The introduction of Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide
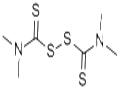
Description
Tetramethylthiuram disulfide (TMTD, thiram) is one of the most essential fungicides widely used in agriculture for seed treatment and crop protection. In many countries, including Russia, a fungicide commonly used to treat garden pea seeds is tetramethylthiuram disulfide[1].
Synthesis method
TMTD is produced by several plants. Its annual sales are estimated at tens of millions of US dollars. The formation of a significant amount of waste, including inorganic salts, thioacids, polysulfides, etc, accompanies the traditional chemical synthesis of thiram. Mulina et al. report an advanced method of TMTD and its structural analogs production, based on using electric current as a critical participant[2].

An undivided cell was equipped with a platinum plate anode (15 cm2 ) and a stainless steel plate cathode (15 cm2 ) and connected to a DC-regulated power supply. The solution of carbon disulfide (20 mmol, 1.522 g), dimethylamine 1a (33% aqueous, 60 mmol, 2.705 g), and KI (10 mmol, 1.660 g) in 150 mL of THF-MeOH (1:1) was electrolyzed under constant current conditions (I = 450 mA, j = 30 mA/cm2 ) at room temperature (τ = 67 min) under magnetic stirring. After that, the reaction mixture was diluted with CHCl3 (100 mL) and washed with a 1 M solution of Na2S2O3 (100 mL), water (100 mL), and brine (100 mL); dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was recrystallized from MeOH to give the desired product tetramethylthiuram disulfide in a 71% yield (1.683 g).
Application
This compound is used as a fungicide, bacteriostat, and pesticide. TMTD is widely used in agriculture. TMTD is known to be active against phytopathogenic fungi from different taxonomic classes, such as Alternaria spp., Fusarium spp., Phytophthora spp., Bortrytis spp., Rhizoctonia spp., Aspergillus niger, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Ascochyta rabiei, Pennicillium italicum, and others. Due to great fungicidal activity, thiram is applied for the seed treatment of various economically important crops: rice, corn, peas, sugar beets, cabbage, tomatoes, cucumbers, lettuce, apples, grapes, strawberries, etc. In addition, TMTD is used to preserve wood, protect textiles and paper, and treat turf diseases. Its activity against nematodes, Japanese beetles, and bacteria is also known. Besides agriculture uses, thiram and its analogs are applied in rubber chemistry as activators and accelerators.
Mode of action
TMTD is a protective contact fungicide that does not penetrate plant tissues or seeds and inhibits spore germination or the initial growth of surface pathogenic mycelium. This compound actively suppresses the development of pathogenic oomycetes and partially inhibits the growth of basidiomycetes. After penetrating the pathogen's cells, TMTD inhibits the activity of enzymes containing copper or sulfhydryl groups. On treated grains in the soil, TMTD retains its fungicidal activity for up to 30 days[1]. In plants and soil, TMTD decomposes to the more toxic and environmentally hazardous metabolites, tetramethyl thiuram monosulfide and tetramethyl thiourea. Among synthetic fungicides, TMTD is the most suitable for treating legume seeds because of its low toxicity to certain rhizobia.
References
[1] Artemii P Gorshkov. “The Fungicide Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide Negatively Affects Plant Cell Walls, Infection Thread Walls, and Symbiosomes in Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Symbiotic Nodules.” Plants-Basel 9 11 (2020).
[2] Olga M. Mulina, Mikhail M. Doronin, Evgeniya D. Bokova and Alexander O. Terent’ev*. “Effective Electrochemical Synthesis of an Important Fungicide Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide and Its Bioactive Analogues.” ACS agricultural science technology 3 9 (2023): 720–724.
You may like
See also
Lastest Price from Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide manufacturers

US $1.00/PCS2025-04-21
- CAS:
- 137-26-8
- Min. Order:
- 1PCS
- Purity:
- 99%
- Supply Ability:
- 10 mt
US $1.00/kg2019-07-06
- CAS:
- 137-26-8
- Min. Order:
- 1kg
- Purity:
- as customer's need
- Supply Ability:
- 100kg


