Description
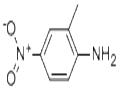
2-Methyl-4-nitroaniline was used in preparing in-plane aligned nanofibers by the electrospinning technique. It was the starting reagent in the synthesis of 3-chloro-5-methylphenyl isocyanate. It was used to deposit polycrystalline thin films on Ag, Cu and Si by conventional and partially ionized beam deposition.
Reference
2. Seo, Kang, and C. Bonner. "Growth of organic thin films on Si (100) surfaces: 2-Methyl-4-Nitroaniline (MNA)." APS Southeastern Section Meeting APS Southeastern Section Meeting Abstracts, 2002.
Chemical Properties
Yellowneedle
Uses
2-Methyl-4-nitroaniline was used in preparing in-plane aligned nanofibers by the electrospinning technique. It was the starting reagent in the synthesis of 3-chloro-5-methylphenyl isocyanate. It was used to deposit polycrystalline thin films on Ag, Cu and Si by conventional and partially ionized beam deposition.
Production Methods
N-Benzenesulfonyl-o-toluidine is dissolved in chlorobenzene at 40 – 50 ℃, and 62 % nitric acid is added gradually to give 5- nitro-N-benzenesulfonyl-o-toluidine, which is isolated and hydrolyzed in sulfuric acid to give 5-nitro-o-toluidine in 80 % yield.
General Description
Yellow needles or mustard yellow powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
2-Methyl-4-nitroaniline is incompatible with acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroformates and strong oxidizing agents.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for 2-Methyl-4-nitroaniline are not available; however, 2-Methyl-4-nitroaniline is probably combustible.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the nitrotoluidine from EtOH. The acetyl and benzoyl derivatives have m 200o and 174o (EtOH) respectively. [Beilstein 12 IV 1809.]