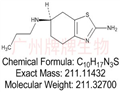
Pramipexole (Item No. 11981) is an agonist of dopamine receptors that has applications in Parkinson’s disease and other disorders. Pramipexole is usually available as a mixture of enantiomers, with the majority of the dopamine receptor-dependent activity resulting from the (S) form. (R)-Pramipexole is an enantiomer of pramipexole that is ~100-fold less active than the (S) form as a dopamine receptor agonist. For this reason, it can be used as a negative control for the (S) form in the study of dopamine receptors. Both isoforms are antioxidants that target mitochondria to prevent apoptosis. This cytoprotective effect of (R)-pramipexole, without dopaminergic side effects, suggests utility in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
(R)-Pramipexole Dihydrochloride (Pramipexole EP Impurity D; Pramipexole BP Impurity D; Pramipexole USP Related Compound D) is the opposite enantiomer of Pramipexole (P700755), a dopamine-D2-receptor agonist. Dexpramipexole is a low-molecular-weight, water-soluble, orally bioavailable, renally excreted compound with linear pharmacokinetics.
These Secondary Standards are qualified as Certified Reference Materials. These are suitable for use in several analytical applications including but not limited to pharma release testing, pharma method development for qualitative and quantitative analyses, food and beverage quality control testing, and other calibration requirements. Pramipexole may be used as a secondary pharma standard for the determination of the analyte in pharmaceutical formulations using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and ultraviolet spectrophotometry technique.
Pharmaceutical secondary standards for application in quality control provide pharma laboratories and manufacturers with a convenient and cost-effective alternative to the preparation of in-house working standards. Pramipexole Related Compound D is a pharmaceutical impurity of pramipexole. Pramipexole is a non-ergot dopamine receptor agonist, widely used in the treatment of Parkinson′s disease.
R-(+)-Pramipexole is a neuroprotective agent; weak non-ergoline dopamine agonist. R-(+)-Pramipexole has been found to have neuroprotective effects and is being investigated for treatment of ALS. It reduces mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, inhibits the activation of apoptotic pathways, and increase cell survival in response to a variety of neurotoxins and β-amyloid neurotoxicity. Compared to the S-(-) isomer, R-(+)-Pramipexole has much lower dopamine agonist activity.