| Description |
Empagliflozin(trade name Jardiance) is an inhibitor of the sodium glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2), and causes sugar in the blood to be excreted by the kidneys and eliminated in urine. On August 1, 2014, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) officially approved the drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, to improve and control blood glucose of adults. Empagliflozin is the third SGLT-2 inhibiting drugs approved by FDA. Another two SGLT-2 inhibitor drugs, canagliflozin and dapagliflozin, belonging to Johnson Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca and Bristol-Myers Squibb respectively, are approved by FDA in November 2013 and January 2014 respectively. The new drug Empagliflozin’s application to FDA can be described as twists and turns. In March 2014, due to a large particle contamination incident at the empagliflozin production plant in Boehringer, the application of new drug submitted by the Boehringer-Eli Lilly Alliance was rejected by FDA. In June 2014, after reviewing the summary and material submitted by Boehring in March, confirming that the quality management and compliance system of the Boehring drug production facility was acceptable, FDA withdrew the previously issued warning letter. The Boehringer-Eli Lilly Alliance also filed an application with the FDA on June 17th. |
| Clinical research |
FDA approval of empagliflozin(Jardiance) was based on the results of seven clinical trials conducted in nearly 4,500 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Compared to the placebo group, all patients taking empagliflozin(Jardiance) had a significantly lower HbA1c level. The most common adverse reactions are urinary tract infections and female reproductive system infections.
On March 21, 2014, European Medicines Agency (EMA) Commission on Human Medicines recommended the approval of the sodium glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor (empagliflozin) for the treatment of adult type 2 diabetes mellitus.
On May 23, 2014, European Medicines Agency (EMA) approved for empagliflozin’s listing in Europe.
On June 16, 2014, the Boehringer-Erya Diabetes Federation released the latest data of empagliflozin Phase II clinical trials at the 74th American Diabetes Association Science Conference (ADA2014). In a two-year study, empagliflozin or glimepiride was used in the treatment of adult patients with type 2 diabetes based on metformin. The results showed that empagliflozin(Jardiance) reduced HbA1c more significantly compared with glimepiride, while the effect of weight and blood pressure treatment are equivalent with glimepiride. Another 52-week study was conducted in patients with type 2 diabetes who were still unable to adequately control blood glucose levels with high doses of insulin (with or without metformin). The results showed that compared with placebo, Jardiance significantly reduced blood glucose levels and weight, and reduced the dose of insulin, with Jardiance or placebo on a daily basis with multiple injections of insulin. In both studies, the safety of empagliflozin was consistent with previous studies.
FDA-related reports write that the drug should not be used in the following types of patients: type 1 diabetes, elevated blood or urine ketones (diabetic ketoacidosis), severe kidney damage, end-stage renal disease or dialysis patients. The most common side effects are urinary tract infections and female genital infections.
Empagliflozin can cause dehydration and lead to decreased blood pressure, resulting in patients with dizziness or fainting and decreased renal function. The risk of older patients, especially those with impaired renal function and diuretics, appears to be greater.
FDA requires Boehring and Eli Lilly to conduct four post-marketing studies: complete ongoing cardiovascular outcome trials, pediatric pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics trials, pediatric safety and efficacy trials, toxicity test for the drug (especially effect for renal function, bone and growth and development) |
| Precautions |
Do NOT use empagliflozin if:
- you are allergic to any ingredient in empagliflozin
- you have type 1 diabetes
- you have high blood or urine ketone levels (diabetic ketoacidosis)
- you have severe kidney problems or are on dialysis
|
| References |
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Empagliflozin
https://www.drugs.com/cdi/empagliflozin.html |
| Uses |
Empagliflozin is a novel, potent and selective SGLT-2 inhibitor, improves glycaemic control and features of metabolic syndrome in diabetic rats. |
| Definition |
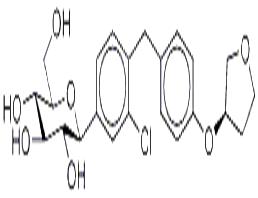
ChEBI: A C-glycosyl compound consisting of a beta-glucosyl residue having a (4-chloro-3-{4-[(3S)-tetrahydrofuran-3-yloxy]benzyl}phenyl group at the anomeric centre. A sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor u ed as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. |

 China
China