Is Quercetin and Quercitrin the same?
No, they are different. Quercetin is the most common flavonoid, existing primarily in its glycoside form as quercitrin (3-rhamnoside). Quercetin (4H-1-benzopyran-4-one, 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-flavon) and quercitrin (2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl6-deoxyalpha-L-mannopyranoside) are a class of natural flavonoids widely found in the flowers, leaves, and fruits of various plants. They have anticancer, antifibrosis, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidation effects. Both quercetin and quercitrin are biological flavonoids, and their structures are similar.

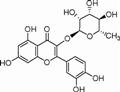
They mainly refer to two benzene rings (A ring and B ring) as the mother nucleus, linked by a central three-carbon chain (C chain). The series of compounds with the C6-C3-C6 basic carbon skeleton contains a plurality of hydroxyl groups (OH) and are highly polar. The basic structure is shown above. It can be speculated from the structure that it can scavenge free radicals. However, the position of the two molecules on the B ring is different, which affects its anti-inflammatory activities and antioxidation effects[1-2].
References
[1] Jie Tang. “Quercetin and Quercitrin Attenuates the Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Cells: In Vitro Assessment and a Theoretical Model.” BioMed Research International 2019 (2019): 7039802.
[2] Xiaoqian Dai. “Quercetin and quercitrin protect against cytokine‑induced injuries in RINm5F β-cells via the mitochondrial pathway and NF-κB signaling.” International journal of molecular medicine 31 1 (2013): 265–71.
You may like
Lastest Price from Quercitrin manufacturers

US $0.00-0.00/KG2024-07-20
- CAS:
- 522-12-3
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99.0%
- Supply Ability:
- 1KG
US $0.00/mg2023-02-24
- CAS:
- 522-12-3
- Min. Order:
- 5mg
- Purity:
- Analytical Standard
- Supply Ability:
- 10 g


