperature, 40% hydrobromic acid was added to the reaction solution to give the final product 1 in 71% overall yield and with 99.3% purity (HPLC). With regard to the preparation of the piperazine ring, although there are many reported methods all of these failed for the synthesis of 1 except the 1,2-dichlorobenzene conditions established in this paper [2-3]. Unsuccessful methods utilized include: aniline and bis(2-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride in 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethanol (150–190 °C, 3–4 h), this gave a dark reactant and the TLC yield was <30% ); aniline and bis(2-chlorethyl)amine hydrochloride(220-240°C, 6–8 h ), this gave a dark reactant and no product; aniline, bis(2-chlorethyl)amine hydrochloride, and potassium carbonate in butanol (reflux 14 h), this gave a dark reactant and no product;10 and ani[1]line and bis(2-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride in chlorobenzene (130–150 °C, 8–12 h), this gave no product.11 The possible reasons include the reaction temperature, solubility, solvent polarity, and other factors that we have not studied.
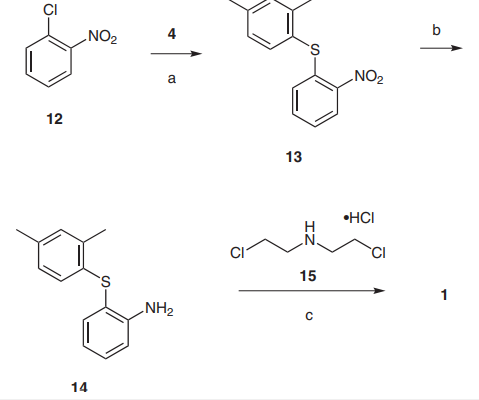
Pic. 2 Reagents and conditions: (a) K2CO3, MeCN, reflux, 10 h, 89%; (b) H2, Raney Ni, MeOH, r.t., 6 h; (c) 1. 1,2-dichlorobenzene, 160– 170 °C, 4 h; 2. 40% HBr, r.t., 71% [4]
A new and practical synthetic route to vortioxetine hydrobromide
As the picture 2 showed, we have developed a new and practical synthetic route to vortioxetine hydrobromide on a hectogram scale [4]. Adopting commercially available materials, through simple and traditional steps, including nucleophilic substitution, catalytic hydrogenation, and cyclization of the piperazine ring, gave the final product in 63.2% yield over three steps and with 99.3% purity (HPLC). Purification methods for the intermediates involved in the route are also given.
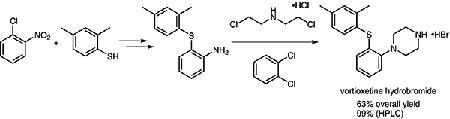
Pic.3 A new synthetic route to vortioxetine hydrobromide [4]
Reference
1 Gibb, A.; Deeks, E. D. Drugs 2014, 74, 135.
2 du Jardin, K. G.; Jensen, J. B.; Sanchez, C.; Pehrson, A. L. Eur. Neu[1]ropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 160.
3 Mahableshwarkar, A. R.; Jacobsen, P. L.; Chen, Y. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2013, 29, 217.
4 Mao, Yongjun; Jiang, Luobin; Chen, Tianyun; He, Haijun; Liu, Gang; Wang, Han (2015). A New and Practical Synthesis of Vortioxetine Hydrobromide. Synthesis, 47(10), 1387–1389.
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Vortioxetine hydrobromide manufacturers

US $0.00-0.00/KG2025-07-09
- CAS:
- 960203-27-4
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99% up , S.impurity≤0.05%
- Supply Ability:
- 20TONS

US $0.00/kg2025-05-09
- CAS:
- 960203-27-4
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- 1000kg



