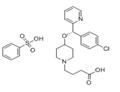
Betotastine was introduced in Japan for the treatment of allergic rhinitis. This
structurally-related derivative of chlorpheniramine and ebastine is prepared by
condensation of optically-resolved 4-[1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2-pyridyl)-methoxy]piperidine
with ethyl 4-bromobutyrate followed by ester hydrolysis. Betotastine is the seventh
marketed non-sedating histamine H1 antagonist. Its very low sedative side effect is due to
very poor penetration in the central nervous system. Besides its potent and long-acting
activity in models of allergic rhinitis, betotastine was also shown to act as a PAF antagonist and inhibit LTD4 in tracheal smooth muscle and ileum, IL-5 production by human peripheral
blood mononuclear cells as well as eosinophil infiltration in the airway and peripheral
blood. As a consequence, it is currently being developed against other allergic and
respiratory disorders.