布帕尼西|T1827|TargetMol
Buparlisib
944396-07-0
944396-07-0
¥233
1mg
起订
¥529
5mg
起订
¥762
10mg
起订
上海 更新日期:2026-01-06
产品详情:
- 中文名称:
- 布帕尼西
- 英文名称:
- Buparlisib
- CAS号:
- 944396-07-0
- 品牌:
- TargetMol
- 产地:
- 美国
- 保存条件:
- In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature.
- 纯度规格:
- 95.32%
- 产品类别:
- 抑制剂
- 货号:
- T1827
公司简介
上海陶术生物科技有限公司为美国Target Molecule Corp. ( Target Mol ) 在上海建立的全资子公司。我们与美国波士顿、德国慕尼黑的同事一起,为北美、欧洲和亚洲从事药物研发和生物学研究的科学家提供优质的产品和专业的服务。公司下设筛选事业部,化学事业部,生物事业部和新材料部。
从虚拟筛选到实体化合物分子供应;从商业化产品销售到个性化定制合成;从对明确靶点的分子筛选到对明确分子的多靶点筛选,从高通量筛选到化学结构优化,我们都可以满足您的科研用品及技术服务的需求。
经过在中国市场五年的精心耕耘,我们已成为筛选化合物领域优秀的供应商,为超过五百家学校和各类企业提供了品质卓越的小分子化合物和药物筛
| 成立日期 | (13年) |
| 注册资本 | 566.2651万人民币 |
| 员工人数 | 100-500人 |
| 年营业额 | ¥ 1亿以上 |
| 经营模式 | 贸易,试剂,定制,服务 |
| 主营行业 | 化学试剂,生物活性小分子 |
布帕尼西相关厂家报价 更多
-
![5-[2,6-二(4-吗啉基)-4-嘧啶基]-4-(三氟甲基)-2-吡啶胺 944396-07-0](https://img.chemicalbook.com/SupplyImg1/2024-12-06/Large/202412061035515375897.jpg)
- 5-[2,6-二(4-吗啉基)-4-嘧啶基]-4-(三氟甲基)-2-吡啶胺 944396-07-0
- 四川省维克奇生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-10
- 询价
-

- NVP-BKM120(Buparlisib)
- 爱必信(上海)生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-10
- ¥831
-

- 布帕尼西
- 湖北永阔科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-10
- 询价
-

- 布帕尼西
- 麻城市进鑫生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-09
- 询价
-
- 泛class IPI3K抑制剂
- 上海泽叶生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-09
- 询价
-
![5-[2,6-二(4-吗啉基)-4-嘧啶基]-4-(三氟甲基)-2-吡啶胺](https://img.chemicalbook.com/SupplyImg/2023-01-03/Large/202301031753015164965.png)
- 5-[2,6-二(4-吗啉基)-4-嘧啶基]-4-(三氟甲基)-2-吡啶胺
- 河南威梯希化工科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-02-05
- 询价
-
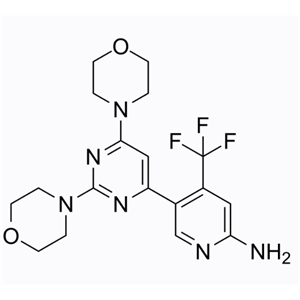
- 944396-07-0
- 广州优南科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-01-08
- 询价
-
![5-[2,6-二(4-吗啉基)-4-嘧啶基]-4-(三氟甲基)-2-吡啶胺](https://img.chemicalbook.com/SupplyImg/2023-06-15/Large/202306151413489154473.png)
- 5-[2,6-二(4-吗啉基)-4-嘧啶基]-4-(三氟甲基)-2-吡啶胺
- 上海升德医药科技有限公司 VIP
- 2026-01-04
- 询价
-
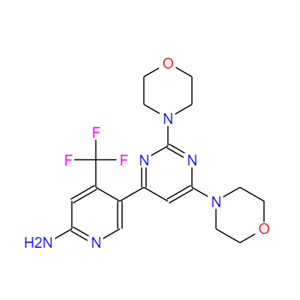
- 布帕尼西
- 陕西西化化学工业有限公司 VIP
- 2025-11-28
- 询价
-
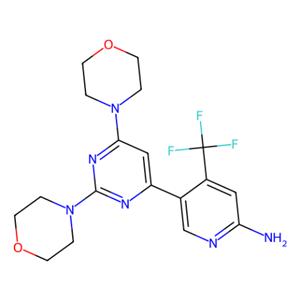
- aladdin 阿拉丁 N127553 BKM120,体外PI3K抑制剂 944396-07-0 ≥99%
- 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司 VIP
- 2025-11-14
- ¥68.90


