苯唑卡因
Benzocaine
94-09-7
94-09-7
询价
1KG/Bag
起订
湖北 更新日期:2022-01-11
产品详情:
- 中文名称:
- 苯唑卡因
- 英文名称:
- Benzocaine
- CAS号:
- 94-09-7
- 保存条件:
- Store sealed and protected from light.
- 纯度规格:
- 99%
- 产品类别:
- Pharmaceuticals
公司简介
穆雷(武汉)新材料科技有限公司是一家集化工中间体产品研发、生产、销售为一体的科技型企业,专业从事有机中间体、医药中间体、化学溶剂和农药产品的生产。我们生产并提供非那西丁粉、非那西丁蓬松粉、非那西丁晶体、α-溴代戊二酮、缬草酮、西瓜酮和椰油酰氯等。
| 成立日期 | (9年) |
| 注册资本 | 300万元整 |
| 员工人数 | 1-10人 |
| 年营业额 | ¥ 100万以内 |
| 经营模式 | 贸易,工厂 |
| 主营行业 | 医药原料 |
苯唑卡因相关厂家报价 更多
-

- 对氨基苯甲酸乙酯 苯佐卡因 94-09-7 支持试样
- 盼得(上海)国际贸易有限公司 VIP
- 2025-01-21
- 询价
-
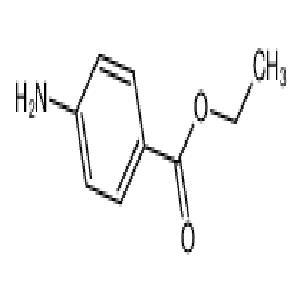
- 苯佐卡因局部麻醉
- 山东宸宜环保科技有限公司 VIP
- 2025-01-21
- 询价
-

- 94-09-7;苯佐卡因
- 普善实业(陕西)有限公司 VIP
- 2025-01-21
- 询价
-

- 对氨基苯甲酸乙酯
- 上海弘顺生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2025-01-21
- ¥1900
-
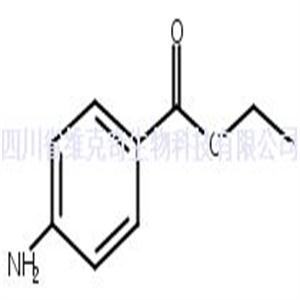
- 4-氨基苯甲酸乙酯 CAS号:94-09-7
- 四川省维克奇生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2025-01-20
- 询价
-

- 苯佐卡因
- 广州远达新材料有限公司 VIP
- 2025-01-20
- ¥120
-

- 苯佐卡因
- 河南仟德药业有限公司 VIP
- 2025-01-20
- ¥255
-

- 苯佐卡因
- 河北陌槿生物科技有限公司 VIP
- 2025-01-20
- 询价
-

- 天山雪莲提取物
- 武汉卡诺斯科技有限公司 VIP
- 2025-01-20
- 询价
-

- 高品质苯佐卡因出售
- 山东强森化工有限公司 VIP
- 2025-01-20
- 询价




