| Description |
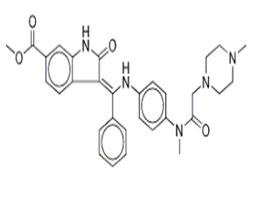
Nintedanib is an oral administrated triple tyrosine kinase inhibitors developed by Boehringer Ingelheim, Germany. Its targets include platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and basic fiber (BFGF), being able to also inhibit the activation of MAPK and Akt. At present, it is mainly used for cancer treatment, such as colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer and multiple myeloma. The study regarding to the respiratory diseases mainly focuses on the clinical treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). In June 2014, Boehringer Ingelheim has announced that the marketing authorization application of Nintedanib for the treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) had been confirmed by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and been included in the accelerated approval list by the EMA. |
| Mechanism of action |
Nintedanib is a small molecule that targets multiple receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and non-receptor tyrosine kinases (nRTKs). Nintedanib inhibits the following RTKs: platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) α and β, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 1-3, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) 1-3, and Fms-like tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3). Among them, FGFR, PDGFR, and VEGFR have been implicated in IPF pathogenesis. Nintedanib binds competitively to the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding pocket of these receptors and blocks the intracellular signaling which is crucial for the proliferation, migration, and transformation of fibroblasts representing essential mechanisms of the IPF pathology. In addition, nintedanib inhibits the following nRTKs: Lck, Lyn and Src kinases. The contribution of FLT3 and nRTK inhibition to IPF efficacy is unknown. |
| indications |
Nintedanib ( Vargatef ) is an oral triple angiokinase inhibitor which simultaneously inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR), platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFR) and fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFR) signalling pathways. Growing scientific evidence shows that these three different angiokinase receptors play an important role not only in angiogenesis but also in tumour growth and metastasis.
Nintedanib is currently being investigated in patients with various solid tumours including Phase III studies in advanced NSCLC, colorectal cancer (refractory to standard treatment) and ovarian cancer, and also in Phase II studies in mesothelioma, kidney cancer (renal cell carcinoma) and liver cancer (hepatic cell carcinoma).
In the EU, nintedanib in the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) has recently received a positive CHMP opinion. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved nintedanib capsules under the brand name OFEV for oral use for the treatment of IPF. |
| Drugbank Description |
Nintedanib is a drug indicated for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) that targets multiple receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and non-receptor tyrosine kinases (nRTKs). Nintedanib inhibits the following RTKs: platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) α and β, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 1-3, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) 1-3, and Fms-like tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3). Among them, FGFR, PDGFR, and VEGFR have been implicated in IPF pathogenesis. Nintedanib binds competitively to the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding pocket of these receptors and blocks the intracellular signaling which is crucial for the proliferation, migration, and transformation of fibroblasts representing essential mechanisms of the IPF pathology. In addition, nintedanib inhibits the following nRTKs: Lck, Lyn and Src kinases. The contribution of FLT3 and nRTK inhibition to IPF efficacy is unknown. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive and ultimately fatal lung disease characterized by a progressive loss of lung function with worsening dyspnoea and cough. Development is thought to be instigated by repetitive lung injury (such as by cigarette smoke, industrial dusts, gastrooesophageal reflux and viral infection) leading to destruction of epithelial alveolar cells. Subsequent dysregulation of the repair process results in the proliferation/migration of fibroblasts and their differentiation into myofibroblasts, abnormal extracellular matrix deposition and excessive collagen accumulation in the lung interstitium and alveolar space, leading to progressive fibrosis and stiffening of the lungs. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) mediate various processes, including fibrogenesis and angiogenesis, and are implicated in the pathogenesis of IPF. By blocking substrate binding and downstream signalling cascades, nintedanib interferes with processes active in fibrosis such as fibroblast proliferation, migration and differentiation, and the secretion of extracellular matrix.
References
https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09079 |
| Uses |
It is an indolinone derivative potently blocking VEGF-, PDGF-, and FGF-receptor kinases; an indolinone as triple angiokinase inhibitors. |
| Uses |
BIBF1120 (Vargatef) is a potent inhibitor of VEGFR1/2/3, FGFR1/2/3 and PDGFRα/β with IC50 of 34 nM/13 nM/13 nM, 69 nM/37 nM/108 nM and 59 nM/65 nM, respectively. |
| Definition |
ChEBI: A member of the class of oxindoles that is a kinase inhibitor used (in the form of its ethylsulfonate salt) for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and cancer. |

 China
China