| Thyroid cancer drugs |
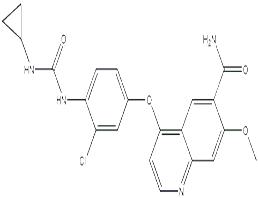
Lenvatinib is a thyroid cancer drug developed by Eisai Corporation of Japan (Code: E7080), belonging to the inhibitor of oral multi-receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) and can inhibit the kinase activity of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) Receptors VEGFR1 (FLT1), VEGFR2 (KDR), and VEGFR3 (FLT4). Lenvatinib can also inhibit the involvement of other RTKs in pathological angiogenesis, tumor growth, and cancer progression except for their normal cellular functions including fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptors FGFR1, 2, 3, and 4; platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR [alpha]), KIT, and RET.
[Indications]: Lenvatinib is suitable for the treatment of patients of thyroid cancer of local recurrence or metastasis type, progressivity type and radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated type.
On February 13, 2015, the US FDA approved anticancer drug Lenvatinib for the treatment of thyroid cancer. Lenvatinib is a multi-target enzyme inhibitor, being capable of inhibiting the VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor). The trade name of Lenvatinib is Lenvima.
On May 20, 2015, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) approved Lenvatinib for the treatment of invasive, locally advanced or metastatic differentiated (papillary, follicular, Hurthle type) thyroid cancer (DTC). In the trial, the median survival time for patients of radioactive iodine-refractory DTC treated with Lenvatinib was 18 months while the value for patients who take placebo is only 3 months.
In Europe, Lenvatinib will compete with Bayer's kinase inhibitor sorafenib (trade name: Nexavar), which had been respectively approved by EMA and the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of radioactive iodine refractory DTC in 2014 and 2013, respectively. At the time, Sorafenib had been reported to be the first targeted therapeutics to be marketed for the past 40 years in the treatment of refractory DTCs. The marketing applications of Lenvatinib in Switzerland, South Korea, Canada, Singapore, Russia, Australia and Brazil are also under review.
Information regarding the pharmacological effects, clinical evaluation, and indication of the thyroid cancer drug Lenvatinib were compiled and edited by Tongtong from Chemicalbook (2015-09-22). |
| Biological activity |
Lenvatinib (E7080) is a multi-target inhibitor with the most potent effect on VEGFR2 (KDR)/VEGFR3 (Flt-4) with an IC50 of 4 nM/5.2 and weaker effect on VEGFR1/Flt-1. The selectivity of targeting on VEGFR 2/ 3 is about 10 times as high as that of targeting on FGFR1 and PDGFRα/β. Phase 3. |
| In vitro study |
E7080 can effectively inhibit the angiogenesis, also significantly inhibit the VEGF/KDR and SCF/KIT signaling pathway. Based on the in vitro receptor tyrosine and serine/threonine kinase assays, the IC50 of E7080 in inhibiting Flt-1, KDR, and Flt-4 were 22, 4.0 and 5.2 nM, respectively. In addition to these kinases, E7080 can also inhibit FGFR1 and PDGFR tyrosine kinases, acting on FGFR1, PDGFRα and PDGFRβ with IC50 values of 46, 51 and 100 nM, respectively. When E7080 acted respectively on HUVECs stimulated by VEGF and VEGF-C, respectively, and effectively inhibit VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 phosphorylation with IC50 of 0.83 nM and 0.36 nM, respectively. Recent studies have shown that treatment with 1 μM and 10 μM and E7080, through inhibiting the FGFR and PDGFR signaling pathway, can significantly inhibit cell migration and invasion. |
| In vivo studies |
Orally administration of E7080 at a dose of 30 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg for the treatment of H146 xenograft tumor model can inhibit the tumor growth in a dose-dependent manner. At 100 mg/kg, it can result in tumor regression. Moreover, treatment with a dose of 100 mg/kg of E7080, compared with the VEGF antibody and Imatinib treatment, can reduce the microvascular density more. |
| Feature |
E7080 is an orally active multi-target kinase inhibitor. |
| Uses |
E7080 (Lenvatinib) is a multi-target inhibitor of VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 with IC50 of 4 nM and 5.2 nM, respectively. |
| Definition |
ChEBI: A member of the class of quinolines that is the carboxamide of 4-{3-chloro-4-[(cyclopropylcarbamoyl)amino]phenoxy}-7-methoxyquinoline-6-carboxylic acid. A multi-kinase inhibitor and orphan drug used (as its mesylate salt) for the treatment of various types of thyroid cancer that do not respond to radioiodine. |

 China
China