Pharmacological activities of Taxifolin
Properties
Taxifolin, a chemical substance extracted from pine plants such as larch and Douglas fir. It belongs to the bioflavonoid pseudo-vitamin P, and its scientific name is dihydroquercetin. Japanese scholar Fukui first isolated it from the leaves of conifers (Chamaecyparis obtusa), and its biological activity was subsequently discovered and confirmed. Studies have shown that it has anti-oxidant, anti-tumor, anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor and other pharmacological activities, and is non-toxic, non-teratogenic, and non-mutagenic. Unfortunately, Taxifolin is difficult to dissolve in water, resulting in low bioavailability, which limits its use in medicine and clinics. It is low in plants, generally 2 to 3%. Taxifolin is mainly derived from pines such as larch and Douglas fir. It belongs to the bioflavonoid pseudo-vitamin P. It is mainly distributed in Siberia, Russia, and it is rare in other regions.
Structural chemistry
Taxifolin is a subclass of flavanonols, an isoflavanone in flavonoids family. The basic structure of two phenyl groups (ring A and ring B) which are joined together by a heterocyclic ring referred to as ring C [1]. The structure contains 3-hydroxyl group at the C ring which is connected to the B ring at carbon-2 [1]. Taxifolin is a pentahydroxyflavone containing five hydroxyl groups at the 3-, 3'-, 4'-, 5- and 7-positions. The IUPAC name is (2R, 3R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one. The molecular weight is 304.25 g/mol with the molecular formula C15H12O7 [2]. It has two stereocenters on the C-ring and 4 stereoisomers. It with the configuration of (2R, 3R) is one of them and it comprises 2 pairs of enantiomers [3].
Pharmacological activities
1 Antioxidant activity
Taxifolin is a kind of flavanonol, whose biological ability. Taxifolin demonstrated 81.02% inhibition of linoleic acid emulsion peroxidation at 30 µg/mL concentration. At the same concentration, standard antioxidants including trolox, α-tocopherol, BHT, and BHA exhibited inhibitions of linoleic acid emulsion as 88.57, 73.88, 94.29, and 90.12%, respectively. Also, it showed effective DMPD√+, ABTS√+, , and DPPH√-scavenging effects, reducing capabilities, and Fe2+-chelating effects. Taxifolin had marked antioxidant, reducing ability, radical scavenging and metal-chelating activities [4].
2 Anti-inflammatory activity
Taxifolin isolated from plants have powerful anti-inflammatory activity. The laboratory has reported its anti-inflammatory activity. Tests have shown that taxifolin can reduce formalin-induced foot edema in mice. Some studies have shown that it also has a certain effect on the activity of serum transaminase and tissue adenosine triphosphate (ATP) phosphohydrolase. [5].
3. Hepatoprotective activity
Silymarin is a widely used hepatoprotective drug in which it is found to be an essential component (Legalon®). Several studies have been reported that taxifolin with the doses of 0.25, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg shows significant hepatoprotective activity in rotenone induced hepatotoxic rats. A significant increase in the total protein concentration, bilirubin, activities of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphate (AKT), gamma glutamyltransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) has been observed in the animals [6]
4. Anti-Alzheimer activity
It is also effective in the treatment of Alzheimer. According to studies, it significantly reduces elevated αβ and C99 levels in N2a Swe cells. Additionally, it is also associated with the synergistic inhibition of the amyloidogenesis via the downregulation of P-JAK2/P-STAT3-coupled NF-κB linked BACE1 expression through the SIRT1 upregulation [7].
5. Antiangiogenic activity
It also showed to have the antiangiogenic activity through the inhibition of the formation of new blood vessels and branches. It associated with in vitro antiangiogenic activity by inhibiting the tube formation on Matrigel matrix which was assessed by tube formation assay in human umbilical vein endothelial cells [8].
6. anticancer activity
Several studies have been performed on numerous pharmacological properties (Fig. 1) have been observed including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, anti-Alzheimer’s, antiangiogenic, antihyperglycemic, cardiovascular disorder, antimicrobial, antipsoriatic, antihyperuricemic, pulmonary, genotoxic activity and anticancer activity.
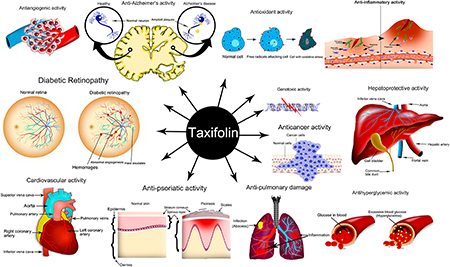
Fig.1 Anticancer activity[10]
Application
Taxifolin is a flavonoid commonly found in onion, milk, French maritime pine bark and Douglas fir bark, as Fig.2 showed. It is also used in various commercial preparations like Legalon™, Pycnogenol®, and Venoruton®. This review focuses on taxifolin’s biological activities and related molecular mechanisms. It showed promising pharmacological activities in the management of inflammation, tumors, microbial infections, oxidative stress, cardiovascular, and liver disorders. The anti-cancer activity was more prominent than other activities evaluated using different in vitro and in vivo models. Further research on the pharmacokinetics, in-depth molecular mechanisms, and safety profile using well-designed randomized clinical studies are suggested to develop a drug for human use.[9]
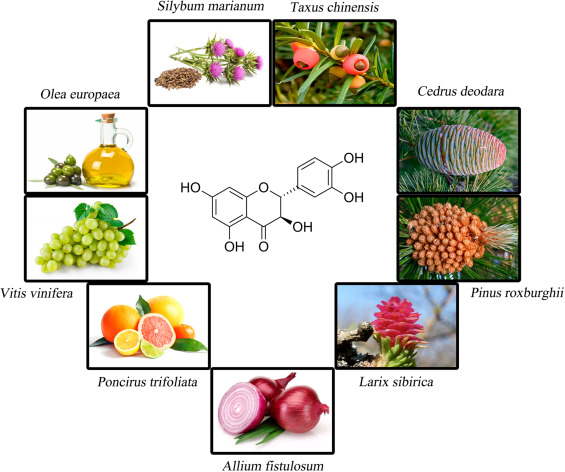
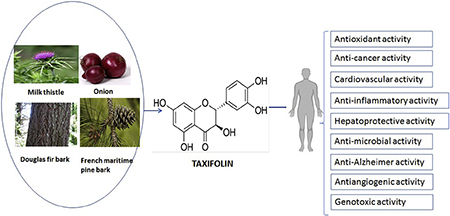
Fig.3 The development of human use [11]
Renference
[1] G.R. Beecher. Overview of dietary flavonoids: nomenclature, occurrence and intake. J. Nutr., 2003, 133: 3248S-3254S.
[2] National Center for Biotechnology Information, PubChem Compound Summary for CID 439533, Taxifolin, 2021.
[3] https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:17948.
[4] Fevzi Topal, Meryem Nar, Hulya Gocer, P?nar Kalin, Umit M. Kocyigit, ?lhami Gülçin & Saleh H. Alwasel. Antioxidant activity of taxifolin: an activity–structure relationship, Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 2016, 31(4): 674-683.
[5] M.B. Gupta, T.N. Bhalla, G.P. Gupata, C.R. Mitra, K.P. Bhargava, Anti-inflammatory Activity of taxifolin, Japanese Journal of Pharmacology, 1971, 21(3): 377-382.
[6] A.R. Tapas, D.M. Sakarkar, R.B. Kakde. Flavonoids as nutraceuticals: a review
Trop. J. Pharm. Res., 2008, 7: 1089-1099.
[7] S.Y. Park, H.Y. Kim, H.J. Park, H.K. Shin, K.W. Hong, C.D. Kim. Concurrent treatment with taxifolin and cilostazol on the lowering of β-amyloid accumulation and neurotoxicity via the suppression of P-JAK2/P-STAT3/NF-κB/BACE1 signaling pathways PLOS One, 2016, 11: 0168286.
[8] H. Wasimul, P.P. Shakti, N.S. Barij. Evaluation of taxifolin and phloretin as antiangiogenic flavonoids: an in vivo, in vitro experimental analysis. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci., 2015, 7: 72-79.
[9] Christudas Sunil, Baojun Xu, An insight into the health-promoting effects of taxifolin (dihydroquercetin), Phytochemistry, 2019, 166: 112066.
[10] Das A, Baidya R, Chakraborty T, et al. Pharmacological basis and new insights of taxifolin: A comprehensive review[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2021, 142: 112004.
[11] Christudas Sunil, Baojun Xu. An insight into the health-promoting effects of taxifolin (dihydroquercetin). Phytochemistry,Volume 2019, 166: 112066.
Related articles And Qustion
Lastest Price from Taxifolin manufacturers

US $0.00-0.00/kg2025-09-08
- CAS:
- 480-18-2
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 98%
- Supply Ability:
- 1

US $0.00-0.00/kg2025-04-27
- CAS:
- 480-18-2
- Min. Order:
- 0.10000000149011612kg
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 100kg




