1/2
4-Phenylbutyric acid NEW
- Min. Order1KG
- Purity99%
- Cas No1821-12-1
- Supply Abilityg-kg-tons, free sample is available
- Update time2024-04-16
| Product Name | 4-Phenylbutyric acid |
| CAS No | 1821-12-1 |
| EC-No | |
| Min. Order | 1KG |
| Purity | 99% |
| Supply Ability | g-kg-tons, free sample is available |
| Release date | 2024/04/16 |
1. Materials information
Names
| Name | 4-phenylbutyric acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
4-Phenylbutyric acid Biological Activity
| Description | Benzenebutyric acid is an inhibitor of HDAC and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, used in cancer and infection research. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | Signaling Pathways >> Cell Cycle/DNA Damage >> HDAC Signaling Pathways >> Epigenetics >> HDAC Research Areas >> Cancer Research Areas >> Infection |
| Target | HDAC |
| In Vitro | Benzenebutyric acid is an inhibitor of HDAC, inhibits the growth of NSCLC Cell Lines at 2 mM. Benzenebutyric acid in combination with ciglitizone results in enhanced growth arrest of cancer cells[1]. Benzenebutyric acid (0-5 mM) inhibits ASFV infection in a dose-dependent manner. Benzenebutyric acid also inhibits the ASFV late protein synthesis and disrupts the virus-induced H3K9/K14 hypoacetylation status. Benzenebutyric acid and enrofloxacin act synergistically to abolish ASFV replication[2]. Addition of bafilomycin A1 results in accumulation of LC3II, whereas Benzenebutyric acid (4-PBA) substantially reduces this accumulation. LPS decreases the level of p62, whereas Benzenebutyric acid reverses this decrease upon LPS stimulation for 48 h. The percentage of cells with LPS-induced AVOs is increased at 48 h, whereas Benzenebutyric acid significantly reduces this percentage. Specifically, the percentage of cells with AVOs decreases from 61.6% to 53.1% upon Benzenebutyric acid treatment, supporting that Benzenebutyric acid inhibits LPS-induced autophagy. As a positive control for autophagy inhibition, bafilomycin A1 is used. The percentage of cells with LPS-induced AVOs is reduced by bafilomycin A1 treatment. The decreased OC area and fusion index observed after Benzenebutyric acid treatment are not observed with knockdown of ATG7. Inhibition of NF-κB using BAY 11-7082 and JSH23 reduce the LC3 II level upon LPS stimulation and completely abolish the inhibitory effect of Benzenebutyric acid on LPS-induced effects[3]. |
| In Vivo | LPS induces significant bone loss and decreases bone mineral density (BMD), bone volume (BV/TV), and trabecular thickness (Tb. Th) compared with PBS alone, whereas trabecular space (Tb. Sp.) is increased. Benzenebutyric acid attenuates LPS-induced bone loss. Treatment with Benzenebutyric acid increases BMD, BV/TV, and Tb. Th. compared with LPS alone, in addition to decreasing the enlargement of Tb. Sp., but no change is observed when mice are treated with Benzenebutyric acid alone. OC.S/BS as assessed by TRAP staining is also significantly reduced when Benzenebutyric acid is administered to LPS-treated mice. However, OC.N/BS tends to decrease, although not with statistical significance, when mice are treated with Benzenebutyric acid and LPS. These results indicate that the effect of Benzenebutyric acid on OC from LPS-treated mice is to reduce its size rather than number. Consistent with these findings, a marker of bone resorption in vivo, serum CTX-1 which is elevated by LPS treatment is decreased when Benzenebutyric acid administered to LPS-injected mice. However, co-treatment with Benzenebutyric acid do not significantly affect the levels of serum ALP and osteocalcin, 2 markers of bone formation in vivo, compared with LPS alone. Benzenebutyric acid also reduces the LPS-induced rise in serum MCP-1, indicating that Benzenebutyric acid decreases systemic inflammation induced by LPS[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Briefly, viable cells, as judged by trypan blue dye exclusion, are seeded at a density of 4×104 cells/mL in 60-mm dishes in RPMI 1640 with 10% fetal bovine serum and 0.35% agarose on a base layer of 0.7% agarose. DMSO, TSA, or PB is added to both bottom and top agarose layers. Assays are performed in triplicate on at least three separate occasions, and colonies are counted at 10-14 days[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Female 10-week-old C57BL/6J mice are housed in the pathogen-free animal facility of IRC. Animals are randomized into the following 4 groups: vehicle control (n=5), vehicle+Benzenebutyric acid (n=6), LPS (n=6), and LPS+Benzenebutyric acid (n=6). Mice are treated with LPS in 200 μL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) once a week (5 mg/kg, i.p.) for 3 weeks. Benzenebutyric acid solution is prepared by titrating equimolecular amounts of Benzenebutyric acid and sodium hydroxide to reach pH 7.4; mice are injected daily intraperitoneally in 200 μL PBS (or with PBS as a vehicle) at a dose of 240 mg/kg for 3 weeks. Mice are sacrificed by CO2 asphyxiation. To determine the bone mineral density (BMD) and microarchitecture of the long bone, the right femur is scanned. Scans are performed with an effective detector pixel size of 6.9 μm and a threshold of 77-255 mg/cc. Trabecular bone is analyzed in a region 1.6 mm in length and located 0.1 mm below the distal femur growth plate[3]. |
| References | [1]. Chang TH, et al. Enhanced growth inhibition by combination differentiation therapy with ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and inhibitors of histone deacetylase in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Clin Cancer Res. 2002 Apr;8(4):1206-12. [2]. Frouco G, et, al. Sodium phenylbutyrate abrogates African swine fever virus replication by disrupting the virus-induced hypoacetylation status of histone H3K9/K14. Virus Res. 2017 Oct 15;242:24-29. [3]. Park HJ, et al. 4-Phenylbutyric acid protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced bone loss by modulating autophagy in osteoclasts. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 May;151:9-17. |
Chemical & Physical Properties
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 290.7±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 49-52ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C10H12O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 164.201 |
| Flash Point | 187.9±13.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 164.083725 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 2.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.535 |
| Water Solubility | 5.3 g/L at 40 ºC |
MSDS
4-Phenylbutyric acid MSDS(Chinese) |
Safety Information
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29163900 |
Synthetic Route
Previous 1/43 Next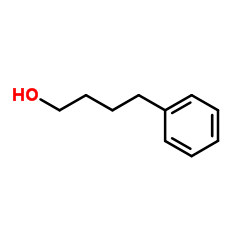 4-Phenylbutan-1... 3360-41-6 ~97% 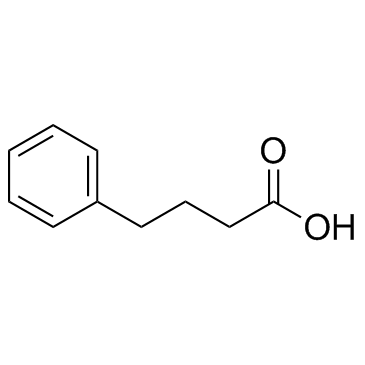 4-Phenylbutyric... 1821-12-1 |
| Literature: Tsunoyama, Hironori; Tsukuda, Tatsuya; Sakurai, Hidehiro Chemistry Letters, 2007 , vol. 36, # 2 p. 212 - 213 |
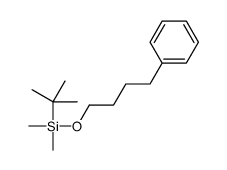 tert-butyl-dime... 72064-43-8 ~86%  4-Phenylbutyric... 1821-12-1 |
| Literature: Karimi, Babak; Rajabi, Jamshid Organic Letters, 2004 , vol. 6, # 17 p. 2841 - 2844 |
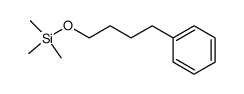 trimethyl(4-phe... 81631-80-3 ~89%  4-Phenylbutyric... 1821-12-1 |
| Literature: Karimi, Babak; Rajabi, Jamshid Organic Letters, 2004 , vol. 6, # 17 p. 2841 - 2844 |
Precursor & DownStream
| Precursor 10 | Previous 1/3 Next |
|---|---|
| |
| DownStream 10 | Previous 1/3 Next |
| |
Customs
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916399090 other aromatic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
Articles68
More Articles| Total Analysis of Microcystins in Fish Tissue Using Laser Thermal Desorption-Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization-High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LDTD-APCI-HRMS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 63 , 7440-9, (2015) Microcystins (MCs) are cyanobacterial toxins encountered in aquatic environments worldwide. Over 100 MC variants have been identified and have the capacity to covalently bind to animal tissue. This st... | |
| Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps). J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI typ... | |
| Different dose-dependent mechanisms are involved in early cyclosporine a-induced cholestatic effects in hepaRG cells. Toxicol. Sci. 141(1) , 244-53, (2014) Mechanisms involved in drug-induced cholestasis in humans remain poorly understood. Although cyclosporine A (CsA) and tacrolimus (FK506) share similar immunosuppressive properties, only CsA is known t... |
Synonyms
| 4-Phenylbutyric acid |
| Butyric acid,4-phenyl |
| Benzenebutanoic acid |
| EINECS 217-341-8 |
| 4-phenylbutyrate |
| 1-Phenylbutyric acid |
| 4-Phenyl-butyric acid |
| g-phenyl-Butyric acid |
| 4-Phenylbutanoic acid |
| g-Phenylbutyric acid |
| Benzenebutyric acid |
| 4-Phenyl-n-butyric acid |
| gama-Phenylbutyric acid |
| g-Phenylbutanoic acid |
| w-Phenylbutanoic acid |
| MFCD00004403 |
| γ-Phenylbutanoic acid |
| 4-PHENYL-BUTANOIC ACID |
2. Packaging of materials
For powders: normal is 25kgs/Drum or bag, or larger/smaller package as request.
For liquids: normal 25kgs/drum, 180-300kgs/bucket, or IBC, determined by the nature of the product.
Or smaller package 1kg/bottle, 10kgs/bottle as request.


3. Shipping & Delivery
By Express
Provide door to door service
Suitable for goods under 50kg
Delivery: 3-7 days
Cost: low cost

By Air
Provide airport to airport service
Suitable for goods over 50kg
Delivery: 3-14 days
Cost: high cost

By Sea
Provide seaport to seaport service
Suitable for goods over 100kg
Delivery: 2-45 days
Cost: low cost

4. Contact information
For more details, pls contact us freely.
Email address: Tina@fdachem.com
Mob: 86 13213167925
WhatsApp/Skype/Wechat/LINE: 86 13213167925
Company Profile Introduction
Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd. is located in the High-tech Development Zone of Henan Province. Specializing in the production and sales of various fine chemical products required for industrial production, including chemical raw materials, organic raw materials, petrochemicals, chemical reagents, solvents, catalysts, and additives, etc.


 CAS#:313058-67-2
CAS#:313058-67-2![N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-4-phenylbutanamide structure](https://www.chemsrc.com/caspic/421/105026-91-3.png) CAS#:105026-91-3
CAS#:105026-91-3 CAS#:10473-01-5
CAS#:10473-01-5 CAS#:67857-97-0
CAS#:67857-97-0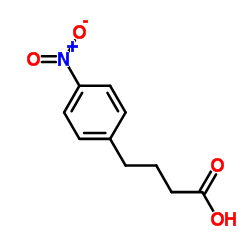 CAS#:5600-62-4
CAS#:5600-62-4

