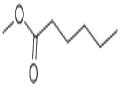
Methyl hexanoate
- Product NameMethyl hexanoate
- CAS106-70-7
- CBNumberCB6755858
- MFC7H14O2
- MW130.18
- EINECS203-425-1
- MDL NumberMFCD00009510
- MOL File106-70-7.mol
- MSDS FileSDS
Chemical Properties
| Melting point | -71 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point | 151 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.885 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 3.7 hPa (20 °C) |
| FEMA | 2708 | METHYL HEXANOATE |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point | 113 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | chloroform: soluble100mg/mL, clear |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. ethereal fruity pineapple apricot strawberry tropical fruit banana bacon |
| Odor Type | fruity |
| biological source | synthetic |
| Water Solubility | 1.325g/L(20 ºC) |
| JECFA Number | 1871 |
| BRN | 1744683 |
| Dielectric constant | 4.7000000000000002 |
Safety
| Symbol(GHS) |

|
|||||||||
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H226 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210 | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 10 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 43-16-36/37/39-7 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3272 3/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | MO8401400 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29159080 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: > 5000 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704: |
|