What is Boron nitride?
Overview
Boron nitride is a material in which the extra electron of nitrogen (with respect to carbon) enables it to form structures that are isoelectronic with carbon allotropes.Boronnitride is manufactured by heatingboron oxide to 800°C on an acid-solublecarrier, such as calcium phosphate,in the presence of nitrogen orammonia. It is isoelectronic with carbonand, like carbon, it has a veryhard cubic form (borazon) and asofter hexagonal form; unlikegraphite this is a nonconductor. It isused in the electrical industrieswhere its high thermal conductivityand high resistance are of especialvalue.
Hexagonal boron nitride powder has a chemical structure similar to graphite and is applied in a wide range of fields as a very chemically stable material. White powder, excellent in thermal conductivity, insulation, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, lubricity, as a filler or additive, and its molded product is excellent in machinability, used in the semiconductor, glass, metallurgy, steel fields It is done.
Physical properties
white powder(s), 1μm or less 99.5% pure; hexagonal graphite-like form or cubic crystal; cubic form similar to diamond in its crystal structure, and reverts to graphite form when heated above 1,700°C; density 2.18 g/cm3; melts at 2,975°C (under nitrogen pressure); sublimes at 2,500°C at atmospheric pressure; insoluble in water and acid; attacked by hot alkalies and fused alkali carbonates; not wetted by most molten metals or glasses.
Most common form: a=0.2504 nm, c=0.6661nm; fcc: a=0.3615nm; hardness: hexagonal like graphite,cub approaches that of diamond; band gap ~7.5 eV at 300K; dielectric 7.1; used in furnace insulation and in crucibles for melting aluminum, boron, iron, and silicon, also as sputtering target for dielectrics, diffusion masks, passivation layers.
Natural occurrence
In 2009, a naturally occurring boron nitride mineral in the cubic form (c-BN) was reported in Tibet, with a proposed name of qingsongite. The substance was found in dispersed micron-sized inclusions in chromium-rich rocks. In 2013, the International Mineralogical Association affirmed the mineral and the name.
Cubic boron nitride VS Hexagonal boron nitride
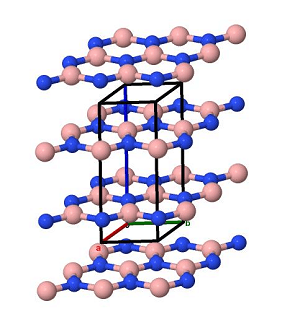
Boron nitride is made up of nitrogen and boron atoms in the crystal, the crystal structure can be divided into: hexagonal boron nitride (HBN), dense rows of hexagonal boron nitride (WBN) and cubic boron nitride, the crystal structure of hexagonal boron nitride have similar graphite layer structure, loose, lubrication, easy absorption of moisture, light and other traits of white powder, so it is also called "white graphite". The expansion coefficient of boron nitride is equivalent to quartz, but its thermal conductivity is ten times that of quartz. It also has good lubricity at high temperatures, is an excellent high temperature solid lubricant, has a strong neutron absorption ability, chemical properties stable, almost all molten metal have chemical inertia.
Hexagonal nitrogen is insoluble in cold water, which hydrolyzes very slowly when boiled and produces a small amount of boric acid and ammonia. It cannot react with weak acid and strong base at room temperature, but is slightly soluble in hot acid. It can only be decomposed by molten sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide treatment.All kinds of inorganic acid, alkali, salt solution and organic solvent have a considerable anti - corrosion ability.Cubic boron nitride (CBN) is a kind of superhard material second only to diamond in hardness. It was first developed by R.H. Wentoff from the United States in 1957. It not only has many excellent properties of diamond, but also has higher thermal stability and chemical stability to iron group metals. Widely used in the processing of hardened steel, cold cast iron, heat resistant alloy and other ferrous metals.
Preparation
Boron nitride is prepared by heating boric oxide with ammonia:
B2O3 + 2NH3 → 2BN + 3H2O
Alternatively, the compound can be prepared by heating boric oxide or boric acid with ammonium chloride or an alkali metal cyanide. Purified product can be obtained by high temperature reaction of boron halide with ammonia:
BCl3 + NH3 → BN + 3HCl
Boron nitride can also be made from the elements by heating boron and nitrogen at red heat.
Application
Consumer Uses
This substance is used in the following products: lubricants and greases and cosmetics and personal care products.
Other release to the environment of this substance is likely to occur from: indoor use as processing aid, outdoor use as processing aid, indoor use in close systems with minimal release (e.g. cooling liquids in refrigerators, oil-based electric heaters) and outdoor use in close systems with minimal release (e.g. hydraulic liquids in automotive suspension, lubricants in motor oil and break fluids).
Article service life
Release to the environment of this substance can occur from industrial use: industrial abrasion processing with low release rate (e.g. cutting of textile, cutting, machining or grinding of metal) and industrial abrasion processing with high release rate (e.g. sanding operations or paint stripping by shot-blasting). This substance can be found in products with material based on: stone, plaster, cement, glass or ceramic (e.g. dishes, pots/pans, food storage containers, construction and isolation material).
Widespread uses by professional workers
This substance is used in the following products: lubricants and greases, hydraulic fluids and metal working fluids. This substance is used in the following areas: scientific research and development. Release to the environment of this substance can occur from industrial use: in the production of articles. Other release to the environment of this substance is likely to occur from: indoor use as processing aid, outdoor use as processing aid, indoor use in close systems with minimal release (e.g. cooling liquids in refrigerators, oil-based electric heaters) and outdoor use in close systems with minimal release (e.g. hydraulic liquids in automotive suspension, lubricants in motor oil and break fluids).
Formulation or re-packing
This substance is used in the following products: coating products, lubricants and greases, metal working fluids, polymers and cosmetics and personal care products. Release to the environment of this substance can occur from industrial use: formulation of mixtures and formulation in materials.
Industrial uses
Boron nitride (BN) has many potential commercial applications. It is a white, fluffy powder with a greasy feel. It is used for heat-resistant parts by molding and pressing the powder without a binder to a specific gravity of 2.1 to 2.25.
BN may be prepared in a variety of ways, for example, by the reaction of boron oxide with ammonia, alkali cyanides, and ammonium chloride, or of boron halides and ammonia. The usually high chemical and thermal stability, combined with the high electrical resistance of BN, suggests numerous uses for this compound in the field of high-temperature technology. BN can be hot-pressed into molds and worked into desired shapes.
BN powders can be used as mold-release agents, high-temperature lubricants, and additives in oils, rubbers, and epoxies to improve thermal conductance of dielectric compounds. Powders also are used in metal- and ceramicmatrix composites (MMC and CMC) to improve thermal shock and to modify wetting characteristics.
The platy habit of the particles and the fact that boron nitride is not wet by glass favors use of the powder as a mold wash, e.g., in the fabrication of high-tension insulators. It is also useful as thermal insulation in induction heating. A cubic form of boron nitride (Borazon) similar to diamond in hardness and structure has been synthesized by the high-temperature, high-pressure process for making synthetic diamonds. Any uses it may find as a substitute for diamonds will depend on its greatly superior oxidation resistance.
Uses at industrial sites
This substance is used in the following products: lubricants and greases, metal working fluids, polymers, metal surface treatment products, coating products, non-metal-surface treatment products, fillers, putties, plasters, modelling clay, hydraulic fluids, inks and toners, laboratory chemicals, paper chemicals and dyes and welding & soldering products. This substance has an industrial use resulting in manufacture of another substance (use of intermediates). This substance is used in the following areas: formulation of mixtures and/or re-packaging and building & construction work.
This substance is used for the manufacture of: mineral products (e.g. plasters, cement), machinery and vehicles, plastic products, fabricated metal products, wood and wood products, pulp, paper and paper products, rubber products and furniture.
Release to the environment of this substance can occur from industrial use: in processing aids at industrial sites, in the production of articles, as an intermediate step in further manufacturing of another substance (use of intermediates), as processing aid and of substances in closed systems with minimal release.
Manufacture
Release to the environment of this substance can occur from industrial use: manufacturing of the substance.
You may like
Related articles And Qustion
Lastest Price from Boron nitride manufacturers

US $0.00/kg2025-11-17
- CAS:
- 10043-11-5
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 20tons

US $1.50/g2025-04-18
- CAS:
- 10043-11-5
- Min. Order:
- 1g
- Purity:
- 99.0% Min
- Supply Ability:
- 100 Tons





