| Fluorescent exploration agent of fluorescent probe technique |
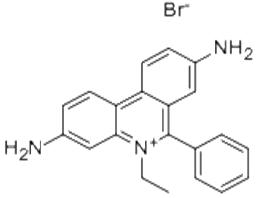
Ethidium bromide (abbreviated EB) is common fluorescent dyes of observing DNA under ultraviolet ray, it belongs intercalating dye because of its polycyclic structure, which enables it to be inserted between nucleotide bases. Since the fluorescence quantum yield of nucleic acids and bases is very low, so that the use of natural fluorescence detection of nucleic acids is more difficult than protein, the fluorescent probe technique in nucleic acid research is particularly important. Ethidium bromide (et-hidium bromide or called ethidium bromide) is used commonly, which has the specifical ability of bond with nucleic acid (DNA, RNA, double-stranded polynucleotide). The minimum detectable amount of desoxyribonucleic acid up to 10ng/ml, and the combination with double-stranded region of the nucleic acid is single-minded, it can distinguish between various configurations nucleic acid by the change of fluorescence intensity which producted by different proportions of the various conformation of nucleic acids. For example, it can discriminate natural nucleic acids and denatured nucleic acid, the distinction between linear DNA, circular DNA and and other super coil DNA. In addition, various acridines, including acridine orange, acridine yellow and former flavin, etc. are commonly used probe agent of nucleic acid.
Fluorescence analysis method can be divided into two kinds which includes direct and indirect determination method. Direct determination method makes use of fluorescence emission of its own, so use "autofluorescence" or "endogenous fluorescence 'to determine. But in nature, only a small portion of the material can emit fluorescence after light excitation, and a considerable part of the material fluoresces weakly or not fluoresce, such as proteins and nucleic acids is the substance which fluoresces weakly. It should be converted into fluorescent material to measure, which in order to take full advantage this feature of the high sensitivity of fluorescence analysis. It can be measured after forming the fluorescent conjugate which generated by covalently or non-covalently bound of some reagent (such as fluorescent dye) with no significant fluorescence and fluorescent substance, it is the so-called "fluorescent probe technology" or" fluorescent label technology". Agents (fluorescent agent) can adsorb on or covalently bound to the macromolecular. Ethyl bromide pyridine dyes of used is called "fluorescent probe." The difference of fluorescence characteristics is due to the exploration agents environmental change signal which caused by the change of macromolecule conformation, so the use of such signal can also get change information of the macromolecule conformation.
The above information is edited by the chemicalbook of Wang Xiaodong.(2016-12-04) |
| Uses |
1. EB can not go through the live cell membrane, but it can dye DNA which goes through the dead cells damaged membrane, it contains a planar perssad which is embeddable stacking basic group, the group fixs position and in close proximity with the basic group, which causing dye bind with DNA and generates fluorescence, because the yield of EB-DNA complexes fluorescence is much greater than the unbound fluorescent dyes, when electrophoresis gel containing free EB, a small amount of DNA can be measured, it is also highly sensitive fluorescent reagent and important fluorescent dye, it is often used to measure DNARNA. When combines with DNA, the replication transcription of DNA can be inhibited.
2. Ethidium bromide is a highly sensitive fluorescent dye for observing DNA of agarose and polyacrylamide gel. Ethidium bromide can emit orange-red signal when it is motivated by standard 302nm ultraviolet light transmittance instrument, Polaroid film or gel image processing system with CCD imaging can be used to shoot. For gel dyes after electrophoresis, storage fluid sample should be diluted to 0.5μg/ml with water, and then gel is incubated for 15-30 minutes. It is usually dispense with bleaching, but if reduces the background color, it can be decolorized in water for 15 minutes. It can then detect DNA bands in UV light box (254nm wavelength).
3. Ethidium bromide (EtBr) is the most commonly used nucleic acid stain for PAGE or agarose gel electrophoresis. The fluorescence of EtBr increases 21-fold upon binding to double-stranded RNA and 25-fold on binding double-stranded DNA so that destaining the background is not necessary with a low stain concentration (10mg/ml). Ethidium bromide has been used in a number of fluorimetric assays for nuc leic acids. It has been shown to bind to single-stranded DNA (although not as strongly) and triple-stranded DNA. Because of its ability to bind to DNA, EtBr is an inhibitor of DNA polymerase. Antiprot ozoal (Trypanosoma). |
| Chemical Properties |
Purple/maroon crystalline powder |
| Uses |
Ethidium bromide (EtBr) is the most commonly used nucleic acid stain for PAGE or agarose gel electrophoresis. The fluorescence of EtBr increases 21-fold upon binding to double-stranded RNA and 25-fold on binding double-stranded DNA so that destaining the background is not necessary with a low stain concentration (10 μg/ml). Ethidium bromide has been used in a number of fluorimetric assays for nucleic acids. It has been shown to bind to single-stranded DNA (although not as strongly) and triple-stranded DNA. Because of its ability to bind to DNA, EtBr is an inhibitor of DNA polymerase. Antiprotozoal (Trypanosoma). |
| Uses |
Intercalating agent and fluorescent label for DNA. |
| Uses |
antiprotozoal, intercalcates with DNA |

 China
China