Applications of phosphorus tribromide
Polarographic Behavior of Phosphorus Tribromide
Phosphorus tribromide gives a one-electron reduction wave at E 1 / 2 -0.6 V on a mercury drop cathode in acetonitrile in the concentration range 0.05-0.5 mM, applicable for analytical purposes. It is proposed that the cathodic process gives rise to an unstable species particle PBr which is adsorbed on the mercury surface[1].
Application of Phosphorus Tribromide in Olefins
We have now shown that phosphorus tribromide can be added, under a variety of conditions, to simple olefins to give 1 : 1 adducts which are undoubtedly β-bromoalkylphosphonous dibromides. These compounds are potentially useful intermediates in the synthesis of phosphorus mustards, and heterocyclic compounds containing phosphorus[2].
The ultraviolet irradiation of a mixture of ethylene and phosphorus tribromide gave 14% of 2-bromoethylphosphonous dibromide, characterized by elemental analysis, by absence of a phosphoryl band in its infrared spectrum, and by oxidative hydrolysis to the known 2-bromoethyl[1]phosphonic acid., The same phosphonous dibromide can be obtained in substantially better yield (40%) by a thermal addition reaction at 150 in the absence of any added initiator.
Ultraviolet irradiation of a mixture of refluxing propene and phosphorus tribromide gave 2-bromo[1]1-methylethylphosphonous dibromide, MeCH- (PBr,) CH,Br, containing a small amount of the isomeric 2-bromopropylphosphonous dibromide, MeCHBrCH,.PBr,. The thermal addition reaction with propene gave a mixture of these isomeric compounds containing 30% of the 2-bromo-isomer. The isomers were distinguished by their lH nuclear magnetic resonance spectra at 60 Mc./sec. The major product of both reactions shows a quartet for the methyl group at δ = 2.25 p.p.m. (downfield from external Me4Si = 0), with JMe-p = 17 c./sec. and JMe-CH = 7 c./sec.; the minor product also shows a quartet, at 6 = 2.67 p.p.m., with JMe-CH- = 7 c./sec., but with JMe-p = 1.5 c./sec. The small value of this last coupling constant indicates the remote position of the methyl group from the PBr, group.
Addition of phosphorus tribromide to hept- 1-ene, oct-1-ene, and cyclohexene can be initiated by ultraviolet radiation, or by peroxides or azo[1]compounds, and yields 1:1 adducts which seem to be mixtures of isomers, since they give two peaks on gas chromatography.
The free-radical nature of the additions reported is substantiated by the observation that addition does not occur at comparable temperatures if the initiators are lacking. The orientation of addition of the major product from propene is unusual, and suggests that both the bromine radical and the phosphorus dibromide radical may be involved in addition steps, and that the chain-transfer step may not be exclusively an abstraction from phosphorus tribromide. The following mechanism is in accord with other observations on the reactivity of phosphorus trihalides with olefins and accounts for the observed products :
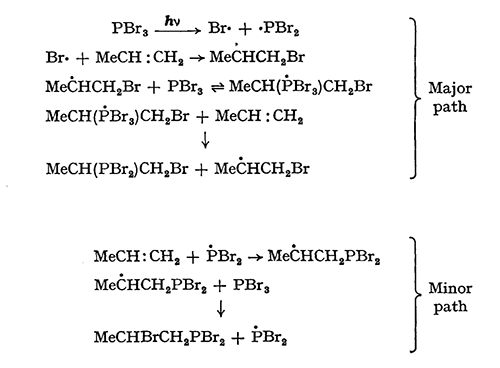
Phosphorus tribromide as acceptor
Lewis acid-base adducts between NMe3, tmeda (N ,N ,N′ ,N′-tetramethylethylenediamine), and 1.4-dimethylpiperazine as donors and PBr3 as acceptor have been prepared and structurally characterized[3]. NMe3 and tmeda form 1:1 adducts (Me3N)PBr3 (1) and (tmeda)PBr3 (2), respectively, while 1,4-dimethylpiperazine adds 2 molecules of PBr3 leading to [(1,4-dimethylpiperazine)( PBr3)2] (3). Adduct 2 is found in two modifications 2a and 2b with different crystal and molecular structures. (Crystal data of 1: monoclinic P21/n, a = 5.983(3), b = 10.821(2), c = 13.877(5) Å, ß = 99.70(2)°, Z = 4. 2a: monoclinic P21/c, a = 7.891(1), b = 12.826(1), c = 12.218(2) Å ,ß = 102.162(6)°, Z = 4. 2b: monoclinic P21/n, a = 11.687(2), b = 8.375(1), c = 12.668(1) Å, ß = 102.74(1)°, Z = 4. 3: monoclinic P21/c, a = 6.383(3), b = 16.36(3), c = 8.407(3) Å , ß = 101.49(2)°, Z= 2). The molecular structures of 1 and 2 indicate a partially ionic character with a strongly bonded amine and one (1 ) or two (2 ) weakly bonded bromine atoms. In 2 the donor tmeda is bonded through both nitrogen atoms to one phosphorus atom. In 3 the 1,4-dimethylpiperazine ring is in chair conformation, the methyl and PBr3 substituents being in equatorial and axial positions, respectively. Due to axial-axial repulsion the N-P donor-acceptor bonds are long while the P-Br bonds are rather uniform in length.
Reference
1 Kisil', L.M., Osadchenko, I.M. & Tomilov, A.P. Polarographic Behavior of Phosphorus Tribromide. Russian Journal of General Chemistry 73, 695–696 (2003).
2 Kuivila, Henry G., and William L. Masterton. "The Reaction between Cyclobutylcarbinol and Phosphorus Tribromide." Journal of the American Chemical Society 74.19 (1952): 4953-4954.
3 Müller, Gerhard, Jörg Brand, and Simone Elisabeth Jetter. "Donor-acceptor complexes between organoamines and phosphorus tribromide." Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B 56.11 (2001): 1163-1171.
Related articles And Qustion
Lastest Price from Phosphorus tribromide manufacturers

US $10.00/KG2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 7789-60-8
- Min. Order:
- 1KG
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 10 mt

US $0.00/kg2025-03-07
- CAS:
- 7789-60-8
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- 20tons



