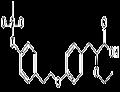
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are activated by fatty acids and eicosanoids as well as antidyslipidemic agents. Among the receptor isotypes, PPARα demonstrates a particular role in fatty acid oxidation whereas PPARγ is known to be involved in adipocyte differentiation and lipid storage. Tesaglitazar, a dihydro cinnamate derivative, is a dual agonist of PPARα and γ that demonstrates IC50 values of 1 and 0.2 μM, respectively in ligand binding assays. At 3 μM/kg/day for three weeks, tesaglitazar has been used to reduce insulin resistance in obese Zucker rats. Furthermore, it has been investigated clinically for its potential to address disorders in glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes.
![(S)-2-ETHOXY-3-[4-[2-(4-METHANESULFONYLOXY-PHENYL)-ETHOXY]-PHENYL]-PROPIONIC ACID](https://www.chemicalbook.com/CAS/GIF/251565-85-2.gif)