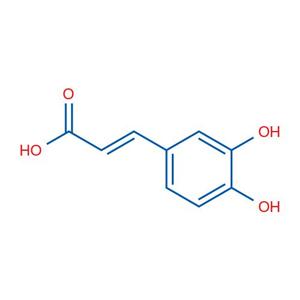
331-39-5Caffeic acid
Caffeic acid
331-39-5
331-39-5
询价
1盒
起订
上海 更新日期:2025-11-06
产品详情:
- 中文名称:
- Caffeic acid
- 英文名称:
- Caffeic acid
- CAS号:
- 331-39-5
- 品牌:
- 一研
- 保存条件:
- Store at -20°C
- 产品类别:
- 抑制剂
- Cas:
- 331-39-5
公司简介
上海一研生物科技有限公司Shanghai yiyan bio-technology Co. Ltd.主要从事免疫学、分子生物学和常规生化试剂等为一体的科研产品销售企业,公司自成立以来,秉承""全心全意服务于科研工作者""的企业理念,立足生物科技领域,运用生物技术和科研试剂,发展现代生物科技,为各类大中小医院及其它医疗机构、高等院校、科研院所、企事业单位提供优质的产品,服务生物科技领域的科学研究人员。
公司具有对普通货物、冷藏及冷冻仓库的存储、包装及运输能力。
公司将始终坚持信誉立业、以人为本、质量保证、诚信服务的宗旨,不断拼搏,开拓进取,与各界朋友携手共创美好未来。
| 成立日期 | (12年) |
| 注册资本 | 100 |
| 员工人数 | 50-100人 |
| 年营业额 | ¥ 100万以内 |
| 经营模式 | 工厂,试剂 |
| 主营行业 | 生化试剂,抗体,细胞培养,分子生物学,免疫安全 |
Caffeic acid相关厂家报价 更多
-

- 咖啡酸;331-39-5;含量98%
- 武汉普世达生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-17
- ¥620
-

- 咖啡酸 331-39-5 含 量HPCL≥99.0% 用于医药中间体
- 武汉麟盛科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-16
- 询价
-

- 3,4-二羟基肉桂酸
- 河南沃咖斯生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-16
- 询价
-
- 咖啡酸
- 中国食品药品检定研究院
- 2026-02-15
- 询价
-

- 咖啡酸 331-39-5
- 西安拉维亚生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-14
- ¥950
-

- 咖啡酸 二羟基肉桂酸
- 山东爱采生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-14
- ¥990
-

- 咖啡酸 ;3,4-二羟基肉桂酸
- 武汉海山科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-13
- 询价
-

- 咖啡酸
- 南通添香生物工程有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-13
- ¥1200
-

- 咖啡酸
- 山东丰泰生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-13
- ¥1200
-

- 咖啡酸
- 武汉逸翮科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-12
- 询价



