| Product features |
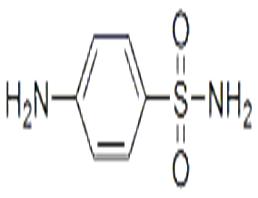
Sulfanilamide is an organic sulfur compound structurally similar to p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) with antibacterial property. Sulfanilamide competes with PABA for the bacterial enzyme dihydropteroate synthase, thereby preventing the incorporation of PABA into dihydrofolic acid, the immediate precursor of folic acid. This leads to an inhibition of bacterial folic acid synthesis and de novo synthesis of purines and pyrimidines, ultimately resulting in cell growth arrest and cell death.Without it, bacteria cannot replicate.
- Mechanism of action: mechanism of action is to interfere with the synthesis of nucleic acids required for pathogenic microorganisms,making bacteria lack of nutrition and stop the growth, development and reproduction, having suppression killing effect on hemolytic streptococcus, staphylococcus and meningococcal.
- Pharmacodynamics: Oral easily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, widely distributed in the body, can penetrate the blood-brain barrier into the brain tissue, and can penetrate the placental barrier into the fetus. Rapid excretion, mainly excreted in metabolites from kidney.
- Clinical application: Mainly used for trauma infection caused by infection hemolytic streptococcus, staphylococcus, and local wound infections.
- Uses: Sulfanilamide is lower toxicity in sulfa drugs, can be applied for infants, pregnant women, pregnant women and during menstruation, but not in large doses. Having effects on hemolytic streptococcal infection (erysipelas, puerperal fever, tonsillitis), urinary tract infection (gonorrhea) and so; also the intermediate for synthesis of other sulfa drug (such as sulfa amidine, pyrimidine and sulfamethoxazole sulfa methoxy-triazine, etc. ).
|
| Chemical properties |
White granular or crystalline powder, odorless. Slightly bitter taste. Slightly soluble in water, ethanol, methanol, ether and acetone, soluble in boiling water, glycerol, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide solution, insoluble in chloroform, ether, benzene, petroleum ether. |
| Uses |
- Sulfanilamide is the main raw material for the synthesis of sulfa drugs.
- Used as a reagent to determine nitrite, also used in the pharmaceutical industry.
- Used as intermediates for the synthesis of other sulfa drugs, even for wound disinfection.
- Amino benzene sulfonamide is intermediate of herbicide asulam, as well as intermediate of sulfa medicine.
- Veterinary medicine, topical anti-inflammatory drugs, for analysis and detection.
- Wide spectrum antibacterial, having antibacterial effects on hemolytic streptococcus, Neisseria meningitidis, Staphylococcus aureus and other Gram-positive and negative bacteria. This product is topical application, it can be partially absorbed from the wound. For trauma infections of hemolytic streptococcus and staphylococcus. It can also be used to quickly stop the bleeding wound.
|
| Production methods |
There are several methods for their preparation.
1. Acetyl aniline used as raw material
The acetanilide reacts with chlorosulfonic acid at 40~50 ℃, and then cooled slowly, added to water for acid decomposition, while precipitation, dried and filtered to give acetaminophen chloride and ammoniated, ammoniated temperature is controlled at 40~45 ℃, hydrolysis, acidification.
2. Method of mixed diphenyl urea
Condensation of aniline and urea is single-phenylurea and diphenyl urea (called mixed urea), and then obtained from chlorosulfonated, amination, hydrolysis, acid precipitation. The reaction procedure is as follows.
(1)Condensation condensation of aniline hydrochloride and urea, at a temperature of 101~110 ℃ reaction for 3~4 h, obtaining mixed diphenyl urea.
(2)Chlorosulfonated Chlorine acid is pressed into the sulfonated pot, stirring cooling, when the temperature drops below 10 ℃, uniformly added mixed phenyl urea under stirring, the reaction temperature is gradually increased, the addition is completed, at the 46~50 ℃ insulation and mixing for 2 h, cooled to below 10 ℃, added water for acid decomposition. Controlling that the decomposition temperature does not exceed 15 ℃, after the addition of water continued stirring for 20min, then by precipitation, washed with water, obtaining mixed phenylurea chloride.
(3)Ammoniated 2% aqueous ammonia is put into ammoniated pan, cooled to 25 ℃, stirring and added into a mixing phenyl urea chloride, control the temperature at 40 ℃, insulation and reaction for 3h, obtaining ammoniated liquid.
(4)Hydrolysis and neutralization The amide is heated up to 90 ℃, is added 3% lye, continue to heat 108~112 ℃, hydrolysis for 5 h, and moved in the crystallization pot, added hydrochloric acid to neutralize crystals and the crystals are cooled to 20 ℃, crystallization, filtration, washed with water, dry, products are obtained. |
| Uses |
The active metabolite of the antibacterial dye, Sulfamidochrysoidine. Inhibits folic acid synthesis in prokaryotes. Antibacterial. |
| General Description |
White powder. pH of 0.5% aqueous solution: 5.8-6.1. |
| Air & Water Reactions |
May be unstable if exposed for long periods air and light . Slightly water soluble. |
| Reactivity Profile |
Sulfanilamide is an amino acid. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. May react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. |
| Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for Sulfanilamide are not available but Sulfanilamide is probably combustible. |

 China
China