1/2
ASP-ARG-VAL-TYR-ILE-HIS-PRO NEW
- Min. Order1KG
- Purity98%
- Cas No51833-78-4
- Supply Abilityg-kg-tons, free sample is available
- Update time2025-09-25
| Product Name | ASP-ARG-VAL-TYR-ILE-HIS-PRO |
| CAS No | 51833-78-4 |
| EC-No | |
| Min. Order | 1KG |
| Purity | 98% |
| Supply Ability | g-kg-tons, free sample is available |
| Release date | 2025/09/25 |
1. Materials information
Names
| Name | Angiotensin (1-7) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
Biological Activity
| Description | Angiotensin (1-7) inhibits purified canine angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activity with an IC50 of 0.65 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | Signaling Pathways >> GPCR/G Protein >> Angiotensin Receptor Signaling Pathways >> Metabolic Enzyme/Protease >> Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE) Research Areas >> Cardiovascular Disease Peptides |
| Target | IC50: 0.65 μM (ACE)[1] |
| In Vitro | Angiotensin 1-7 (Ang 1-7) acts as a local synergistic modulator of kinin-induced vasodilation by inhibiting ACE and releasing nitric oxide (NO). Angiotensin (1-7) augments the vasodilation induced by bradykinin (BK) in a concentration-dependent manner in rings preconstricted with the thromboxane analog U46619. The EC50 of BK (2.45±0.51 nM versus 0.37±0.08 nM) is shifted leftward by 6.6-fold in the presence of 2 μM concentration of Angiotensin (1-7). The BK-induced relaxation response is augmented by Angiotensin (1-7) (0.1 to 2 μM) in a dose-dependent manner. At a concentration of 2 μM Angiotensin (1-7), relaxation to BK is increased 92% compared to BK alone (41±4.4% versus 92±2.5%, P<0.01). Angiotensin (1-7) possesses novel biological functions that are distinct from Ang II. In contrast to Ang II, Angiotensin (1-7) is not a dipsogen or an aldosterone secretagogue, but similar to Ang II, it stimulates the release of vasopressin, prostaglandins, and NO. Angiotensin (1-7) counteracts several actions of Ang II. In both canine and porcine coronary arteries, Angiotensin (1-7) causes vasodilation, while Ang II divergently constricts the coronary arteries. Angiotensin (1-7) inhibits cultured vascular smooth muscle cell growth, whereas equal molar concentration of Ang II stimulates cell growth[1]. Angiotensin 1-7 (Ang 1-7) abrogates the methylglyoxal-modified albumin (MGA)-stimulated myofibroblast phenotype by inhibiting the chronic stimulation of the TGF-β-ERK pathway in NRK-52E cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | A seven fold decrease in the plasma level of Angiotensin 1-7 (Ang 1-7) is demonstrated in dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) treated mice compare to untreated (UT) group at day 7 post colitis induction. On the other hand, a significant increase in Ang 1-7 is observed in colon homogenates of DSS treated mice at day 7 (0.09 ng/mL) compare to UT mice (0.04 ng/mL)[3]. The ovariectomized (OV) female Wistar-rats receive estradiol (500 μg/kg/week) or vehicle for two weeks. The animals are anesthetized, cannulated, and the responses including mean arterial pressure, renal blood flow (RBF), and renal vascular resistance at the constant level of renal perfusion pressure to graded infusion of Angiotensin 1-7 (Ang 1-7) at 0, 100 and 300 ng/kg/min are determined in OV and OV estradiol-treated (OVE) rats, treated with vehicle or MasR antagonist; A779. RBF response to Ang 1-7 infusion increased dose-dependently in vehicle (Pdose<0.001) and A779-treated (Pdose<0.01) animals. However, when MasR is blocked, the RBF response to Ang 1-7 significantly increases in OV animals compare with OVE rats (P<0.05). When estradiol is limited by ovariectomy, A779 increases RBF response to Angiotensin (1-7) administration, while this response is attenuated in OVE animals[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | Competition assays using purified canine ACE are determined using a fixed concentration of the substrate Hip-His-Leu (1 mM) and varying the concentrations of the competing agents [Lisinopril (0.1 to 100 nM), Angiotensin (1-7) (10 nM to 10 μM), or Sar1, Thr8-Ang II (10 nM to 10 μM)]. Inhibitory constants (IC50) are determined from the respective competition curves. To study the effect of Angiotensin (1-7) on BK metabolism in intact coronary rings, 125I-[Tyr0]-BK (final concentration of 1 nM) is added to the tubes containing three rings preincubated with 1 mL Krebs' buffer and aerated with 95% O2 and 5% CO2 at 37°C. Lisinopril (2 μM), Angiotensin (1-7) (2 μM), or Krebs' buffer as control are added to the rings 10 minutes before addition of the radiolabeled BK. Aliquots of the incubation medium are removed at 5, 10, and 20 minutes and diluted with 1% HFBA to inhibit peptidase activity[1]. |
| Cell Assay | 500 μM Methylglyoxal is incubated with 100 μM BSA dissolved in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for 24 hours, then washed on 10 kDa filters to remove excess methyl glyoxal, reconstituted with DMEM/F12 serum free media and passed through a 0.2 μmicron filter. TGF-β (5 ng/mL) is prepared to treat cells in a subset of experiments. Cells are co-treated with one or combinations of the following: Angiotensin (1-7) (100 nM), D-Ala7-Ang-(1-7) (10 μM), ERK1/2 kinase inhibitor, PD 98059 (1 μM), TGF-β receptor kinase inhibitor; SB525334 (1 μM), the AT1 receptor antagonist Losartan (1 μM), the renin inhibitor Aliskerin (1 μM) and the ACE inhibitor Lisinopril (1 μM)[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Male and female BALB/c mice (1:1 ratio, 6-10 weeks old, mean weight 20 g.) are used. Angiotensin fragment 1-7 acetate salt hydrate (Ang 1-7) is dissolved in 0.9% saline (vehicle) at 1 mg/mL and stored at -80°C. Various doses (0.01, 0.06, 0.1, 0.3 and 1 mg/kg) are freshly prepared from the stock each day of the experiment, and administered to mice by daily intra-peritoneal (i.p) injections in a volume of 500 μL per injection, either before (prophylactic approach) or after (treatment approach) DSS treatment. A779 (MAS-1 R antagonist) is similarly dissolved in distilled water at 1 mg/mL and stored at -80°C. A freshly prepared dose of 1 mg/kg is administered to a second group of mice by daily i.p injections in a volume of 500 μL daily (for 4 days) along with colitis induction (prophylactic approach). A third group of mice receive DSS containing water and daily i.p injections of 0.9% saline (vehicle). The fourth group receive DSS containing water along with daily i.p injections with Dexamethasone (DEX) at doses of 0.01-1.0 mg/kg or its vehicle (0.9% saline) (prophylactic approach). Rats[4] Twenty six ovariectomized female Wistar rats weighing 200±20 g are used. Angiotensin (1-7) is administered intravenously by a microsyringe pump at two different continuous doses of 100 and 300 ng/kg/min after antagonist/saline infusion. Each dose is infused for 15 min; and MAP, RPP, and RBF are recorded during Angiotensin (1-7) infusion and the last 3-5 min of each dose measured as “response to Angiotensin (1-7) infusion”. During Angiotensin (1-7) infusion, RPP is sustained at pre-Ang1-7 infusion levels via an adjustable aortic clamp. At the end of the experiment, the rats are humanely killed by anesthetic overdose, and the left kidneys are removed and weighed immediately. |
| References | [1]. Li P, et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) augments bradykinin-induced vasodilation by competing with ACE and releasing nitric oxide. Hypertension. 1997 Jan;29(1 Pt 2):394-400. [2]. Alzayadneh EM, et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) abolishes AGE-induced cellular hypertrophy and myofibroblast transformation via inhibition of ERK1/2. Cell Signal. 2014 Sep 19. pii: S0898-6568(14)00314-3. [3]. Khajah MA, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Action of Angiotensin 1-7 in Experimental Colitis. PLoS One. 2016 Mar 10;11(3):e0150861. [4]. Saberi S, et al. Role of Mas receptor in renal blood flow response to angiotensin-(1-7) in ovariectomized estradiol treated rats. Res Pharm Sci. 2016 Jan-Feb;11(1):65-72. |
Chemical & Physical Properties
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C41H62N12O11 |
| Molecular Weight | 899.005 |
| Exact Mass | 898.466125 |
| PSA | 377.24000 |
| LogP | 0.24 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.666 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
Safety Information
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|---|
Synthetic Route
Total: 1 Page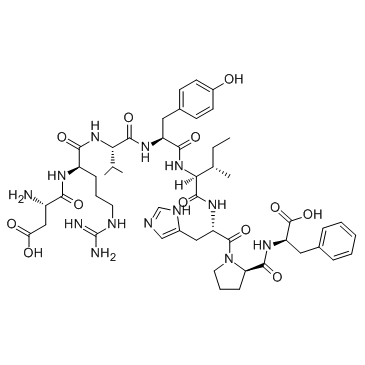 Angiotensin II ... CAS#:4474-91-3 ~% 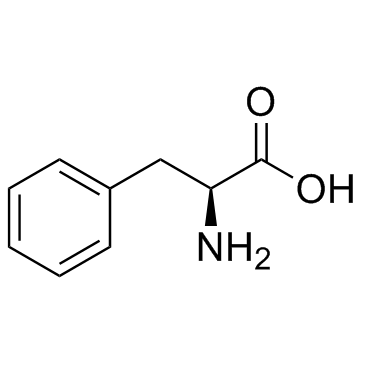 L-Phenylalanine CAS#:63-91-2 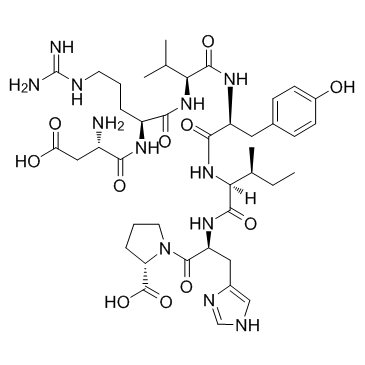 Angiotensin I/I... CAS#:51833-78-4 |
| Literature: Umetsu, H.; Ichishima, E. Phytochemistry (Elsevier), 1983 , vol. 22, # 2 p. 591 - 592 |
Precursor & DownStream
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| |
2. Packaging of materials
For powders: normal is 25kgs/Drum or bag, or larger/smaller package as request.
For liquids: normal 25kgs/drum, 180-300kgs/bucket, or IBC, determined by the nature of the product.
Or smaller package 1kg/bottle, 10kgs/bottle as request.


3. Shipping & Delivery
By Express
Provide door to door service
Suitable for goods under 50kg
Delivery: 3-7 days
Cost: low cost

By Air
Provide airport to airport service
Suitable for goods over 50kg
Delivery: 3-14 days
Cost: high cost

By Sea
Provide seaport to seaport service
Suitable for goods over 100kg
Delivery: 2-45 days
Cost: low cost

4. Contact information
For more details, pls contact us freely.
Email address: Tina@fdachem.com
Mob: 86 15225627621
WhatsApp/Skype/Wechat/LINE: 86 15225627621
Company Profile Introduction
Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd. is located in the High-tech Development Zone of Henan Province. Specializing in the production and sales of various fine chemical products required for industrial production, including chemical raw materials, organic raw materials, petrochemicals, chemical reagents, solvents, catalysts, and additives, etc.


 China
China

