化合物 H 89 2HCl|T6250|TargetMol
H-89 dihydrochloride
130964-39-5
130964-39-5
¥318
5mg
起订
¥485
10mg
起订
¥987
25mg
起订
上海 更新日期:2025-11-17
产品详情:
- 中文名称:
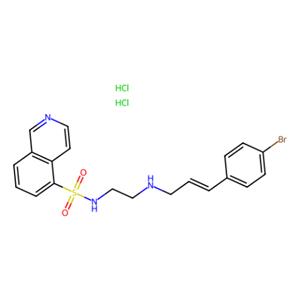
- 化合物 H 89 2HCl
- 英文名称:
- H-89 dihydrochloride
- CAS号:
- 130964-39-5
- 品牌:
- TargetMol
- 产地:
- 美国
- 保存条件:
- In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature.
- 纯度规格:
- 99.40%
- 产品类别:
- 抑制剂
- 货号:
- T6250
公司简介
TargetMol Chemicals Inc. 总部位于马萨诸塞州波士顿,致力于为全球生化领域科学家的研究提供专业的产品和服务。TargetMol?品牌的客户群分布于40多个国家和地区,已发展成为全球知名的化合物库和小分子化合物研究供应商。 TargetMol?可提供160多种满足不同需求的化合物库,以及多种类型的生化试剂产品,包括12000多种抑制剂、16000多种天然产物和各类多肽、抗体、生命科学试剂盒等,此外,我们还建设有CADD(计算机辅助药物设计)研究中心、药理实验室、药化合成平台三大技术中心,全方位满足客户的定制需求。 凭借我们优质的产品和服务、快速高效的全球供应链和专业的技术支持,我们将有效帮助您缩短研发周期,取得更成功的结果。
| 成立日期 | (13年) |
| 注册资本 | 566.265100万人民币 |
| 员工人数 | 100-500人 |
| 年营业额 | ¥ 1亿以上 |
| 经营模式 | 贸易,工厂,试剂,定制,服务 |
| 主营行业 | 天然产物,生化试剂,分子生物学,分子砌块,生物技术服务 |
化合物 H 89 2HCl相关厂家报价 更多
-

- H 89 2HCl;
- 上海切尔齐生物科技有限公司
- 2025-04-23
- 询价
-

- H 89 2HCl;
- 上海切尔齐生物科技有限公司
- 2024-10-20
- 询价
-

- H-His(Nτ-Me)-OMe·2HCl
- GL Biochem(Shanghai) Ltd.
- 2026-01-16
- 询价
-

- aladdin 阿拉丁 H129712 H 89 2HCl,激酶抑制剂 130964-39-5 ≥98%
- 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司 VIP
- 2025-11-14
- ¥265.90
-
- aladdin 阿拉丁 H408541 H 89 2HCl 130964-39-5 10mM in DMSO
- 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司 VIP
- 2025-05-16
- ¥435.90


