Methyl benzenesulfonate: Complexes Synthesis and its Applications in Ethylene Polymerization
Description
Methyl benzenesulfonate is the effective methylating reagent of synthetic multiple organic intermediate.

Complexes Synthesis
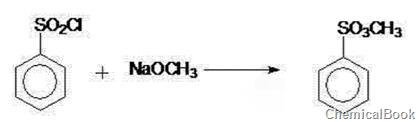
The invention discloses a method for preparing methyl benzenesulfonate, which comprises the following steps: adding benzene sulfonyl chloride into a reaction kettle, dropwisely adding a sodium methoxide methanol solution, keeping the temperature of 25-35 DEG C for 30 minutes, neutralizing to the pH value of 7-7.2, filtering, heating the filtrate to remove methanol, cooling to room temperature, and carrying out decolorization filtration to obtain a colorless transparent liquid methyl benzenesulfonatesulfonate, wherein the mol ratio of benzene sulfonyl chloride to sodium methoxide is 1:(1.2-1.4). The white crystal product can be prepared by changing the synthesis conditions; and thus, the invention is simple to operate, has the advantages of fewer steps, high yield and high practicality, can easily implement industrial production, and can generate high economic benefit and social benefit.
Applications in Ethylene Polymerization
A reaction between sodium 2-formylbenzenesulfonate and aniline revealed the near-quantitative (91%) formation of sodium-2-((phenylimino)methyl)benzenesulfonate L1. The identity of L1 was unambiguously ascertained using spectroscopic and analytical methods. The scope of this methodology was widened and various electron-donating amines were treated with sodium 2-formylbenzenesulfonate, and a small library of 6 imine ligands L2–L6 was generated. When L2 was treated with [(COD)PdMeCl], instead of the anticipated [L2PdMe(DMSO)] complex, the formation of [(DMSO)2Pd2Cl2Me2] Pd-Dim was observed. Nevertheless, the desired imino-methyl benzenesulfonate-ligated palladium complex [L2PdMe(Lu)] C1 was obtained by in situ abstraction of chloride and addition of bulky 2,6-lutidine as the donor group. The observation of characteristic Pd–Me protons at 0.06 ppm and the corresponding carbon at −8.1 ppm indicated the formation of C1. These 1D NMR observations were corroborated by 2D C–H correlation spectra and mass analysis, and the existence of C1 was unambiguously ascertained. Along the same lines, L4 and L5 were treated with a palladium precursor to produce [L4/5PdMe(Lu)]-type complexes C2–C3 in 55–84% yield, and their identity was established by using a combination of spectroscopic tools, analytical methods, and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. The synthetic utility of C1–C3 has been demonstrated by utilizing these complexes in the insertion polymerization of ethylene to polyethylene.1
Hazard
Thermal decomposition can lead to release of irritating gases and vapors. Methyl benzenesulfonate causes burns of eyes, skin and mucous membranes.
Reference
1. Deshmukh SS, Gaikwad SR, Mote NR, M M, Gonnade RG, Chikkali SH. Neutral Imino-Methyl Benzenesulfonate-Ligated Pd(II) Complexes and Implications in Ethylene Polymerization. ACS Omega. 2019; 4(5): 9502-9511.
You may like
Related articles And Qustion
Lastest Price from Methyl benzenesulfonate manufacturers

US $10.00/KG2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 80-18-2
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 10 mt

US $10.00/kg2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 80-18-2
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 20 ton