N-Bromosuccinimide:Chemical synthesis,Reactions
N-Bromosuccinimide or NBS is a chemical reagent used in radical substitution, electrophilic addition, and electrophilic substitution reactions in organic chemistry. NBS can be a convenient source of Br•, the bromine radical. NBS gives bromination of donor-acceptor cyclopropanes by an electron-transfer (ET) mechanism. Its appearance is as follows:

Figure 1 Appearance of
N-Bromosuccinimide can be synthesize by single step according to the previous work [2]. Pb(OAc)4 (2.0 or 4.0 mmol) was dissolved in MeCN (20 mL). ZnBr2 (2.0 or 4.0 mmol) was added to the MeCN solution, and the mixture was stirred for 5 min at r.t. The nitrogen heterocycle (2 mmol) or carbonyl compound (2 mmol) was added to the resulting solution. The resulting mixture was stirred at r.t. until nitrogen heterocycle or carbonyl compound disappeared. After evaporating the solvent under reduced pressure, the resulting residue was applied to the top of an open-bed silica gel column (3.0 × 7 cm). The column was eluted with CH2Cl2 or CH2Cl2-n-hexane (1:1). Fractions containing the product were combined and evaporated under reduced pressure to give monobromides or dibromides. Yield 93%. The crude NBS (200 g) is dissolved as quickly as possible in 2.5 L of preheated water at 90–95 ◦C. As filtration is usually unnecessary, the solution is then chilled well in an ice bath to effect crystallization. After most of the aqueous portion has been decanted, the white crystals are collected by filtration through a bed of ice and washed well with water. The crystals are dried on the filter and then in vacuo. The purity of NBS may be determined by the standard iodide–thiosulfate titration method. 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ (ppm): 6.95 (g, broad, 0.850H), 2.76 (f1, broad, 1.556H), 2.58 (f2, broad, 0.421H), 1.66 (e, broad, 1.962H), 1.30 (b, c, d, broad, 5.971H), 0.87 (a, broad, 3.000H).
Reactions
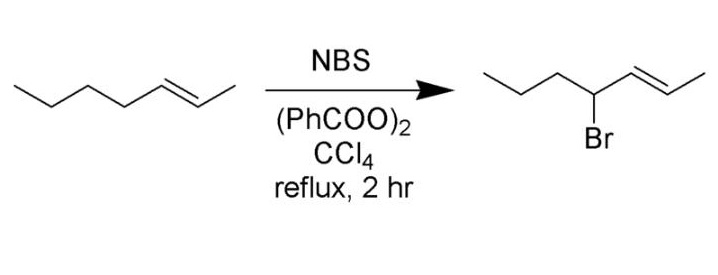
NBS can be used in many organic reactions. For example, allylic bromination of alkenes can be used with the NBS.
Handling and storage
One of the advantages of using NBS is that it is easier and safer to handle than bromine; however, the solid is an irritant and bromine may be released during some operations. Therefore, precautions should be taken to avoid inhalation of the powder and contact with skin. All operations with this reagent are best conducted in an efficient fume hood. In addition, since reactions involving NBS are generally quite exothermic, large-scale operations (> 0.1 mol) should be approached with particular caution [1]. In general, reactions involving NBS are exothermic. Therefore, extra precautions should be taken when used on a large scale.
References
[2]Kim et al. Conversion of nucleophilic halides to electrophilic halides: efficient and selective halogenation of azinones, amides, and carbonyl compounds using metal halide/lead tetraacetate. Synlett, 2006, (2): 194-200
[3]Zong et al. UV irradiation through Pyrex (λ > 313 nm) can lead to Cl- and Cl3C- substituted products from the solvent CCl4. Futamura. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 65, 345.
[4]Gribble et al. NBS in anhydrous DMSO converts dihydropyrans to α-bromolactones. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 5878.
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from N-Bromosuccinimide manufacturers

US $0.00-0.00/KG2025-12-01
- CAS:
- 128-08-5
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 98
- Supply Ability:
- 10000KGS

US $1.00-0.10/kg2025-10-31
- CAS:
- 128-08-5
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 300tons