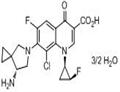
The fluoroquinolone antibacterial agent sitafloxacin hydrate
was developed by Daiichi Sankyo and was approved
and launched last year in Japan. Sitafloxacin’s mode of action
is through inhibition of DNA gyrase and topoisomerase
IV. It is indicated for the treatment of inflammatory infections
such as laryngopharyngitis, adenoiditis, acute bronchitis,
pneumonia, secondary infections due to chronic respiratory
lesions, cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis, cervicitis,
otitismedia, sinusitis, periodontitis, and pericoronitis and jaw
inflammation. Due to its broad spectrum of potent antibacterial
activity, sitafloxacin is expected to be clinically effective
in treating severe cases of bacterial infection, relapse/recrudescence of infection and infections in which resistant
bacteria are suspected to be the cause.