BETA- AMYLOID (1-16)
BETA- AMYLOID (1-16) 性质
| 密度 | 1.57±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
|---|---|
| 储存条件 | -15°C |
| 溶解度 | 溶于二甲基亚砜 |
| 形态 | 固体 |
| 颜色 | 白色至米白色 |
| 水溶解性 | Soluble in water or aqueous buffer |
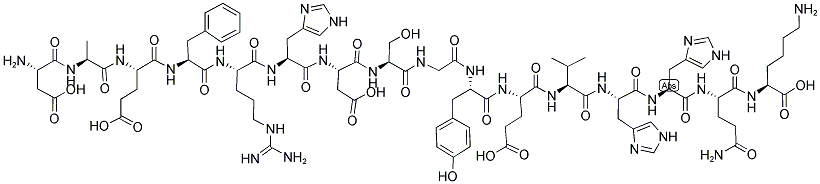
| 序列 | H-Asp-Ala-Glu-Phe-Arg-His-Asp-Ser-Gly-Tyr-Glu-Val-His-His-Gln-Lys-OH |
BETA- AMYLOID (1-16) 用途与合成方法
Amyloid-β
β-amyloid (1-16) fragment is considered as valid models to examine the contribution of the key histidine residues (His , His in mouse and His , His , His in human fragments) to the Ab–Cu 2+ interaction. Oxidation targets for β-Amyloid (1-16) are the histidine residues coordinated to the metal ions. Copper is bound to Aβ in senile plaque of Alzheimer’s disease with β-Amyloid (1-16) taking part in the coordination of the Cu 2+ ions. Cu 2+ and Zn 2+ are linked with the neurotoxicity of -Amyloid and free radical damage. β-amyloid (1-16) is the minimal amino acidic sequence display a Cu coordination mode which involves three Histidines (His6, His13 and His14). β-amyloid (1-16) is supposed to be involved in metal binding. Human β-amyloid interacts with zinc ions through its metal-binding domain 1-16. The C-tails of the two polypeptide chains of the rat Aβ(1-16) dimer are oriented in opposite directions to each other, which hinders the assembly of rat Aβ dimers into oligomeric aggregates. Thus, the differences in the structure of zinc-binding sites of human and rat β-Amyloid (1-16), their ability to form regular cross-monomer bonds, and the orientation of their hydrophobic C-tails could be responsible for the resistance of rats to Alzheimer's disease.
纯度(HPLC) ≥98.0%
醋酸根含量5.0%~12.0%
水分含量≤8.0%
肽含量≥80.0%
BETA- AMYLOID (1-16) 价格(试剂级)
| 更新日期 | 产品编号 | 产品名称 | CAS号 | 包装 | 价格 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025-12-22 | HY-P1466 | BETA- AMYLOID (1-16) | 131580-10-4 | 1mg | 1100 |
| 2025-12-22 | HY-P1466 | BETA- AMYLOID (1-16) | 131580-10-4 | 5mg | 3900 |

