网站主页
化工产品目录
生物化工
抗体
凋亡与自噬
Mitochondrial Control of Apoptosis
TMS1 MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY
TMS1 MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY
TMS1 MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY
TMS1 Monoclonal Antibody
上海 更新日期:2026-02-15
产品详情:
- 中文名称:
- TMS1 MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY
- 英文名称:
- TMS1 Monoclonal Antibody
- 产品类别:
- 抗体 凋亡与自噬
公司简介
碧云天由美国哈佛大学的留学人员创办于2001年,为上海市高新技术企业,公司核心团队由来自美国哈佛大学、NIH、UCLA、香港大学、南京大学、中国科技大学、中国科学院等著名大学和科研机构的高水平科研人员及默克、诺华等顶尖医药企业的管理人员组成。十多年来,碧云天已经成为世界一流的生物、医学研究用试剂、试剂盒和消耗品的研发和生产企业,同时提供生命科学研究的技术服务和一站式实验仪器设备采购平台。目前已有近50000篇注明使用碧云天产品的研究论文发表在包括Nature、Cell等国际高水平学术期刊,日均逾33.37篇!碧云天将继续致力于科研用技术和产品的研发,用我们最顶尖的技术、最成熟的产品、最热情的服务,服务科研人员,造福生命健康
| 成立日期 | (19年) |
| 注册资本 | 1000.000000万人民币 |
| 员工人数 | 500人以上 |
| 年营业额 | ¥ 500万-1000万 |
| 经营模式 | 试剂 |
| 主营行业 | 生化试剂,核苷,核苷酸,寡核苷酸,抗体,蛋白组学,生物活性小分子 |
TMS1 MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY相关厂家报价
-
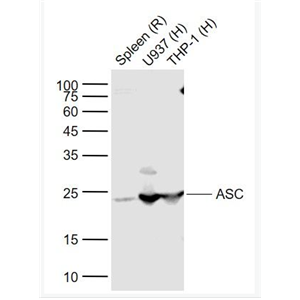
- Anti-ASC/TMS1 antibody-凋亡相关斑点样蛋白ASC抗体
- 上海沪震实业有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-27
- ¥1098
-

- Anti-Human ASC/TMS1/PYCARD Nanobody (SAA1187)
- 武汉佰乐博生物技术有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-27
- 询价
-
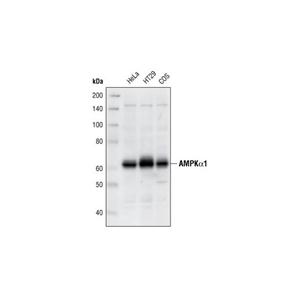
- AMPK ALPHA 1 RABBIT MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY
- 武汉艾美捷科技有限公司
- 2026-02-15
- ¥5850


