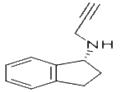
Rasagiline is a selective and irreversible propargylamine inhibitor of monoamine oxidase (MAO) B (IC50s = 4.43 and 412 nM for MAO-B and MAO-A, respectively) that has been used to increase the availability of dopamine at striatal receptors as a strategy to treat Parkinson’s disease. Rasagiline is metabolized by hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP)-1A2 to the neuroprotective compound aminoindan. In PC-12 and neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells, rasagiline exhibits neuroprotective and antiapoptotic activity against ischemia and several neurotoxins, including SIN-1, MPTP, 6-hydroxydopamine, and N-methyl-(R)-salsolinol.