Synthesis and Application of Chenodeoxycholic Acid
General description
Chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) as a natural primary bile acid is one of the main organic compounds in the bile of chicken, duck, goose and so on. It has the function of sterilization, anti-inflammatory and dissolution of gallstones. In clinical practice, chenodeoxycholic acid is the drug for treatment of cholesterol gallstones. Ursodeoxycholic acid is the largest amount of drug for the treatment of gallstone disease, and chenodeoxycholic acid is the raw material for the synthetic of ursodeoxycholic acid. The application value in medicine promotes the preparation methods of chenodeoxycholic acid gradually improved. In recent years, great progress has been made in the research of chenodeoxycholic acid derivatives. Study on application of chenodeoxycholic acid has been extended to biological medicine, molecular recognition, functional materials and other fields [1].
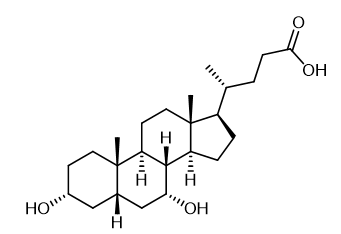
Fig. 1 The structure of Chenodeoxycholic acid.
Synthetic routes
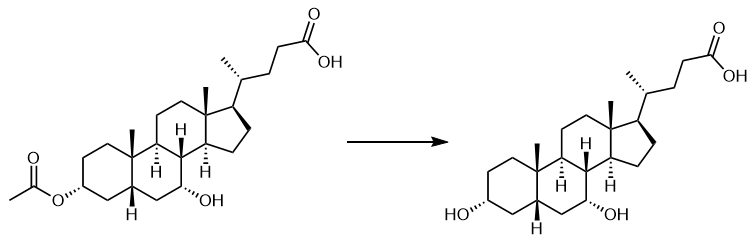
Fig. 2 The synthetic scheme 1 of Chenodeoxycholic acid.
To a stirred solution of methyl 3α-acetoxyl-7α-hydroxyl-5β-cholanoate (0.2 mmol) in MeOH (4 mL) and H2O (1 mL) was added NaOH (0.0441 g, 1.1 mmol) at room temperature. The mixture was heated at reflux for 1 h, and then adjusted to pH 1-2 with 1 M HCl aq to afford compound CDCA (0.0427 g, 97% yield); mp 119-121 °CFTIR (KBr, cm–1) 3450 and 3304 (O-H), 1703 (C=O); 1H NMR (600 MHz, CD3OD) δ 3.81-3.78 (m, 1H, 7β-H), 3.40 – 3.35 (m, 1H, 3β-H), 0.96 (d, J = 6.5 Hz, 3H, 21-H), 0.93 (s, 3H, 19-H), 0.70 (s, 3H, 18-H); 13C NMR (151 MHz, CD3OD) δ 178.4 (C-24), 72.1 (C-3), 68.6 (C-7), 55.7, 50.4, 42.7, 41.4, 39.8, 39.6, 39.4, 35.3, 35.3, 35.0, 34.5, 32.8, 30.8, 30.6, 29.7, 28.1, 23.7, 22.7, 20.5, 18.2, 11.7; HRMS (ESI, m/z) Calcd for C24H40O4 392.2927; found: 391.2864 [M-H]- (Calcd 391.2848) [2].
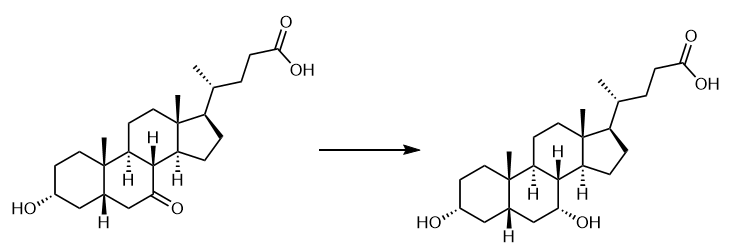
Fig. 3 The synthetic scheme 2 of Chenodeoxycholic acid.
7α-HSDHCa from C. absonum DSM 599 is an NADPH-dependent enzyme. The 5-mL reaction starting from the CDCA consisted of 100 mM phosphate buffer (pH 8.0), 10 mM CDCA, 0.5 mM NADP+ and combine with 0.5 U mL-1, 1.0 U mL-1, or 2.0 U mL-1 7α-HSDHCa and 7α-HSDHRt respectively. Perform the 5-mL reaction starting from the UDCA at 30℃ by incubating a mixture consisting of 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 8.0, 10 mM CDCA, 30 mM sodium pyruvate, 0.5 mM NAD+, 5 U mL-1 or 15.0 U mL-1 LDH and 0.5 U mL-1, 1.0 U mL-1 or 5.0 U mL-1 E. coli 7α-HSDH respectively. Stop the reaction by adding 1 M HCl to lower the pH to 3. Extract the crude product with diethyl ether.a Evaporate the organic layer and add methanol to the mixture for HPLC analysis [3].
Application
CDCA for Cholesterol Gallstones
Several studies have investigated the effect exerted by different doses of CDCA on gallbladder stones dissolution. In a meta-analysis, published in 1993, May et al. reported pooled data from 11 studies involving 1,062 patients, and concluded that complete gallstone dissolution occurred overall in 13.6% (95% C.I. 12–16%) of patients treated with CDCA. The trials were dishomogeneous, because, among other factors, CDCA was used at different doses. Subsequent sub-analysis of these studies allowed to identify trials in which patients were administered at a dose of CDCA <10 mg/kg or <750 mg/day (467 patients, low dose) and nine studies in which 589 patients were administered a higher dose (>10 mg/kg or >750 mg/day) for more than 6 months. The gallstone dissolution rate was 8.1% (95% C.I. 5.8–11%) with the low dose and 18.0% (95% C.I. 15–21%) with the higher doses. High-dose CDCA dissolved significantly more stones than low-dose CDCA (χ’ = 20.7, P < 0.001). The results of this meta-analysis were largely confirmatory of the disappointing results obtained in the largest of these trials, the National Cooperative Gallstone Study published in 1981, that reported a dissolution rate of 13.2% in patients administered 750 mg/day and 5.2% in patients taking 375 mg/day. Side effects including clinically significant hepatotoxicity occurred in 3% of patients treated with 750 mg/day and were always reversible biochemically. Elevations of 10% or more of serum cholesterol, mostly LDL, occurred in 85.2% of patients treated with the higher dose [4].
References
[1] Hu X, Wang J. Preparation and Application of Chenodeoxycholic Acid and Its Derivatives[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2016, 28(6): 814.
[2] Liang Y Y, Huang H, Li Y, et al. Efficient synthesis of cholic acid derivates through stereoselective C–H functionalization from hyodeoxycholic acid[J]. Steroids, 2020, 157: 108594.
[3] Zheng M M, Wang R F, Li C X, et al. Two-step enzymatic synthesis of ursodeoxycholic acid with a new 7β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Ruminococcus torques[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2015, 50(4): 598-604.
[4] Fiorucci S, Distrutti E. Chenodeoxycholic acid: an update on its therapeutic applications[J]. Bile Acids and Their Receptors, 2019: 265-282.
Related articles And Qustion
See also
Lastest Price from Chenodeoxycholic acid manufacturers

US $0.00/kg2025-09-10
- CAS:
- 474-25-9
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 99%min
- Supply Ability:
- 2000KGS

US $2.00/g2025-06-05
- CAS:
- 474-25-9
- Min. Order:
- 1g
- Purity:
- 99.99%
- Supply Ability:
- 10000


