4YR企业会员
发布人:维百奥(北京)生物科技有限公司
发布日期:2026/1/30 14:59:46

Nebulabio is a leading biotechnology company specializing in antibody discovery and engineering, providing end-to-end solutions from early-stage development to preclinical research. With an experienced scientific team and state-of-the-art platforms, we offer expertise in phage display, single B cell screening, and antibody humanization, having successfully supported numerous therapeutic candidates into clinical stages.
✍Our Phage Display Platform
Phage display is a powerful in vitro selection technology that enables the rapid identification of high-affinity antibody fragments against specific targets by displaying them on the surface of bacteriophages. Our comprehensive platform covers custom library construction, diversified screening strategies, and pre-made library screening to accelerate your antibody discovery projects.
✍ Supported Antibody Formats:
◆ Fab Libraries: Maintain full-length antibody structure for optimal antigen recognition and function.
◆ scFv Libraries: Single-chain variable fragments offering smaller size, better tissue penetration, and ease of genetic manipulation.
◆ VHH/Nanobody Libraries: Derived from camelids, these single-domain antibodies provide superior stability, solubility, and unique epitope access.
◆ Pre-made Libraries: Ready-to-screen libraries constructed from naïve, immune, or synthetic repertoires to expedite project timelines.
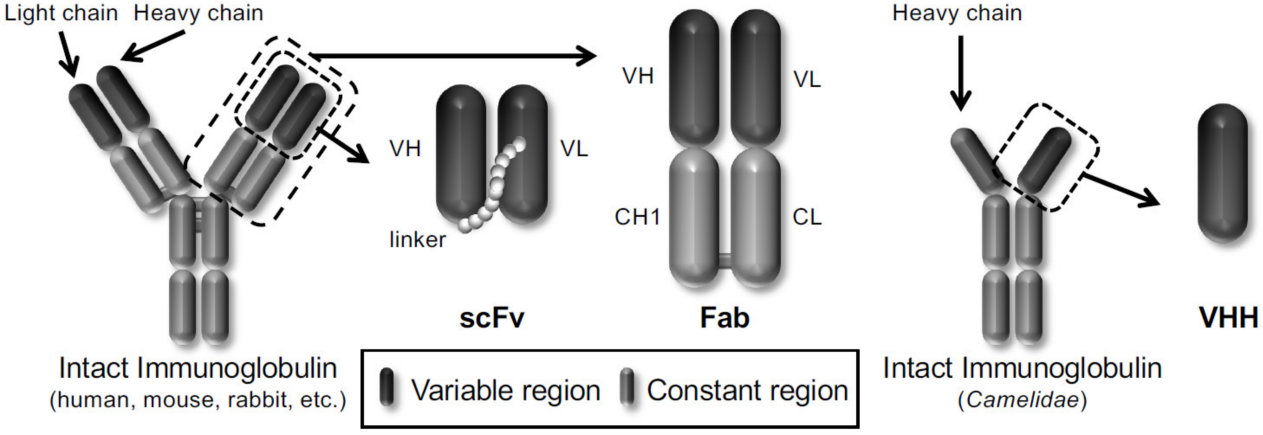
Figure 1.Schematic representation of different types of antibody formats displayed on the phages.
(Nagano, K.; Tsutsumi, Y. Phage Display Technology as a Powerful Platform for Antibody Drug Discovery. Viruses 2021, 13, 178. )
✍ Principle of phage display
Phage display technology allows the construction of libraries in which various peptides and proteins are displayed on the phages, and then the most suitable clone is selected from the library by in vitro panning. Therefore, the clones with an affinity for the target of interest or those with the ability to migrate to the target tissue are enriched from the library. Therefore, the development of phage display technology provides optimal sequences to target peptides or proteins, unlike conventional alanine scanning and other methods, and aids understanding of their molecular evolution.
✍ Our Service Workflow
1. Phage Display Library Construction
We deliver high-quality custom antibody libraries tailored to your project needs.Key Steps:
▸ Project Design: Select antibody format (Fab/scFv/VHH) and library strategy .
▸ Genetic Material Sourcing: RNA extraction from immunized spleen cells, PBMCs, or synthetic gene synthesis.
▸ Library Assembly:PCR amplification → Cloning into phage vector → Electroporation into host cells → Primary library expansion
▸ QC & Validation:Library size determination (typically 10^9–10^11 CFU); Diversity assessment via random clone sequencing; Insert rate and frame correctness verification
2. Phage Display Library Screening
We employ optimized panning protocols to isolate specific binders from custom or pre-made libraries.
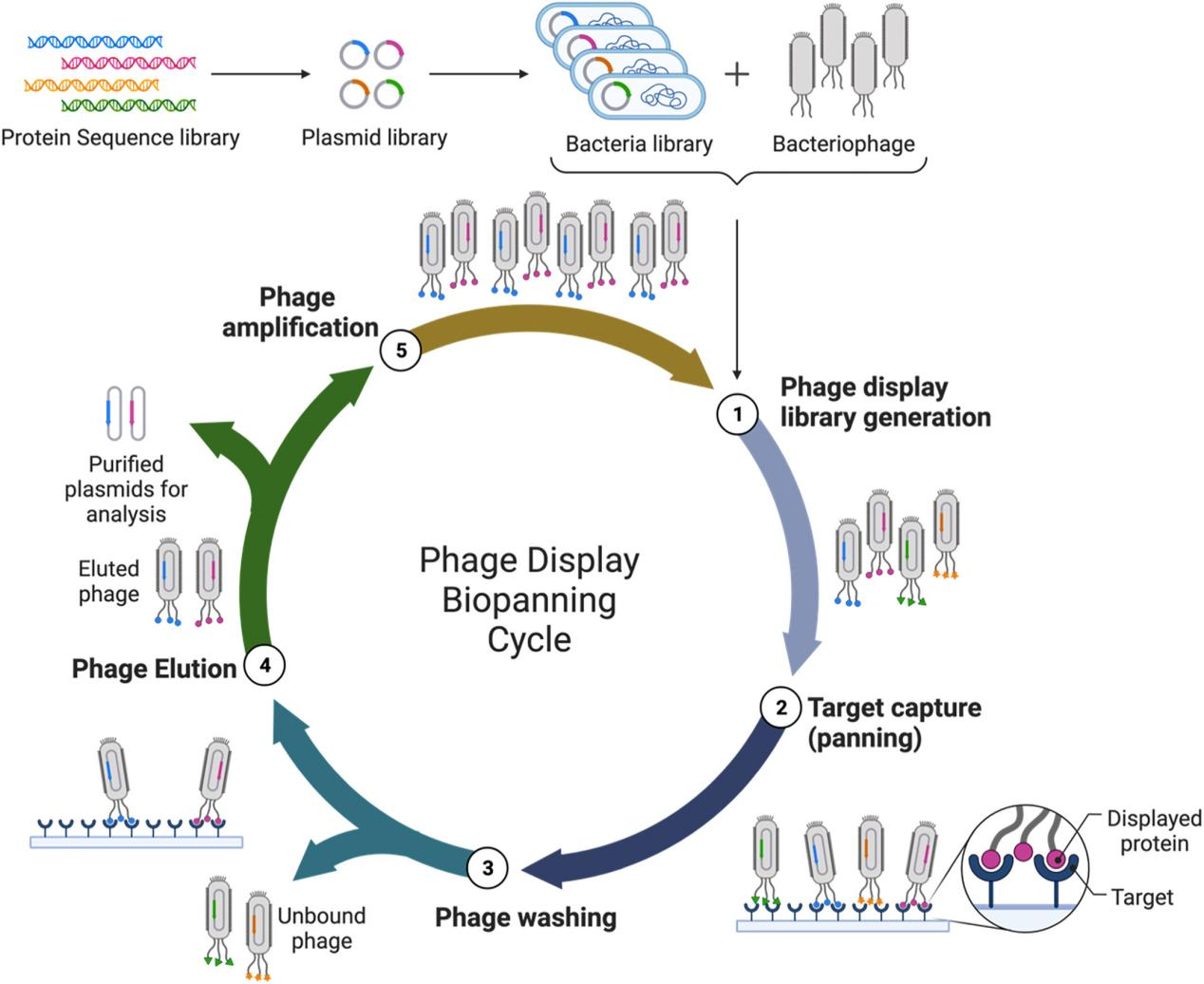
Figure 2. Phage Display Biopanning Cycle. Step 1, phage display libraries are prepared. Step 2, initial capture assessment of target performed. Step 3, the unbound phage washed off the target substrate. Step 4, the bound phage is eluted from the target substrate. Step 5, viral amplification of the eluted phage. Steps 2 through 5 repeated to determine high-affinity phage display peptides.
(L.Tian, K. Jackson, M. Chan, A. Saif, L. He, T. Didar, Z. Hosseinidoust,Smart Med.2022,1(1), e20220015.)
✍ Featured Applications of Phage Display
1. Therapeutic Antibody Discovery
▸ Lead Candidate Identification: Rapidly discover fully human antibodies against novel drug targets, including difficult targets like GPCRs, ion channels, and intracellular antigens.
▸ Antibody Humanization & Optimization: Convert murine or other non-human antibodies into humanized or human versions with reduced immunogenicity. Perform in vitro affinity maturation to enhance binding strength and therapeutic potency.
▸ Bispecific & Multispecific Antibodies: Engineer antibodies that can engage two or more different targets simultaneously, enabling novel mechanisms of action for cancer immunotherapy and beyond.
2. Diagnostic & Detection Reagent Development
▸ Immunoassay Antibodies: Select pairs of antibodies (matched antibody pairs) with high specificity and affinity for developing sensitive ELISA, lateral flow assays, and other diagnostic tests.
▸ Imaging & Biosensor Probes: Develop antibody fragments (like VHHs) for in vivo imaging (e.g., PET, SPECT) due to their excellent tissue penetration and rapid clearance. Create stable binders for integration into biosensor platforms.
3. Cell & Gene Therapy Targeting
▸ CAR-T Cell Targeting Domains: Discover and optimize single-chain variable fragments (scFvs) that serve as the antigen-recognition domain of Chimeric Antigen Receptors (CARs), crucial for next-generation cancer therapies.
▸ Targeted Drug Delivery: Identify ligands that specifically bind to markers on target cells (e.g., tumor cells), enabling the development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) or other targeted delivery systems
4. Protein Engineering & Epitope Mapping
▸ Affinity Reagent Generation: Create high-quality binders to any protein of interest for use in pull-down assays, Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and functional inhibition studies.
▸ Epitope Mapping & Characterization: Define the precise binding site (epitope) of an antibody on its target antigen, which is critical for understanding mechanism of action, patent protection, and biosimilar development.
▸ Protein Interaction Studies: Map protein-protein interaction interfaces to understand signaling pathways and identify sites for therapeutic intervention.
5. Vaccine & Infectious Disease Research
▸ Antigen Identification: Use phage display libraries to identify peptides or antibody fragments that bind to neutralizing antibodies from convalescent patients, helping to pinpoint protective epitopes for vaccine design.
▸ Antiviral & Antimicrobial Agents: Discover antibody fragments that neutralize viruses or target bacterial surface proteins, offering potential pathways for novel anti-infective therapies.
相关新闻资讯