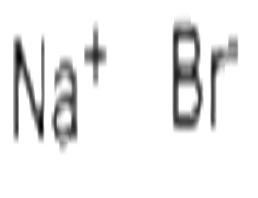| Physical and chemical properties |
At room temperature, sodium bromide is a colorless cubic crystal or white granular powder, and belongs to isometric system. It is odorless, and has slightly bitter and briny taste but high toxicity. It is easily to absorb moisture and caking but without deliquescence. It is slightly soluble in alcohol and easily soluble in water (at 100 °C, the solubility in 100ml water solubility is 121g), its aqueous solution is neutral with electronic conductivity. The anhydrous sodium bromide crystal will be precipitated out at 51°C with dihydrate compound forming at temperature lower than 51 °C. Its bromide ion can be substituted by fluorine, and chlorine. Under acidic conditions, it can be oxidized by oxygen and release free bromine; this process is taken advantage of by industry for producing bromine. It can have reaction with dilute sulfuric acid to produce hydrogen bromide. However, hydrobromic acid is a strong acid which can’t be produced through the reaction with dilute sulfuric acid and can only made through high-boiling point acid to make low-boiling point acid. However, we should avoid to use concentrated sulfuric acid which has strong oxidation effect and thus converting bromine (-1) into bromine element and release reddish-brown gas. This method can be used to identify sodium iodide (Heating sodium iodide and concentrated sulfuric acid together will release red-purple gases), Thereby, we can only take the concentrated phosphoric acid together with sodium bromine for heating to produce hydrogen bromine.
Bromide ions can enhance the inhibitor process of brain cortex, and promote their concentration. Therefore, medically it can be used as tranquilizers, and hypnotic or anticonvulsant drugs. When human swallow or inhale the compounds, it will cause harm to central nervous system, brain, and eye while causing irritation response of skin, eyes and also the respiratory tract. |
| Solubility in water (g/100ml) |
Solubility (grams) per 100 ml of water at different temperatures:
80.2g/0 ℃; 85.2g/10 ℃; 90.8g/20 ℃; 98.4g/30 ℃; 107g/40 ℃
118g/60 ℃; 120g/80 ℃; 121g/90 ℃; 121g/100 ℃ |
| Toxicity |
We should prevent its ingestion and inhalation; avoid the contact of eye and skin with it. If intake or inhalation happens, adverse reactions include dizziness, nausea, and vomiting can occur. In these cases, we should immediately consult a doctor for treatment. Upon being splashed in the eyes, we should immediately rinse with fresh water for 20 min; upon skin contact with sodium bromide, we should also rinse with plenty of water.
The above information is edited by the chemicalbook of Dai Xiongfeng. |
| Chemical Properties |
Sodium bromide is a colorless cubic crystal or white granular powder. It is odorless, and has slightly bitter and briny taste but high toxicity. It is easily soluble in water (at 100 °C, the solubility in 100ml water solubility is 121g), but slightly soluble in alcohol. |
| Uses |
1. It can be used as raw material in the preparation of liquid photographic film; medically as sedative, the brominating agent in printing and dyeing; it can also be used in synthetic fragrances and other chemicals.
2. Photographic industry applies it for the preparation of liquid photosensitive film. It is medically used for the production of diuretics and sedatives. Perfume industry uses it for the production of synthetic fragrances. Printing and dyeing industry use it as a brominating agent. In addition, it can be also be used for organic synthesis and so on.
3. It is used for the photographic industry, spices, pharmaceutical and printing industries.
4. It is used for the reagents for analysis, and can also be used for the synthesis of inorganic and organic compounds and pharmaceutical industry.
5. It is sued for photographic film, medicines, perfumes, dyes and other industries.
6. It can be applied to determination of trace cadmium and Manufacturing of bromide. It can also be applied to inorganic and organic synthesis, photogravure and pharmaceuticals. |
| Production method |
Urea reduction: dissolve soda ash (sodium carbonate), urea in hot water, and fed into the reactor; gradually add bromine for reaction and generate sodium bromide. Then further add active carbon for decolorization; further undergo filtration, evaporation, crystallization, centrifugal separation, and drying to obtain sodium bromide products. The reaction is as following:
3Br2 + 3Na2CO3 + NH2CONH2 → 6NaBr + 4CO2 ↑ + N2 ↑ + 2H2O
Neutralization method: add about 40% hydrobromic acid into the reactor, stir and slowly add 40% caustic solution for neutralization to Ph 7.5~8 for generating sodium bromide; after isolated by centrifugation, evaporation, crystallization and centrifuged again separation, then we can obtain the final product of sodium bromide. the reaction is:
HBr + NaOH → NaBr + H2O |
| Chemical Properties |
white powder |
| Definition |
ChEBI: An inorganic sodium salt having bromide as the counterion. |
| Uses |
In photography. |

 China
China