Side effects of Sparfloxacin
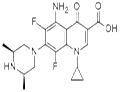
Sparfloxacin (AT-4140, CI-978, PD 131501) is a newer-generation aminodifluoroquinolone with broad spectrum antibacterial activity. It has the chemical formula 5-amino-1-cyclopropyl-7-(cis-3,5-dimethylpiperazin- 1-yl)-6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinolone-3-carboxylic acid. The main potential advantages of sparfloxacin over older fluoroquinolones are its improved activity against Grampositive pathogens (such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus), Mycobacteria, and Chlamydophila spp. and its long halflife that allows once-daily dosing. Because of concerns about cardiac risks related to QT interval prolongation and an increased risk of phototoxic reactions, sparfloxacin was withdrawn from the American market in 2001, but it remains available in Japan, India, and parts of Europe as a 200-mg tablet.

Bioavailability
Sparfloxacin is readily absorbed and has oral bioavailability of 92% and a half-life of 16–20 hours.It is 37–45% protein bound. Foods, including milk or high-fat meals, do not significantly alter sparfloxacin absorption.
Excretion
Sparfloxacin is eliminated primarily by nonrenal mechanisms, including hepatic biotransformation, biliary excretion, and possibly transluminal secretion across the enteric mucosa. Sparfloxacin undergoes metabolism to a glucuronide form, which is detectable in plasma at about 30–40% of the unchanged sparfloxacin concentration, and in urine and bile at 2- to 3-fold and 4- to 20-fold the unchanged sparfloxacin concentration, respectively. The glucuronidation pathway is not cytochrome P450 dependent.
Side effects
Sparfloxacin has a similar rate of adverse reactions as ciprofloxacin and other commonly used fluoroquinolones. In a review of six phase III trials in which 1585 patients in the sparfloxacin arms received a 400-mg loading dose followed by 200 mg daily, most common sideeffects were gastrointestinal (such as nausea, diarrhea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, vomiting, or flatulence; 22.3%), photosensitivity reactions (7.4%), headache (1.9%), insomnia (1.5%), and dizziness (1.1%). QT interval prolongation was seen in 1–3%, but values returned to baseline within 48 hours of drug cessation. The Food and Drug Administration received 145 reports of QT-related cardiac events before sparfloxacin was withdrawn from the American market.
Experimental modeling shows that sparfloxacin induces greater degrees of QT prolongation than telithromycin, moxifloxacin, or erythromycin. Phototoxic reactions in sparfloxacin recipients have an average onset 6.374.5 days (range, 1–14 days) after commencing the drug. Mostly this consists of erythema on the face and hands, which lasts an average of 6.474.2 days. The hierarchy of phototoxic risk among the fluoroquinolones is lomefloxacin, fleroxacinWsparfloxacinWenoxacinWpefloxacinWciprofloxacin, grepafloxacinWnorfloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, trovafloxacin, gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin. Photoonycholysis has also been reported with sparfloxacin use.
Lastest Price from Sparfloxacin manufacturers
US $1.00/KG2021-08-25
- CAS:
- 110871-86-8
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 10T

US $1.10/g2021-07-20
- CAS:
- 110871-86-8
- Min. Order:
- 1g
- Purity:
- 99.9%
- Supply Ability:
- 100 Tons min


