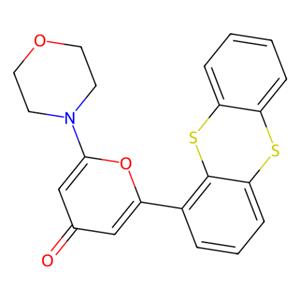
| 名称 | KU-55933 |
| 描述 | KU-55933 (ATM Kinase Inhibitor) is an ATM inhibitor (IC50=12.9 nM; Ki=2.2 nM) that is selective and ATP-competitive. KU-55933 induces apoptosis and has antitumor effects. |
| 细胞实验 | U2OS cells are exposed to ionizing radiation (3, 5, or 15 Gy) or UV (5 or 50 J/m2) and the ATM response determined by Western blot analysis of p53 serine 15 phosphorylation and stabilization of wild-type p53. Whole cell extracts are obtained from each time point, proteins separated by SDS-PAGE, and the ATM-specific increase in phosphorylated serine 15 measured with a p53 phospho-serine 15 specific antibody. Overall p53 stabilization with time is also observed with a p53-specific antibody (DO-1). Similarly, for studying ATM-dependent phosphorylations on H2AX, CHK1, NBS1, and SMC1, the following antibodies are used: CHK1 phospho-serine 345 and NBS1 phospho-serine 343 antibodies. Histone H2A (H-124) and CHK1 antibodies are also used, as well as SMC1 and SMC1 phospho-serine 966 antibodies. For determination of a cellular IC50 for KU-55933, the peak response time for p53 serine 15 phosphorylation of 2 hours is used to monitor inhibition of ATM. KU-55933 is titrated onto cells and preincubated for 1 hour before ionizing radiation. Using scanning densitometry, the percentage inhibition relative to vehicle control is calculated, and the IC50 value is calculated as for the in vitro determinations.(Only for Reference) |
| 激酶实验 | Purified enzyme assays: ATM for use in the in vitro assay is obtained from HeLa nuclear extract by immunoprecipitation with rabbit polyclonal antiserum raised to the COOH-terminal 400 amino acids of ATM in buffer containing 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 2 mM MgCl2, 250 mM KCl, 500 μM EDTA, 100 μM Na3VO4, 10% v/v glycerol, and 0.1% v/v Igepal. ATM-antibody complexes are isolated from nuclear extract by incubating with protein A-Sepharose beads for 1 hour and then through centrifugation to recover the beads. In the well of a 96-well plate, ATM-containing Sepharose beads are incubated with 1 μg of substrate glutathione S-transferase–p53N66 (NH2-terminal 66 amino acids of p53 fused to glutathione S-transferase) in ATM assay buffer [25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 75 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, 50 μM Na3VO4, 500 μM DTT, and 5% v/v glycerol] at 37 °C in the presence or absence of inhibitor. After 10 minutes with gentle shaking, ATP is added to a final concentration of 50 μM and the reaction continued at 37 °C for an additional 1 hour. The plate is centrifuged at 250 × g for 10 minutes (4 °C) to remove the ATM-containing beads, and the supernatant is removed and transferred to a white opaque 96-well plate and incubated at room temperature for 1.5 hours to allow glutathione S-transferase-p53N66 binding. This plate is then washed with PBS, blotted dry, and analyzed by a standard ELISA technique with a phospho-serine 15 p53 antibody. The detection of phosphorylated glutathione S-transferase-p53N66 substrate is performed in combination with a goat antimouse horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody. Enhanced chemiluminescence solution is used to produce a signal and chemiluminescent detection is carried out. |
| 体外活性 | 方法:HCT116 和 U2OS 细胞用 KU-55933 (10 µM) 和 camptothecin (0-10 nM) 处理 16 h,通过 clonogenic assay 检测细胞生存。
结果:KU-55933 (10 µM) 使 p53 功能和功能失调的 HCT116 和 U2OS 细胞对 camptothecin 的敏感性相似。[1]
方法:U2OS 细胞用 IR (5 Gy) 和 KU-55933 (10 µM) 处理 10 min-4 h,通过 Western Blot 检测靶点蛋白表达水平。
结果:p53 (serine 15) 在 10 min 后反应明显,并在电离辐射诱导后持续 4 h。当该实验在 10 µM KU-55933的存在下进行时,电离辐射诱导的 p53 (serine 15) 磷酸化完全不存在。[2] |
| 体内活性 | 方法:为检测体内抗肿瘤活性,将 KU-55933 (1 mg/kg) 腹腔注射给携带 E0771 异种移植物的 C57BL/6 小鼠,每天一次,持续四周。
结果:KU-55933 治疗还通过抑制 GLUT1 易位和波形蛋白表达来抑制小鼠乳腺肿瘤体内的肿瘤生长和转移。[3] |
| 存储条件 | store at low temperature,keep away from moisture | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice/Shipping at ambient temperature. |
| 溶解度 | Ethanol : 19.8 mg/mL (50.06 mM), Sonication is recommended.
DMSO : 16.67 mg/mL (42.15 mM), Sonication is recommended.
10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween 80+45% Saline : 2 mg/mL (5.06 mM), Sonication is recommended.
|
| 关键字 | PI3K | mTOR | KU-55933 | KU55933 | KU 55933 | Inhibitor | inhibit | DNA-PK | DNAPK | Autophagy | ATR | ATM/ATR | ATM and RAD3 related | ATM | Ataxia telangiectasia mutated |
| 相关产品 | Naringin | Guanidine hydrochloride | Gefitinib | Aceglutamide | Alginic acid | Cysteamine hydrochloride | Sodium butanoate | Hyaluronic acid | Hydroxychloroquine | Stavudine | Paeonol | Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate |
| 相关库 | 抑制剂库 | 经典已知活性库 | 抗癌活性化合物库 | 抗癌化合物库 | 已知活性化合物库 | 抗癌细胞代谢库 | 氧化还原化合物库 | 激酶抑制剂库 | 高选择性抑制剂库 | 抗衰老化合物库 | NO PAINS 化合物库 | 免疫/炎症分子化合物库 |